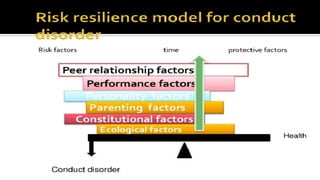
Conduct disorder is a psychological disorder diagnosed in childhood or adolescence that involves persistent antisocial behavior violating the rights of others. It affects around 1-10% of children globally. Symptoms are grouped into aggressive conduct, deceitful behavior, violation of rules, and destructive behavior. Risk factors include child abuse, family dysfunction, and peer pressure. Treatment involves family therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, parenting skills training, and sometimes medication. About 25-40% of those diagnosed may develop antisocial personality disorder as adults if conduct disorder is not effectively treated.