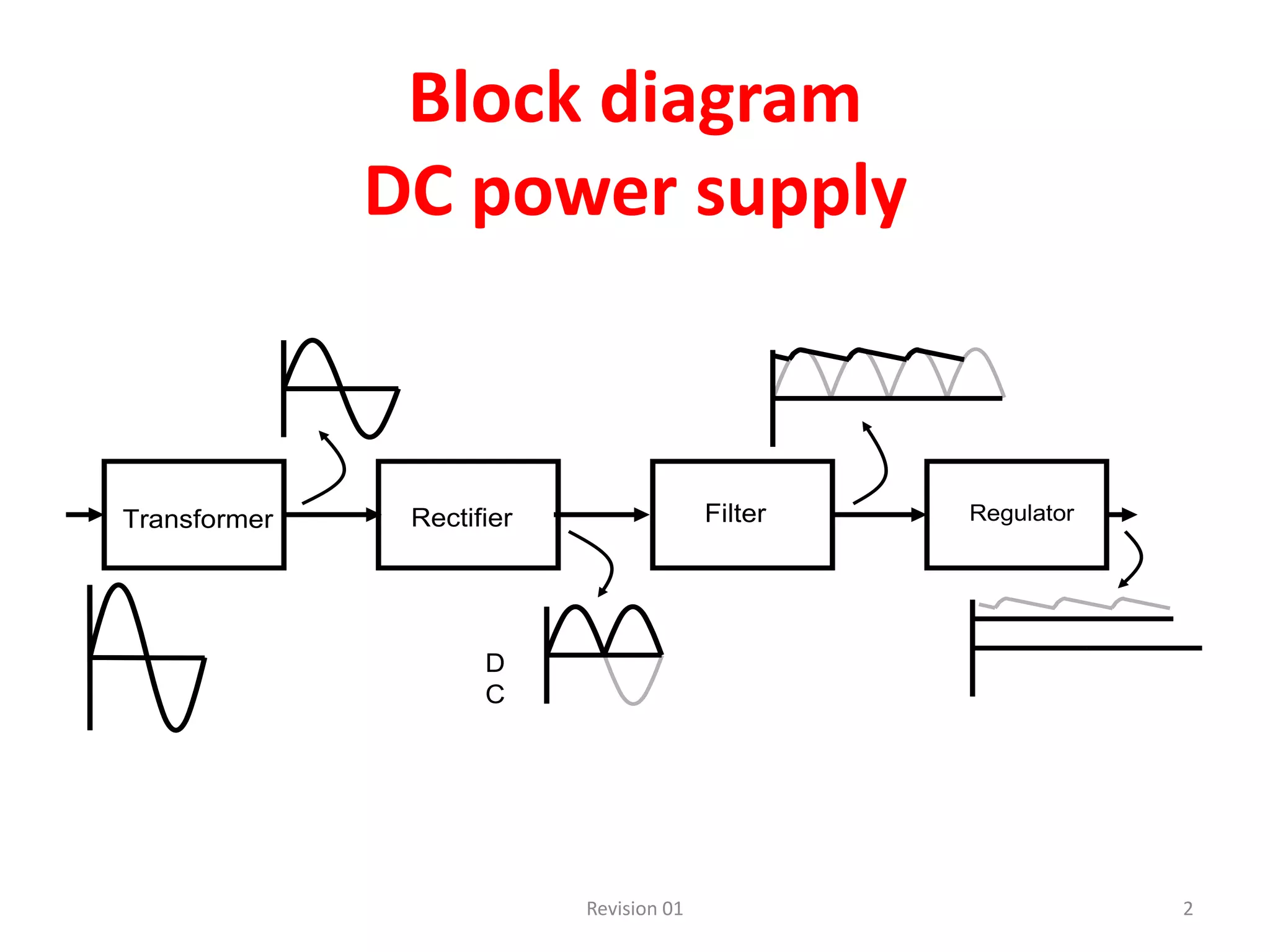
