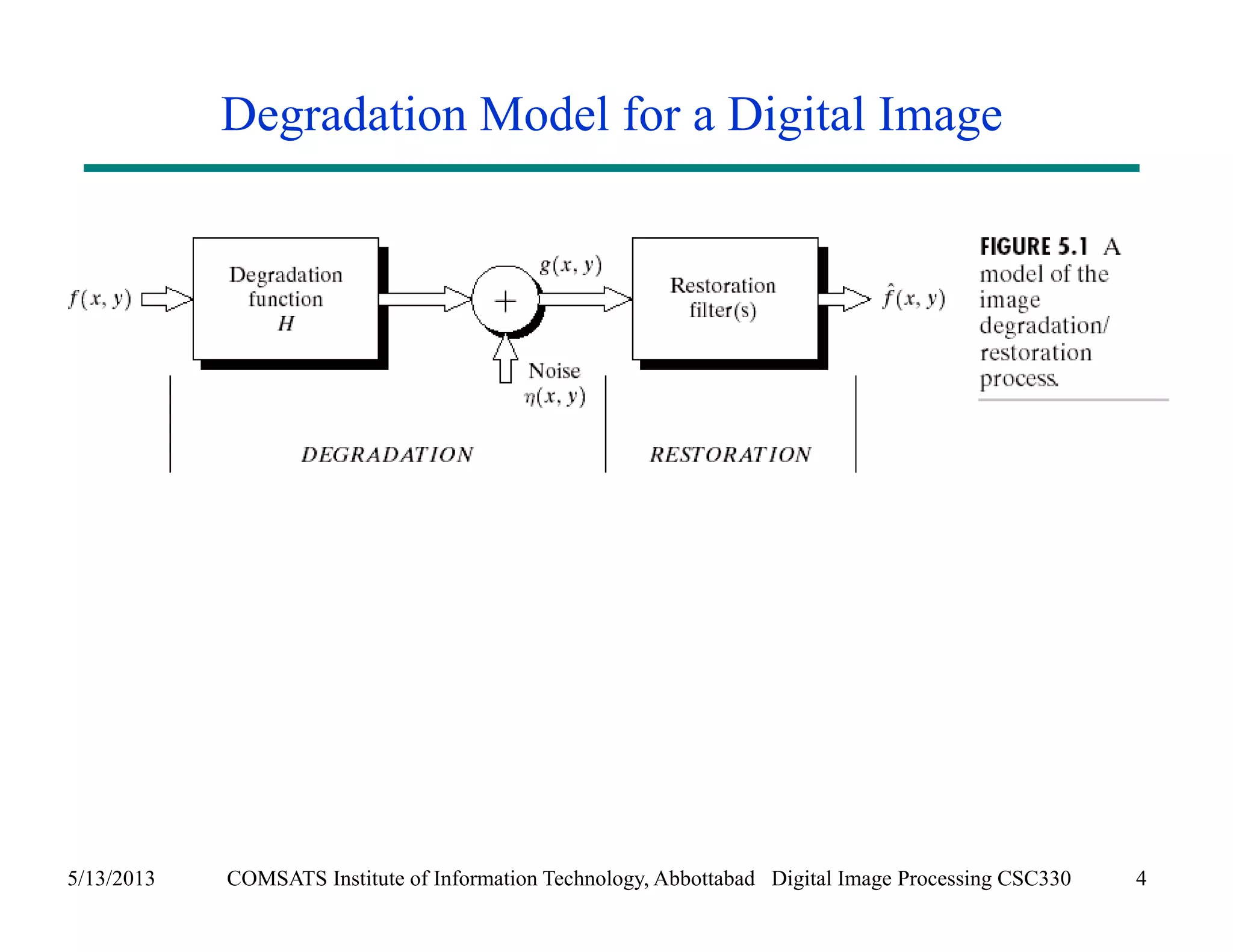
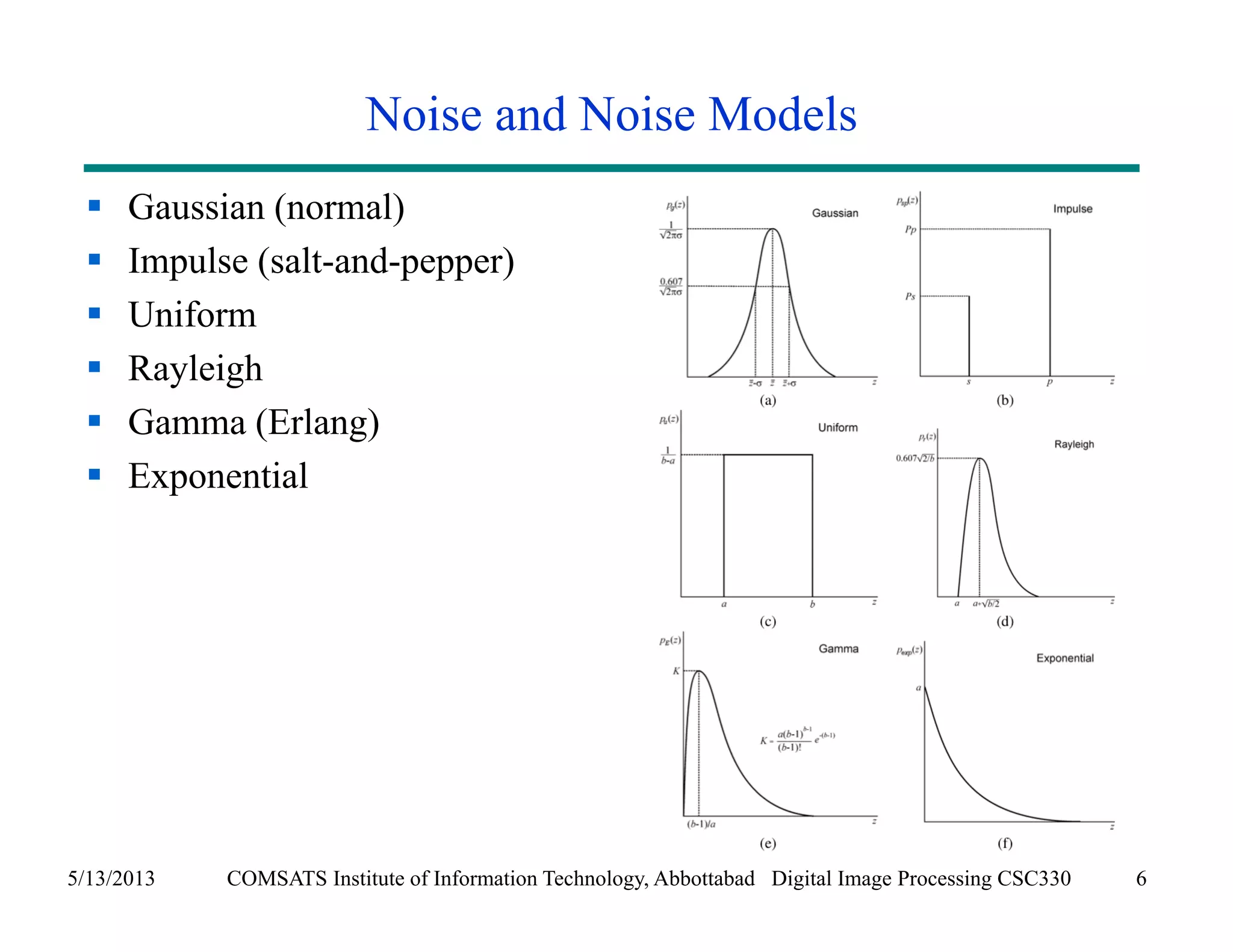
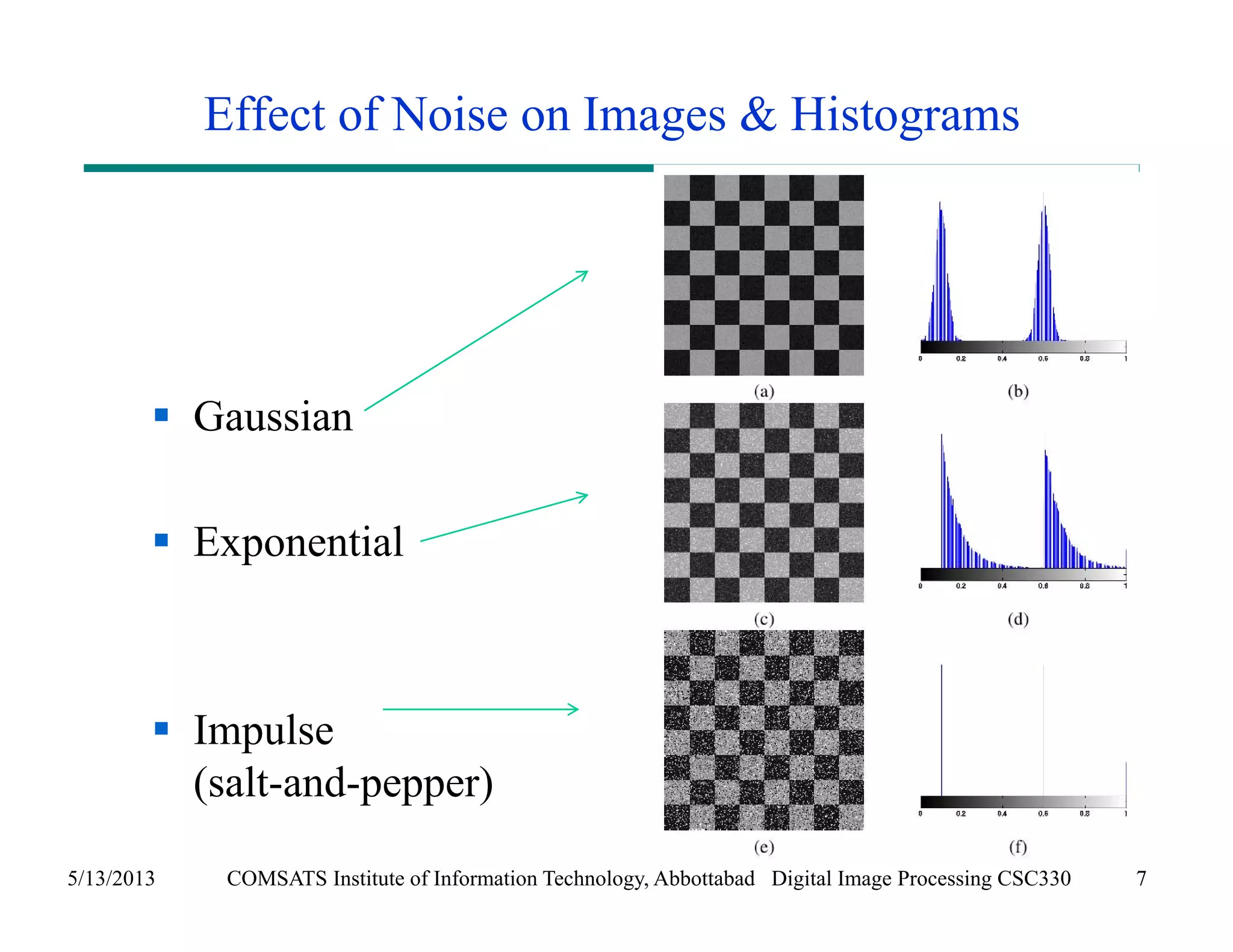
