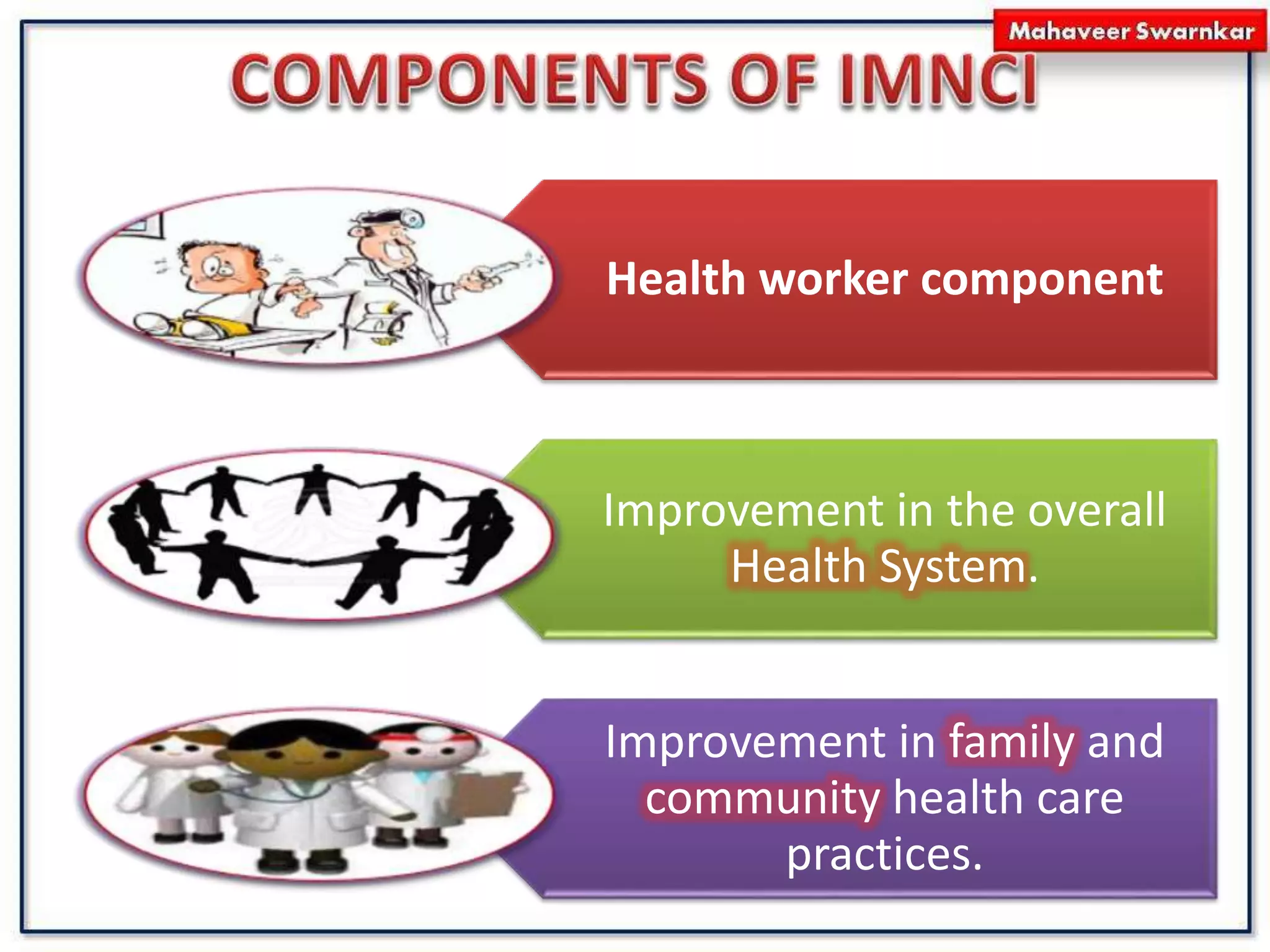
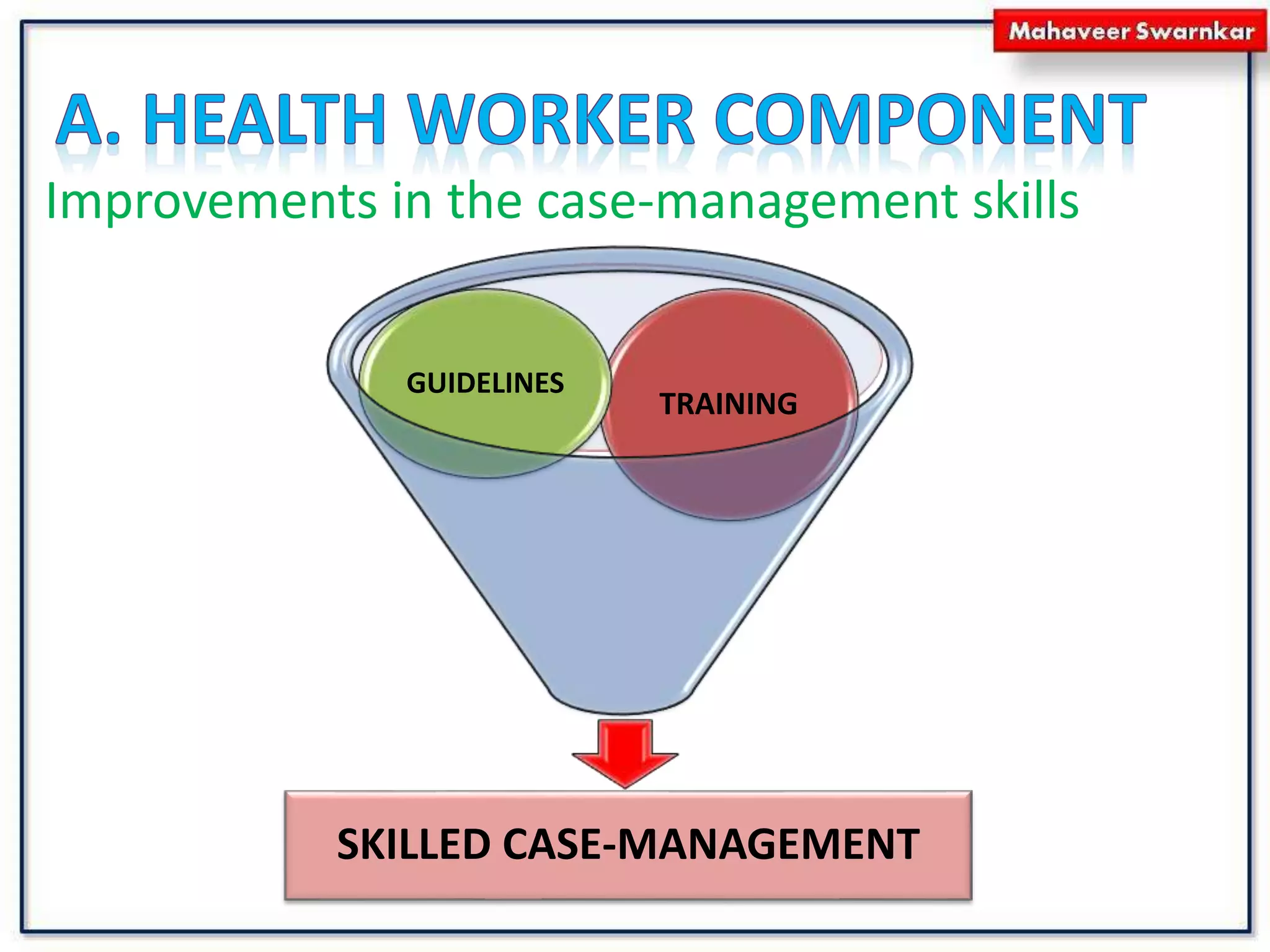
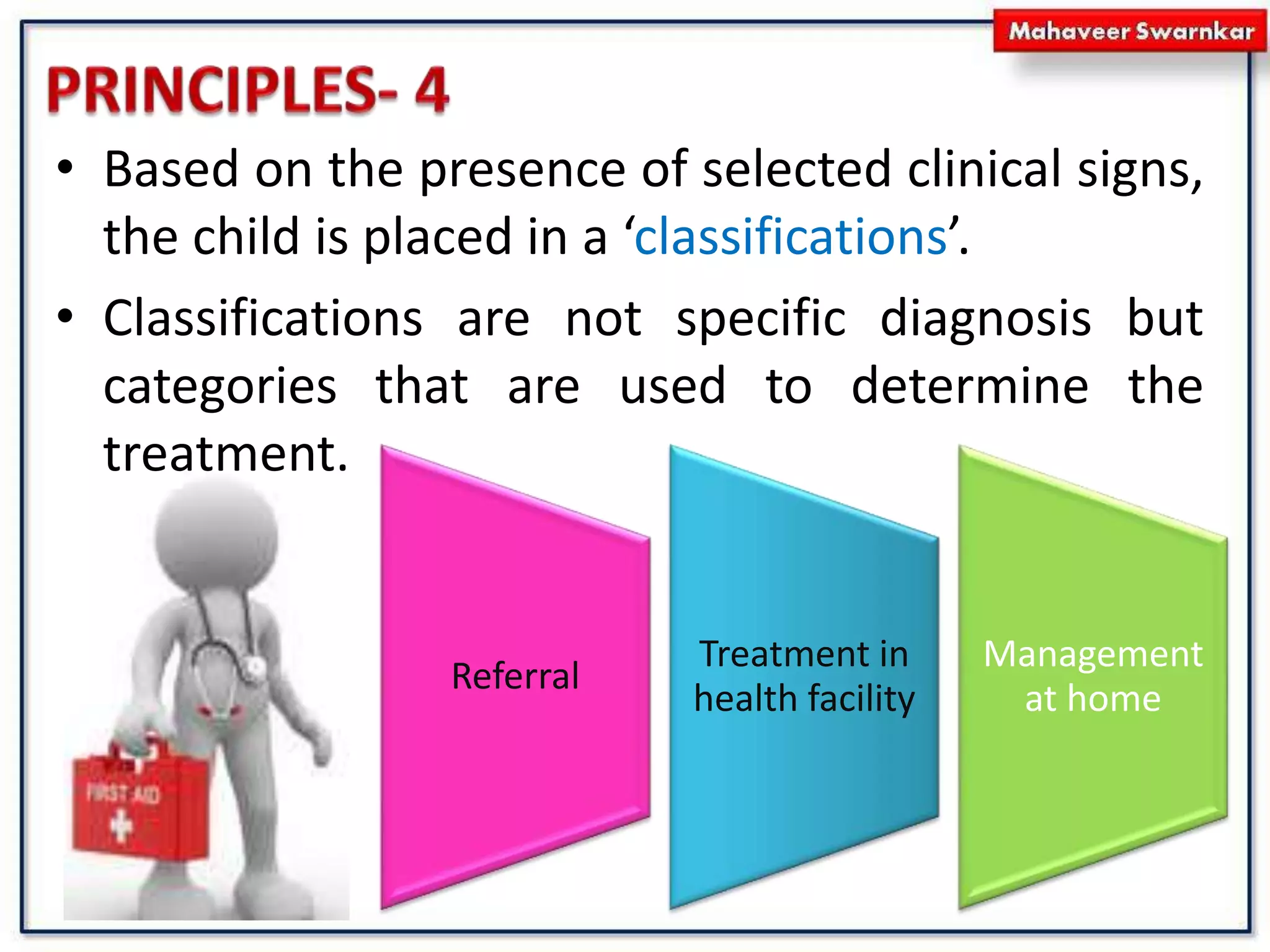
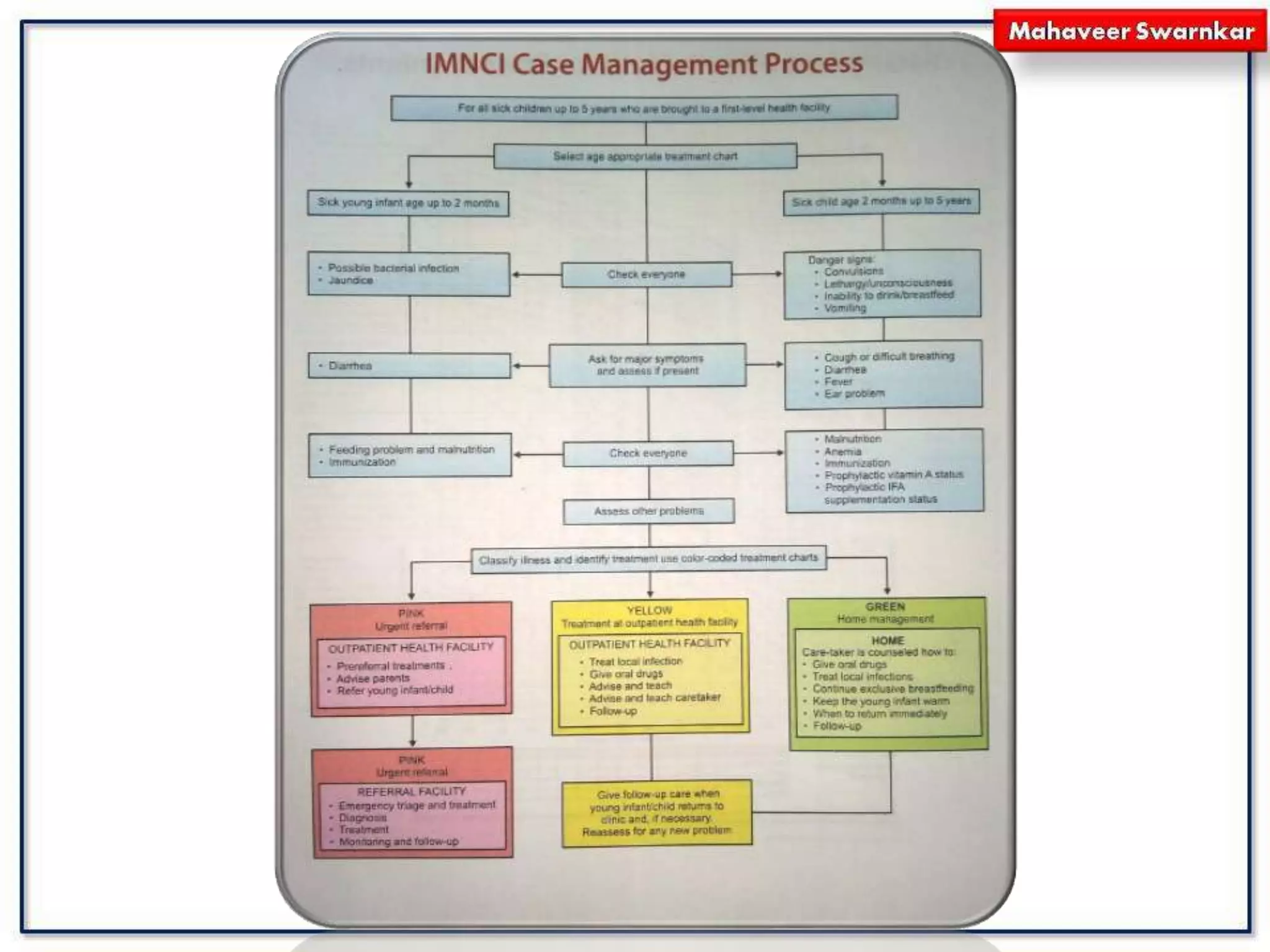