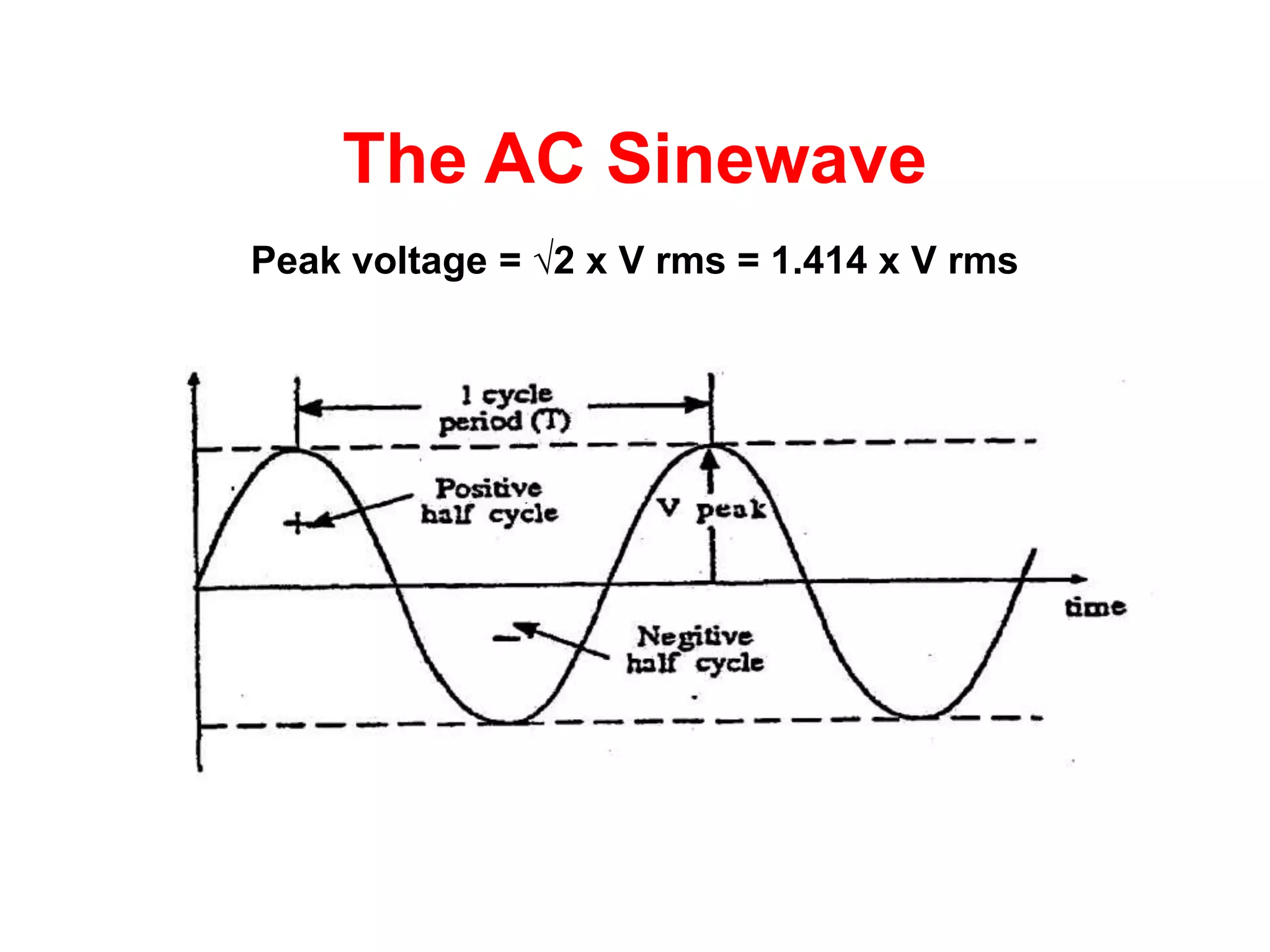