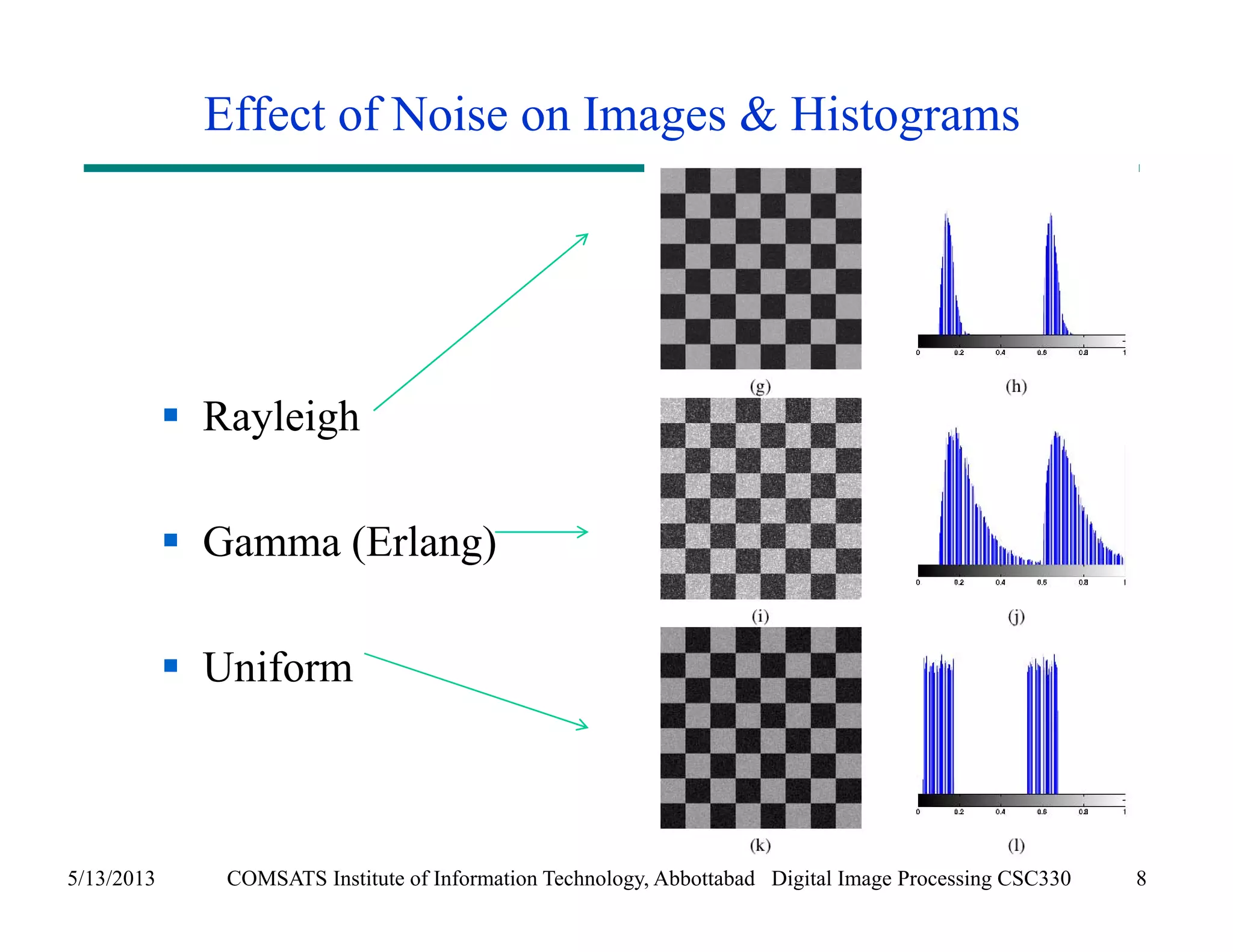
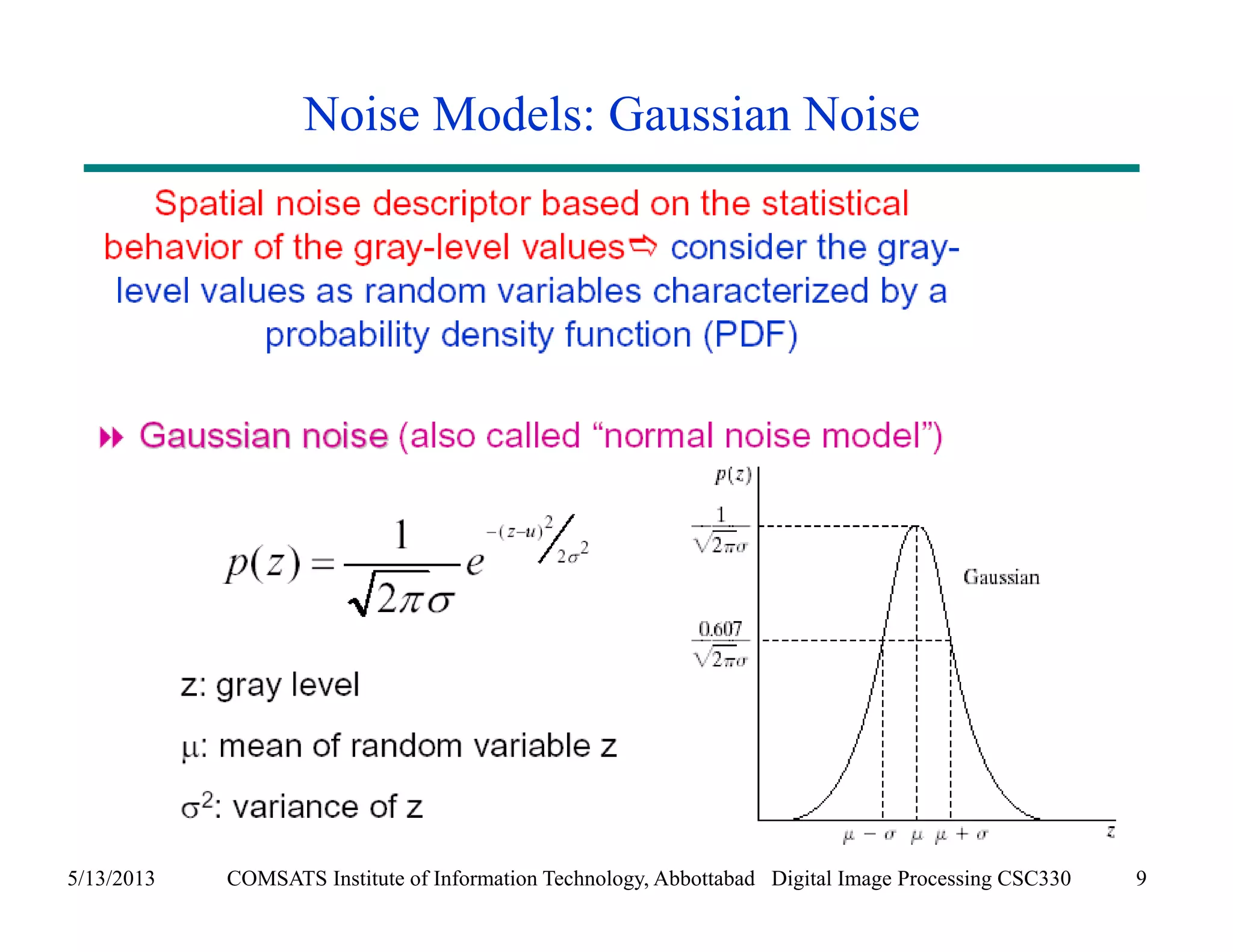
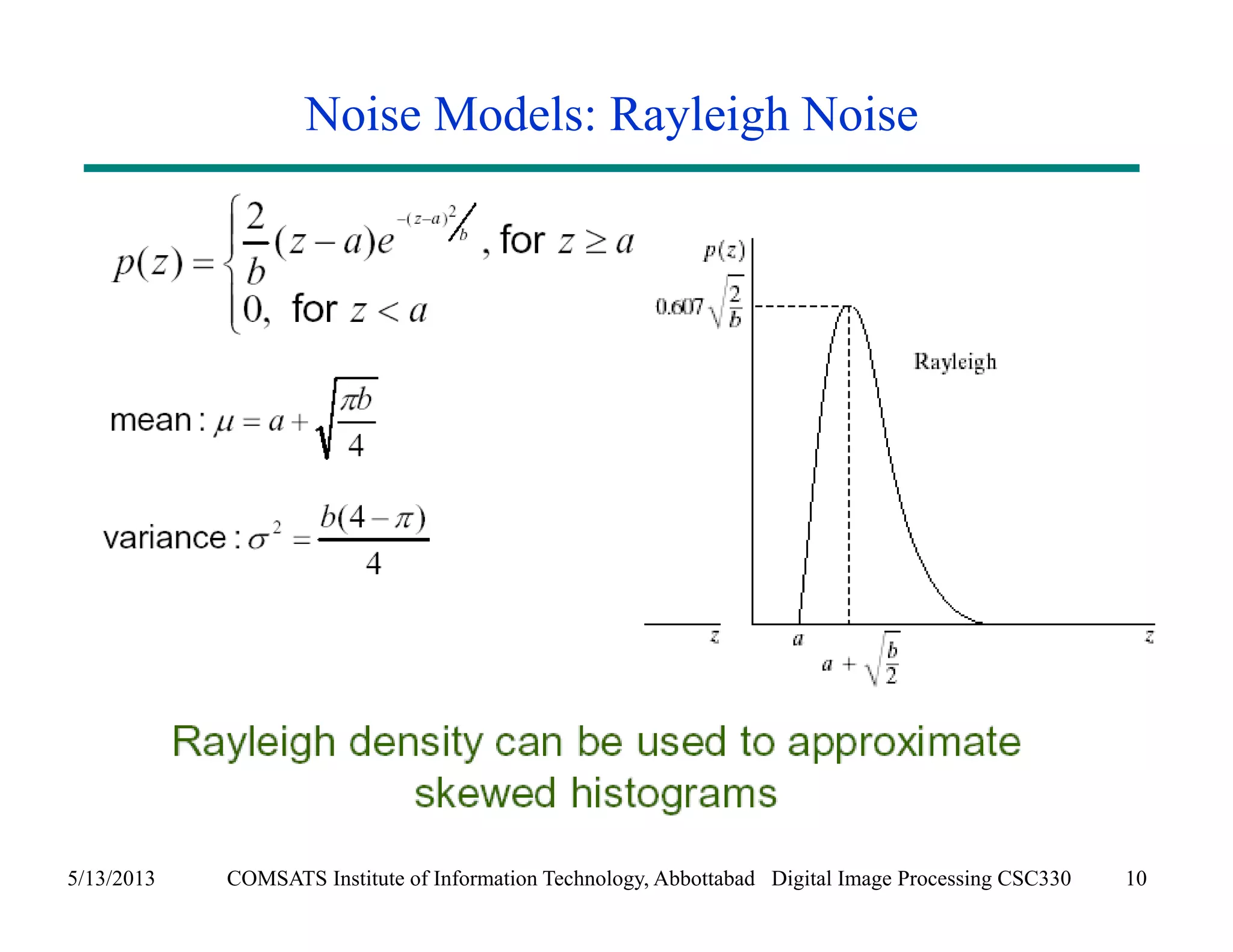
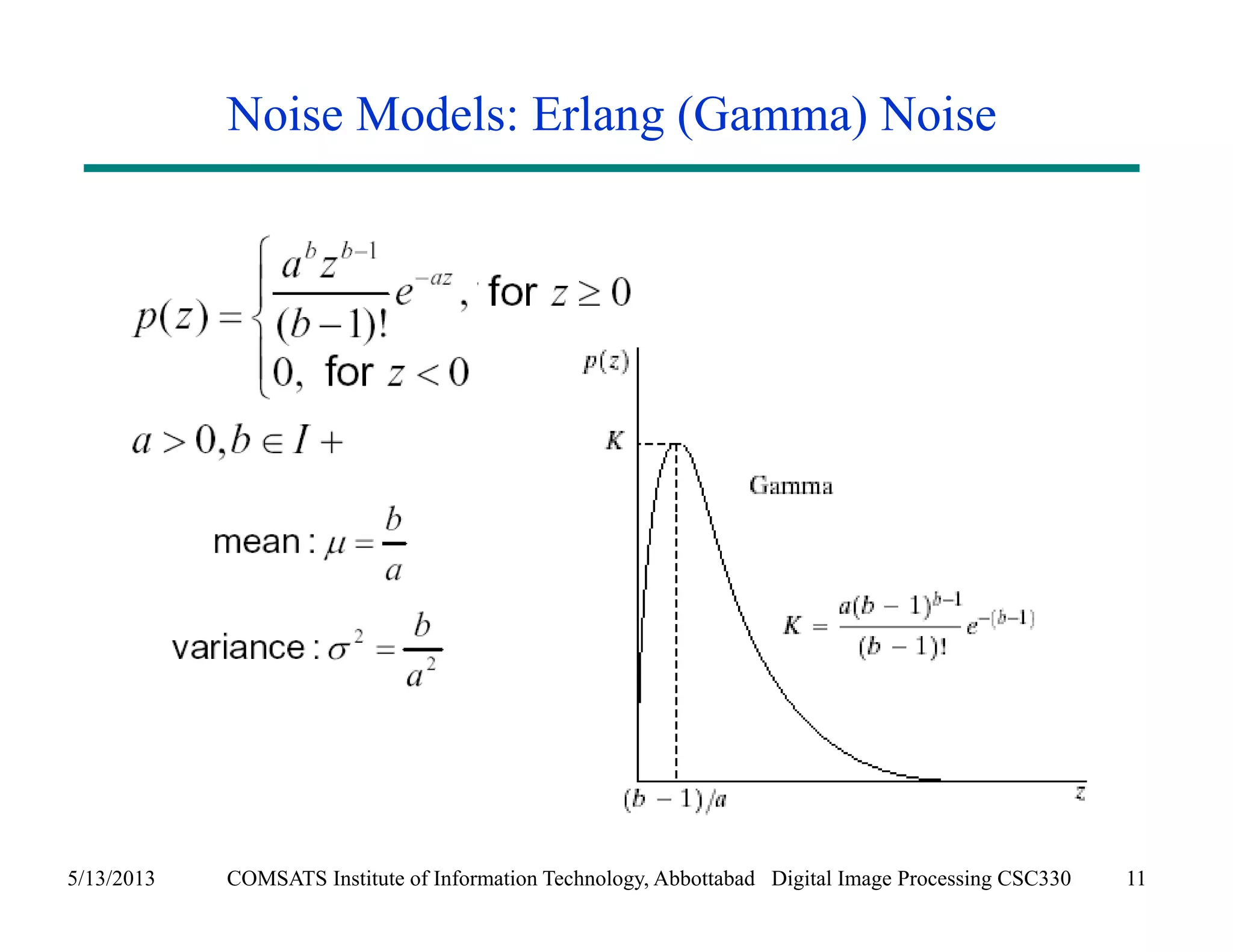