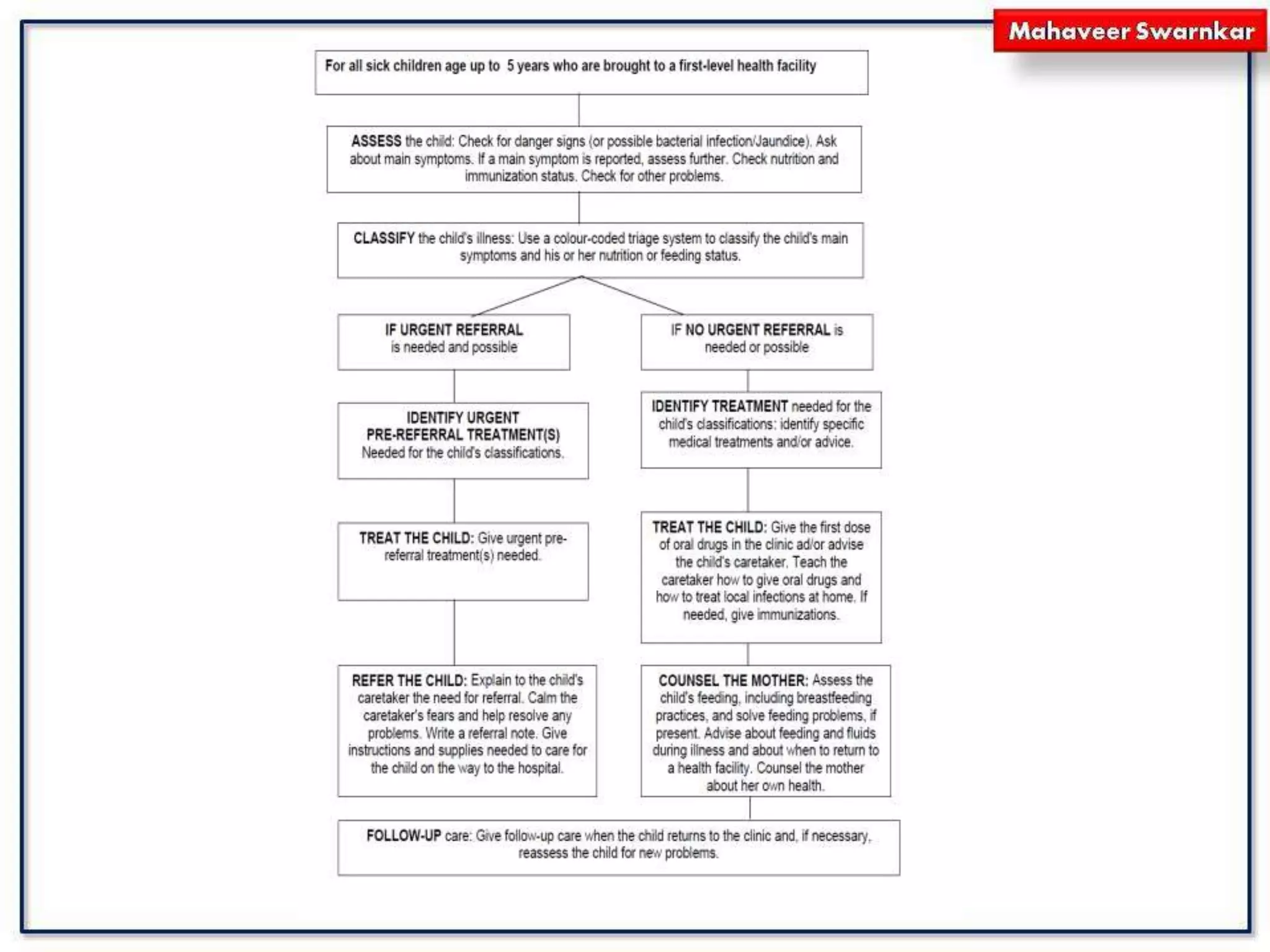
The document discusses India's adoption of the Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI) strategy. IMNCI aims to reduce mortality, illness, and disability in children under 5 by improving case management skills, health systems, and family/community health practices. It standardizes the assessment and treatment of common pediatric problems in children under 2 months and 2 months to 5 years. The integrated approach has advantages like speeding treatment, recognizing serious conditions, involving parents, cost-effectiveness, and reducing resource duplication.