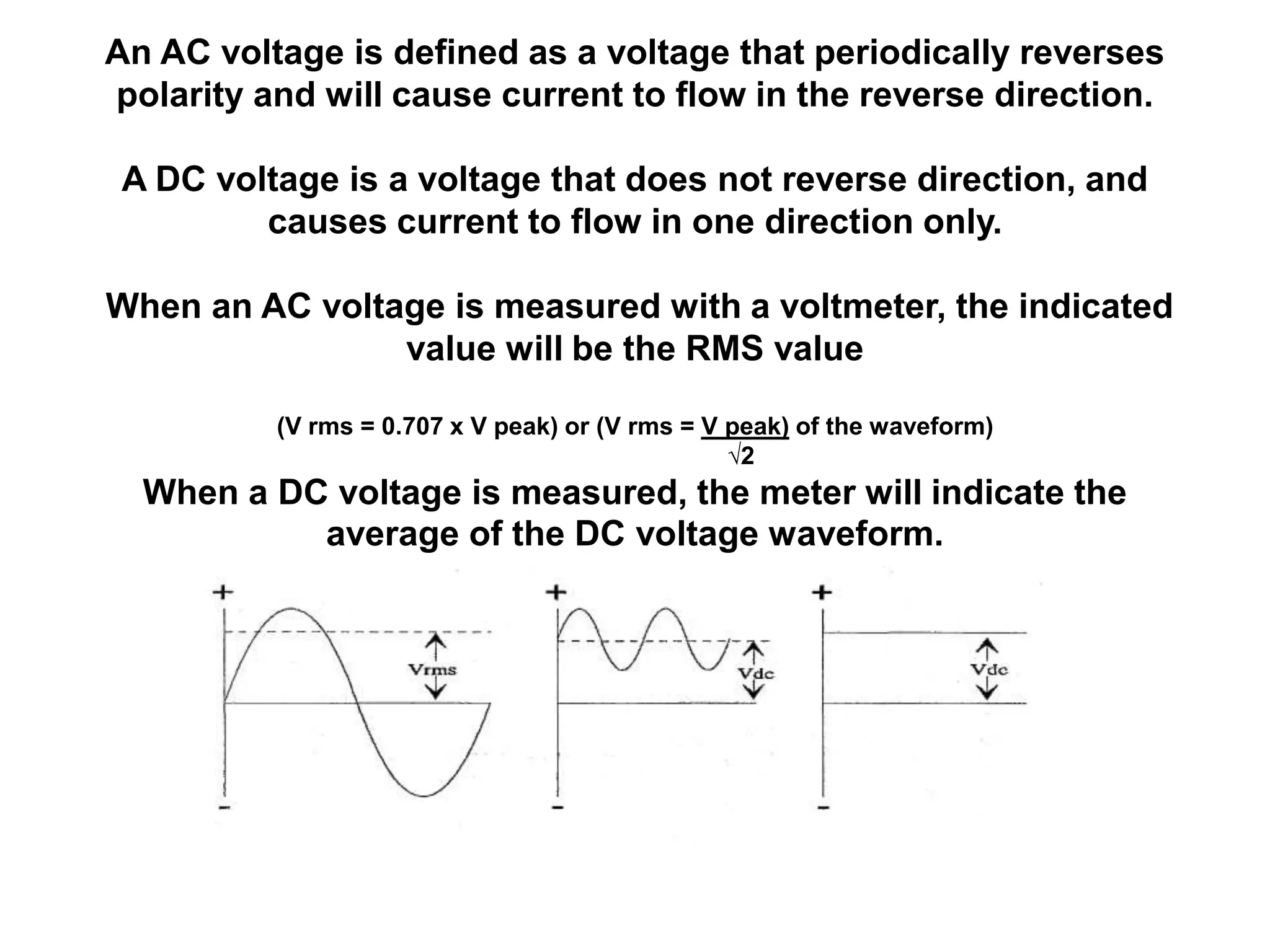