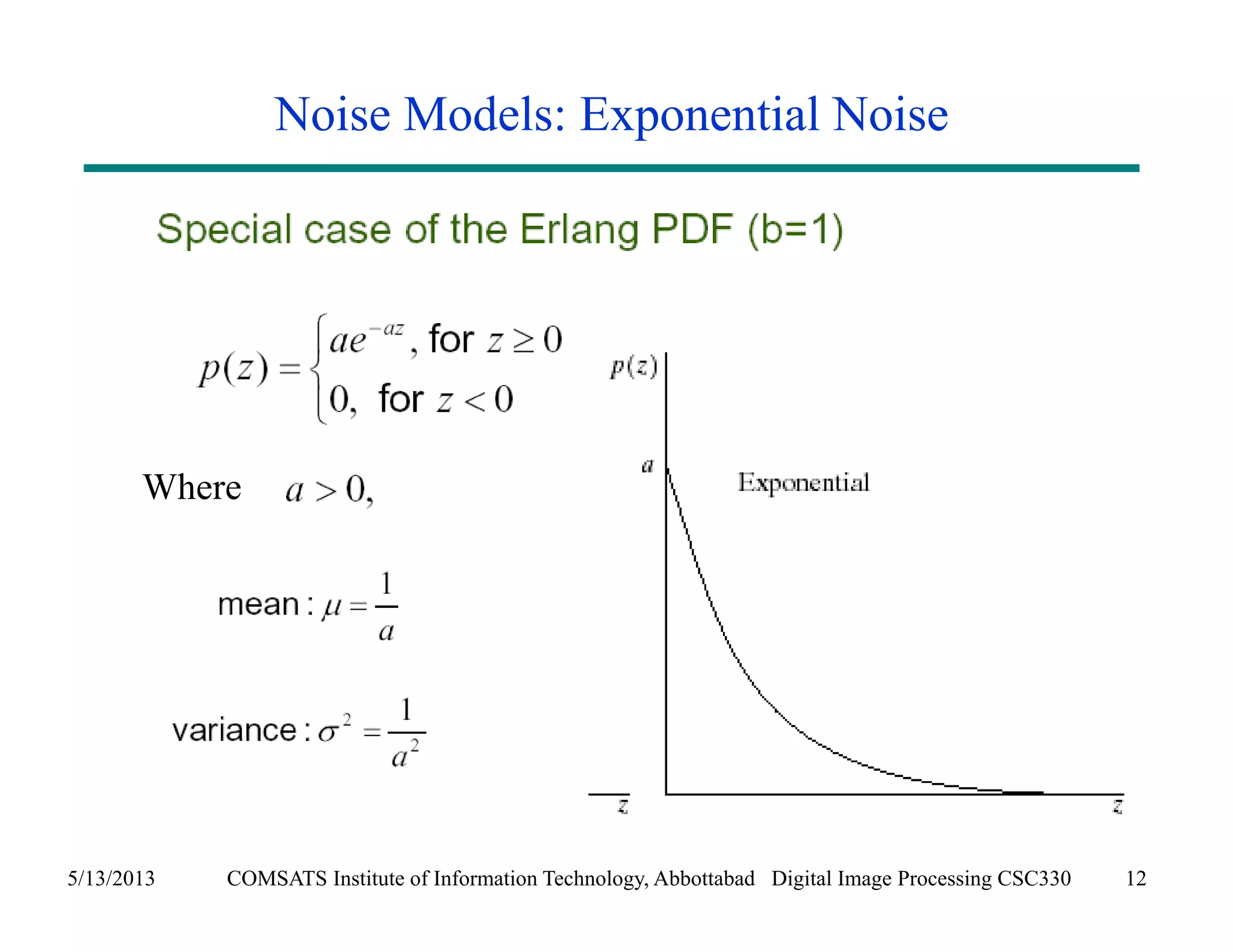
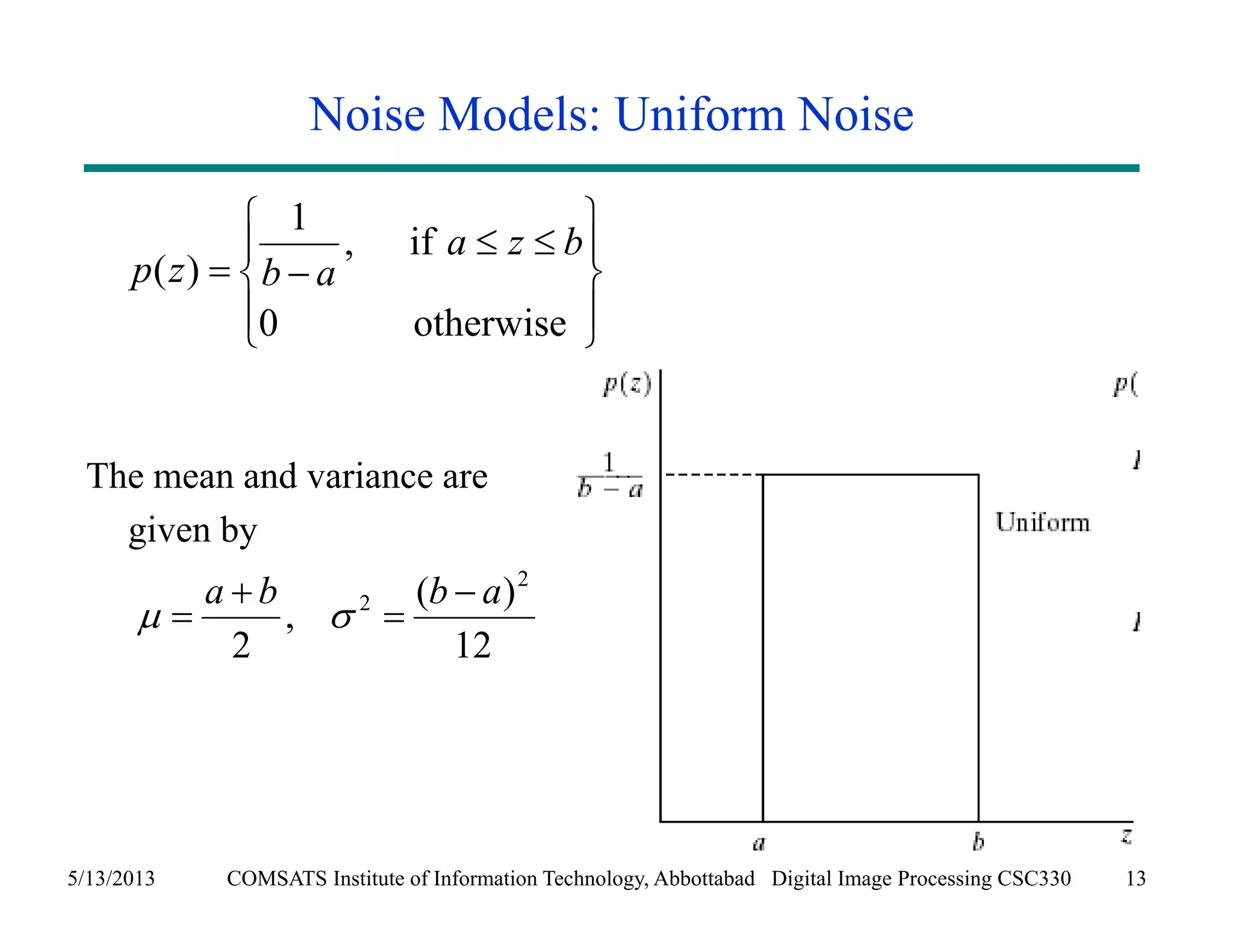
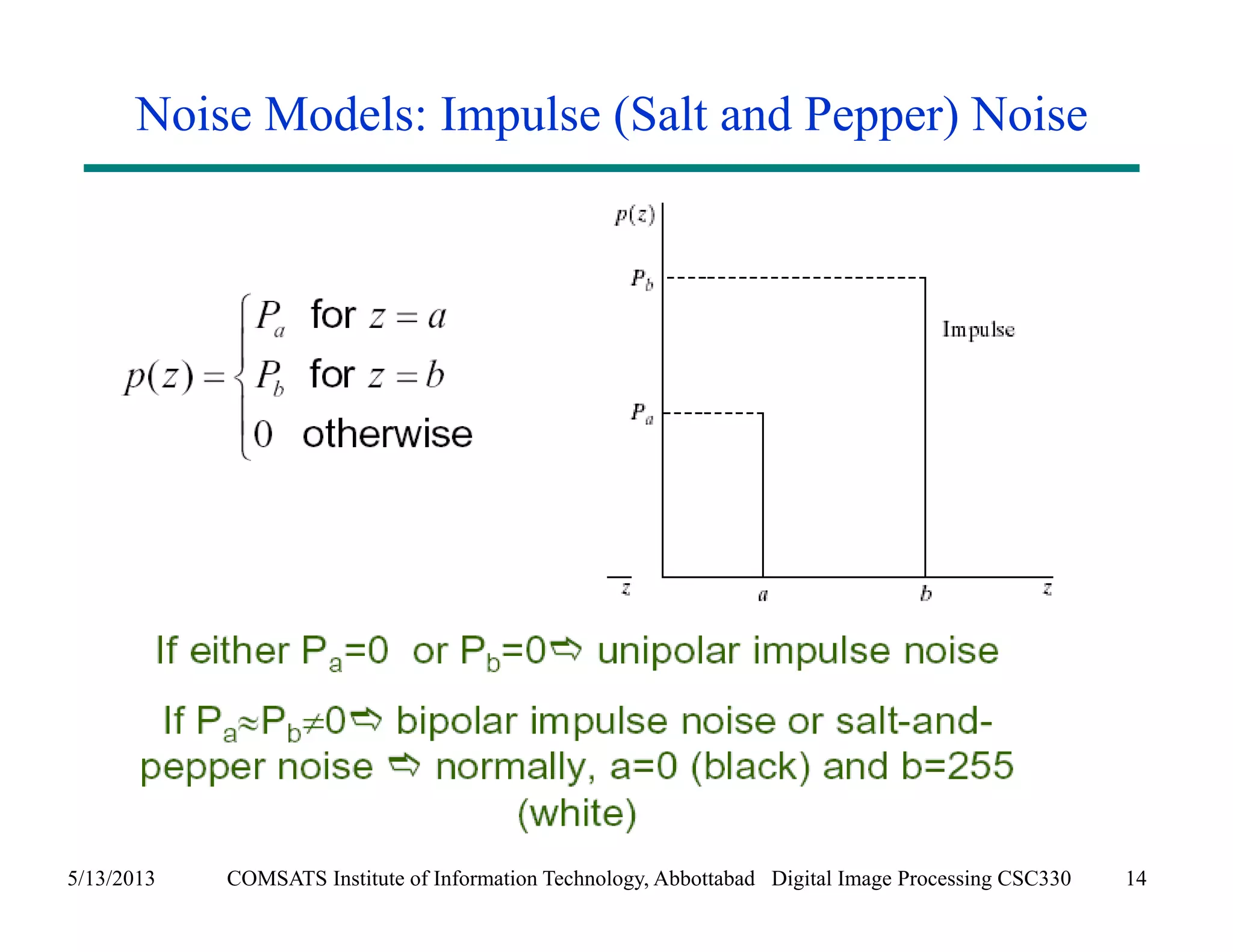