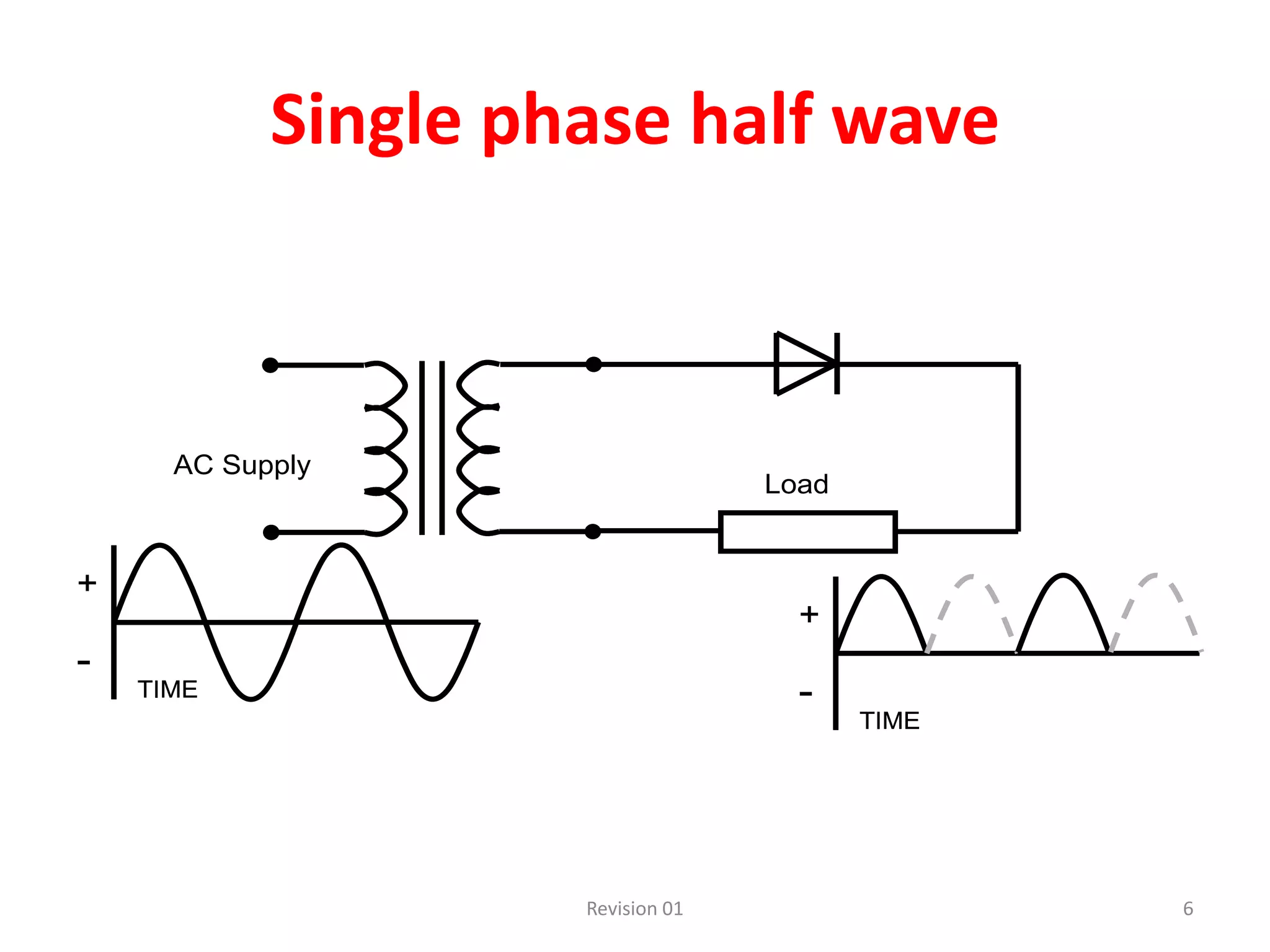