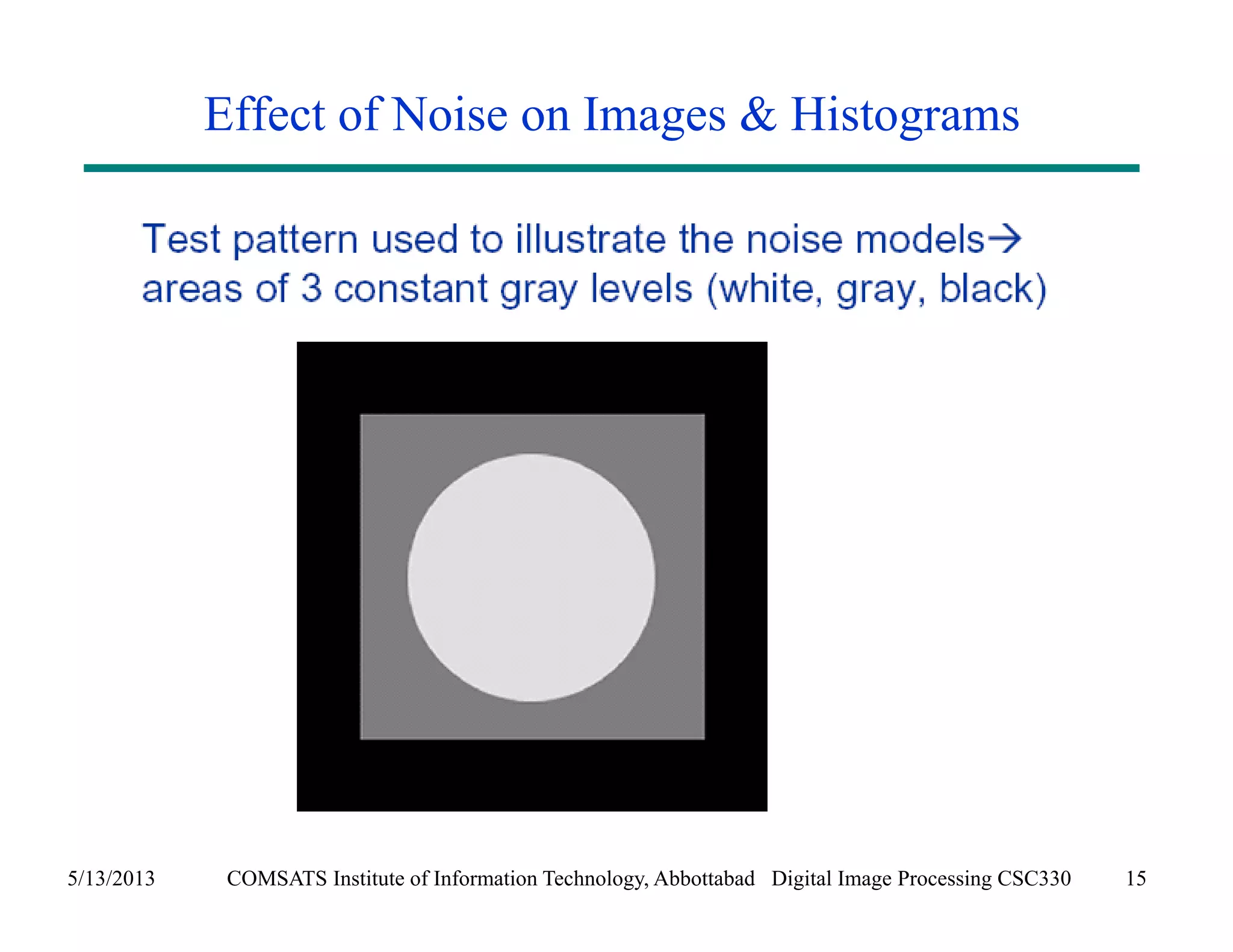
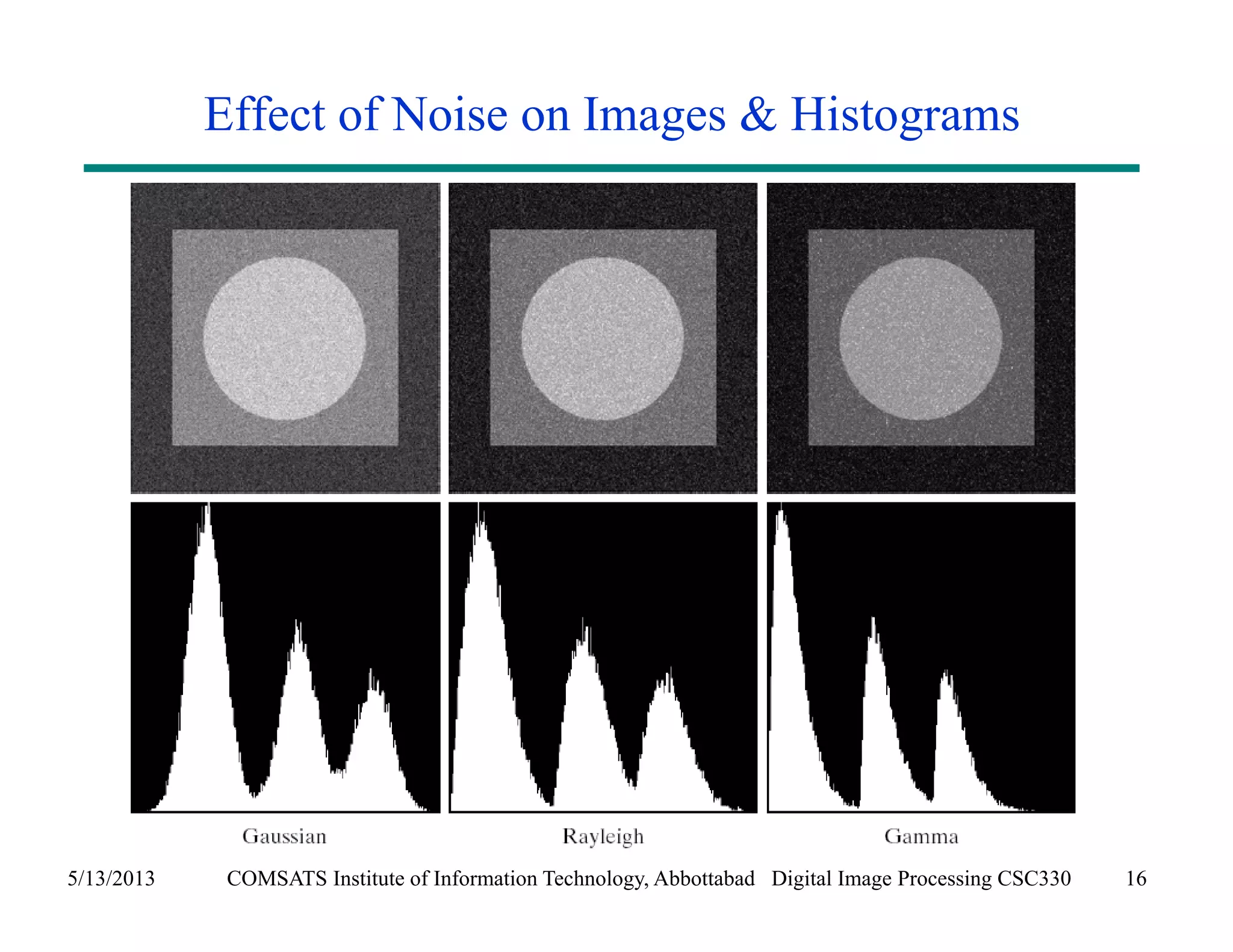
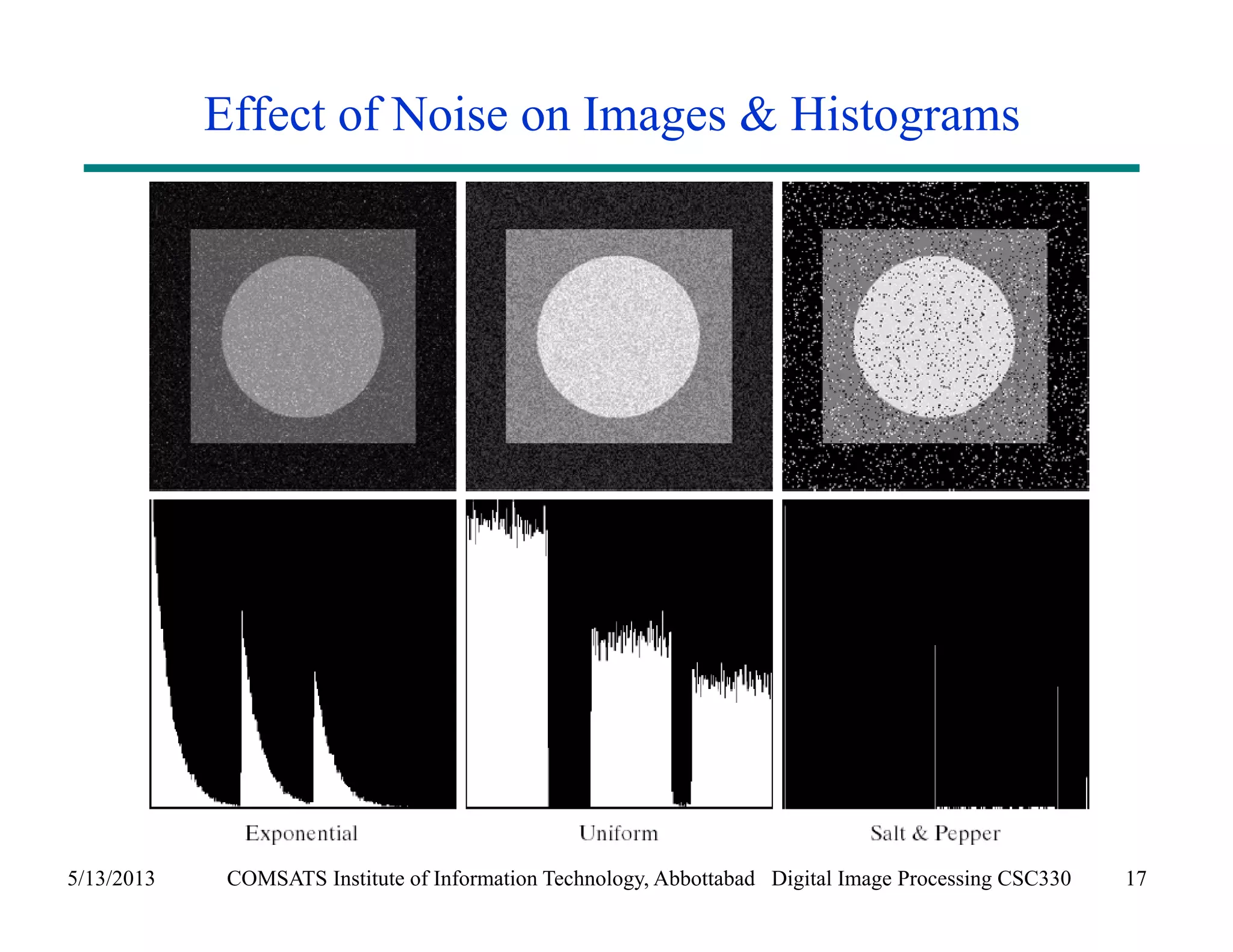