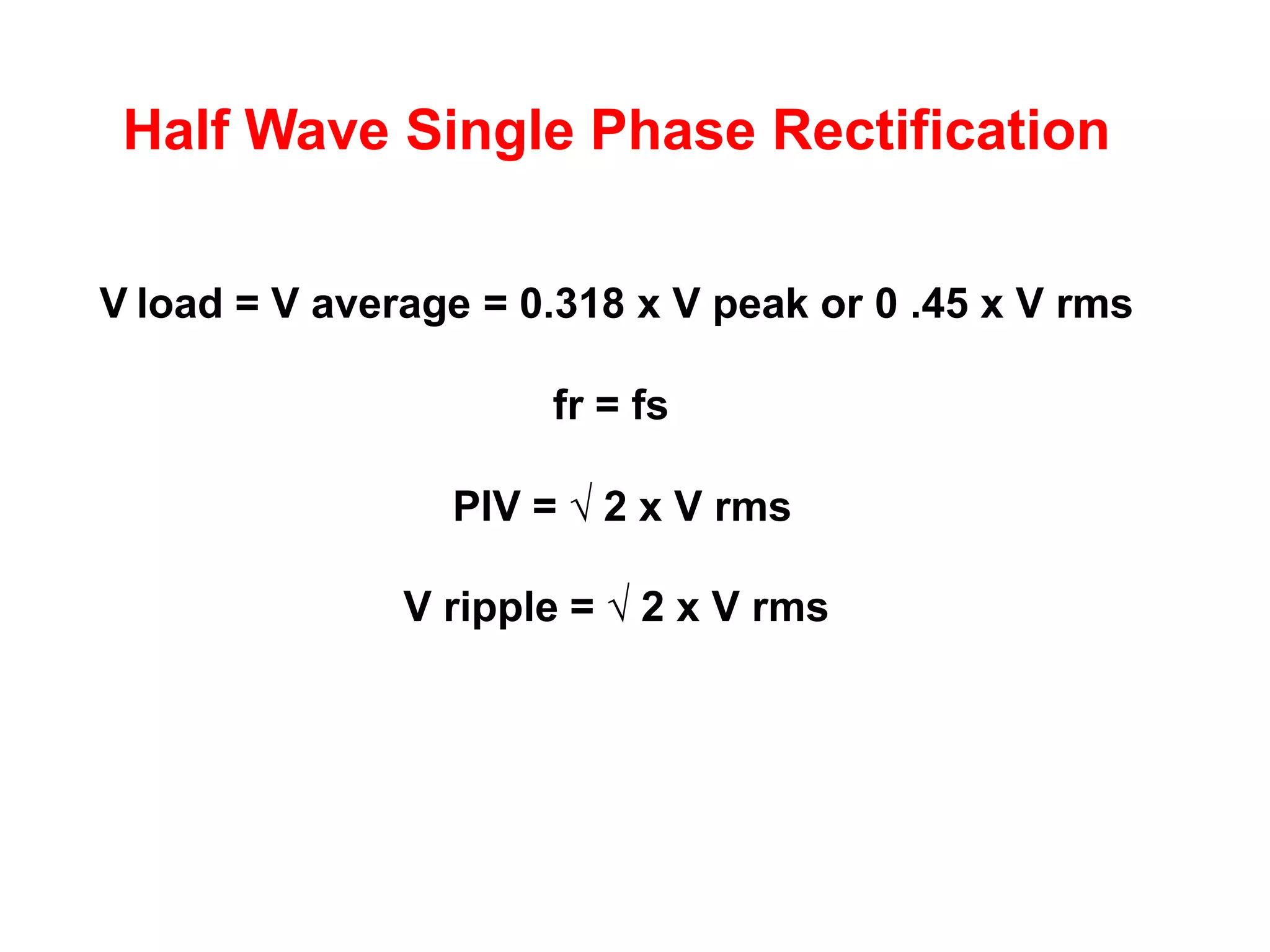
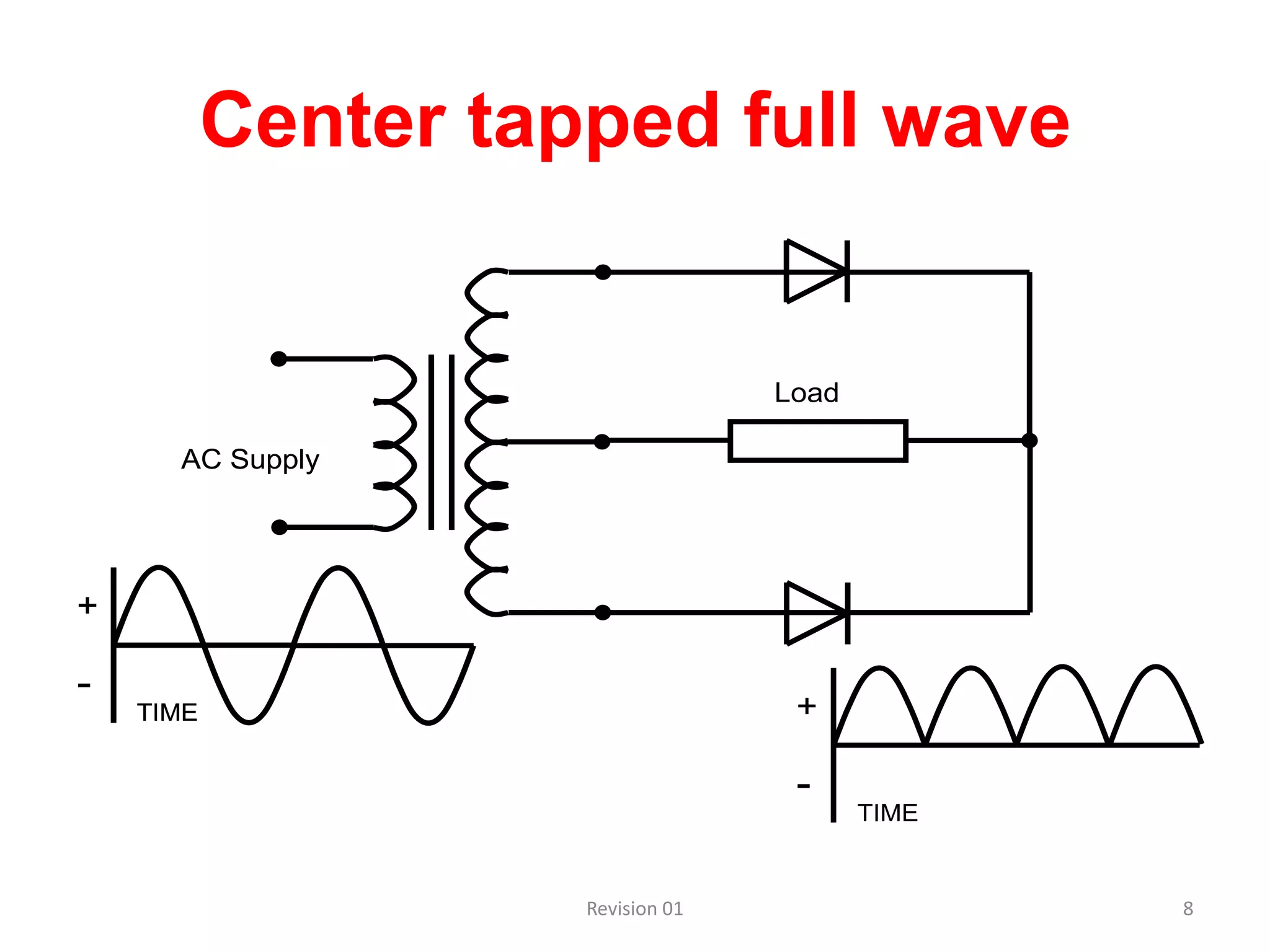