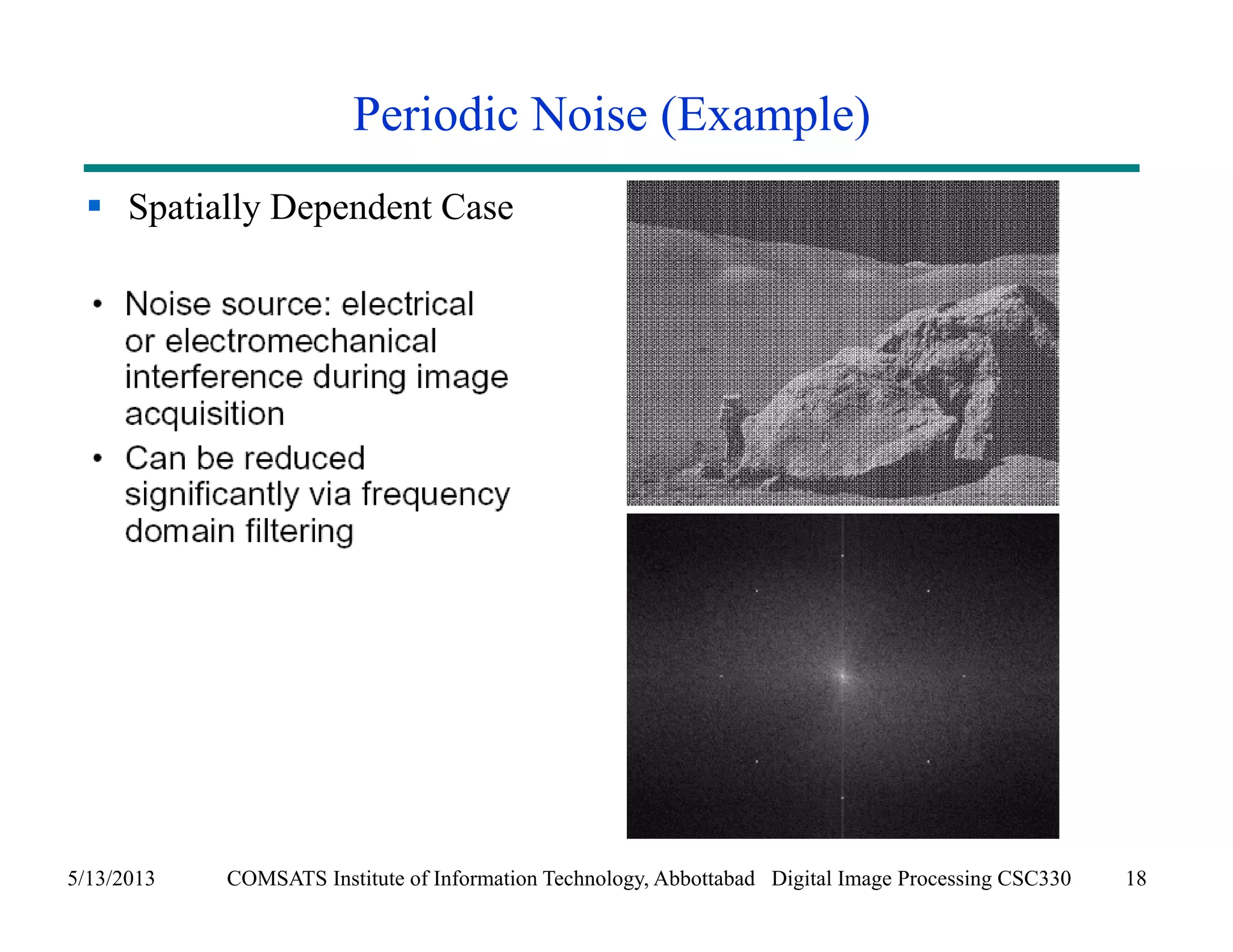
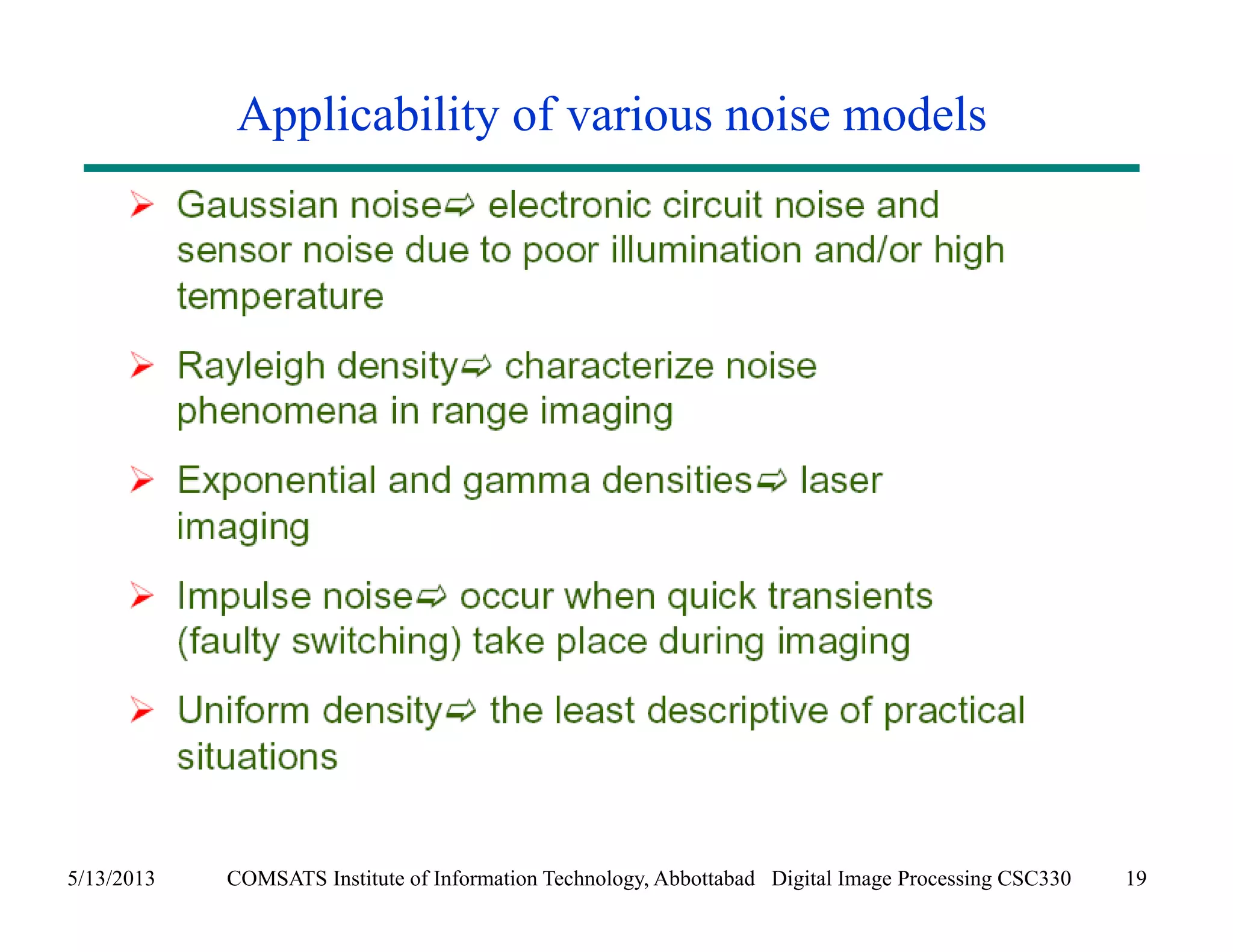
This document discusses noise models and additive noise removal in digital image processing. It covers several types of noise that can affect images, including Gaussian, impulse, uniform, Rayleigh, gamma, exponential, and periodic noise. Various noise models are presented, such as definitions and equations for Gaussian, Rayleigh, gamma, exponential, uniform, and impulse noise. Examples of how different noise types affect images and histograms are also shown.