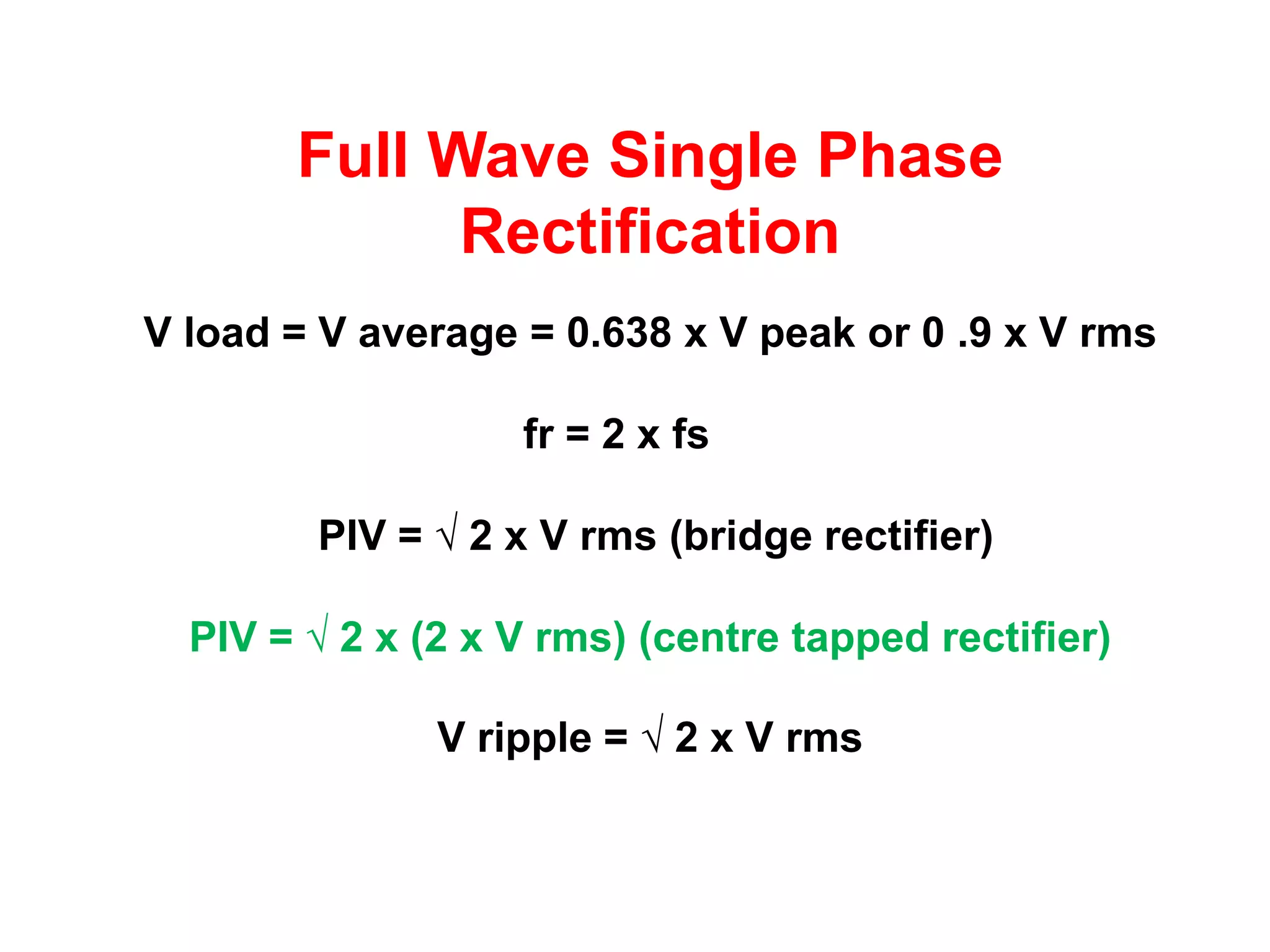
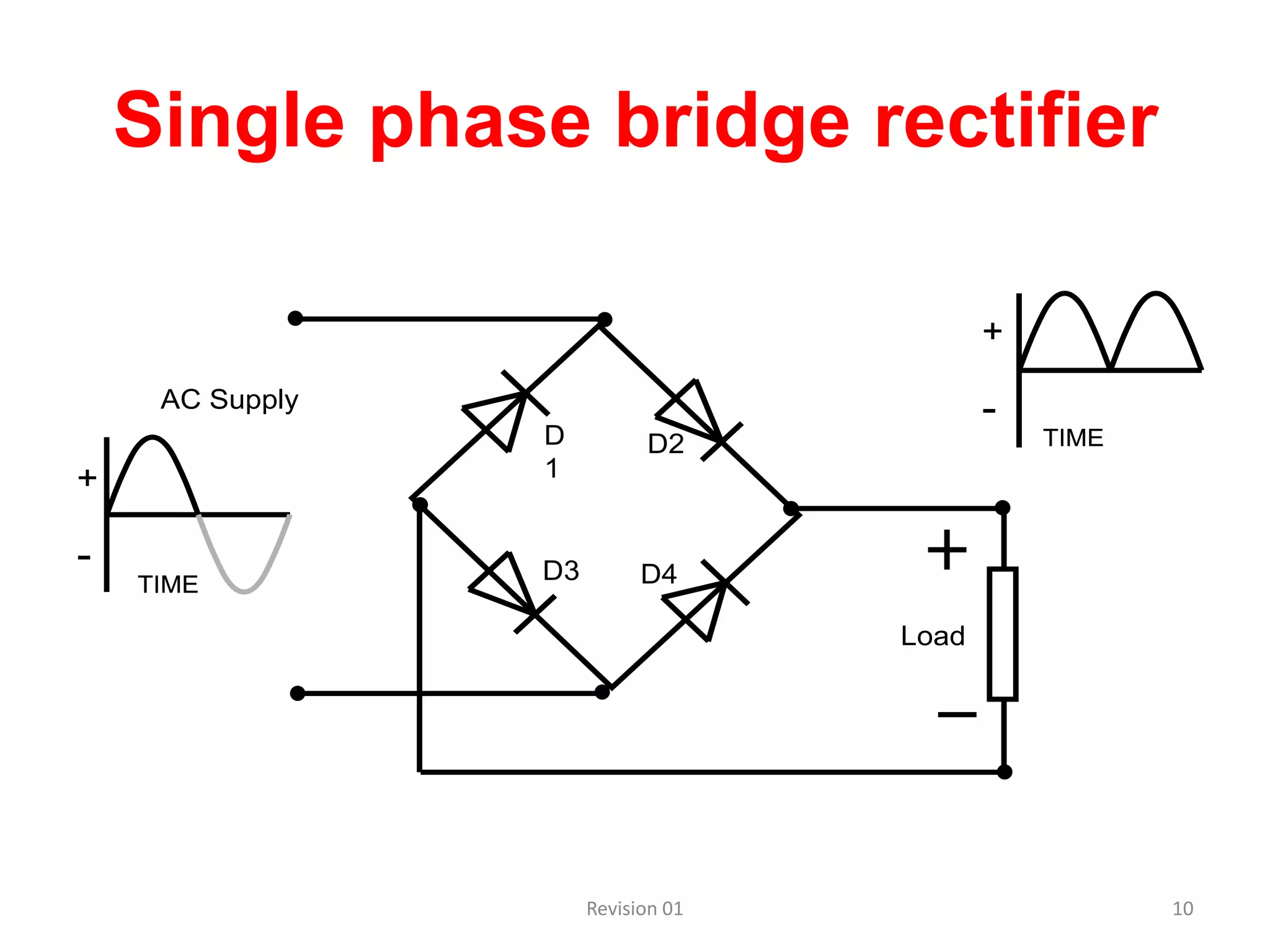
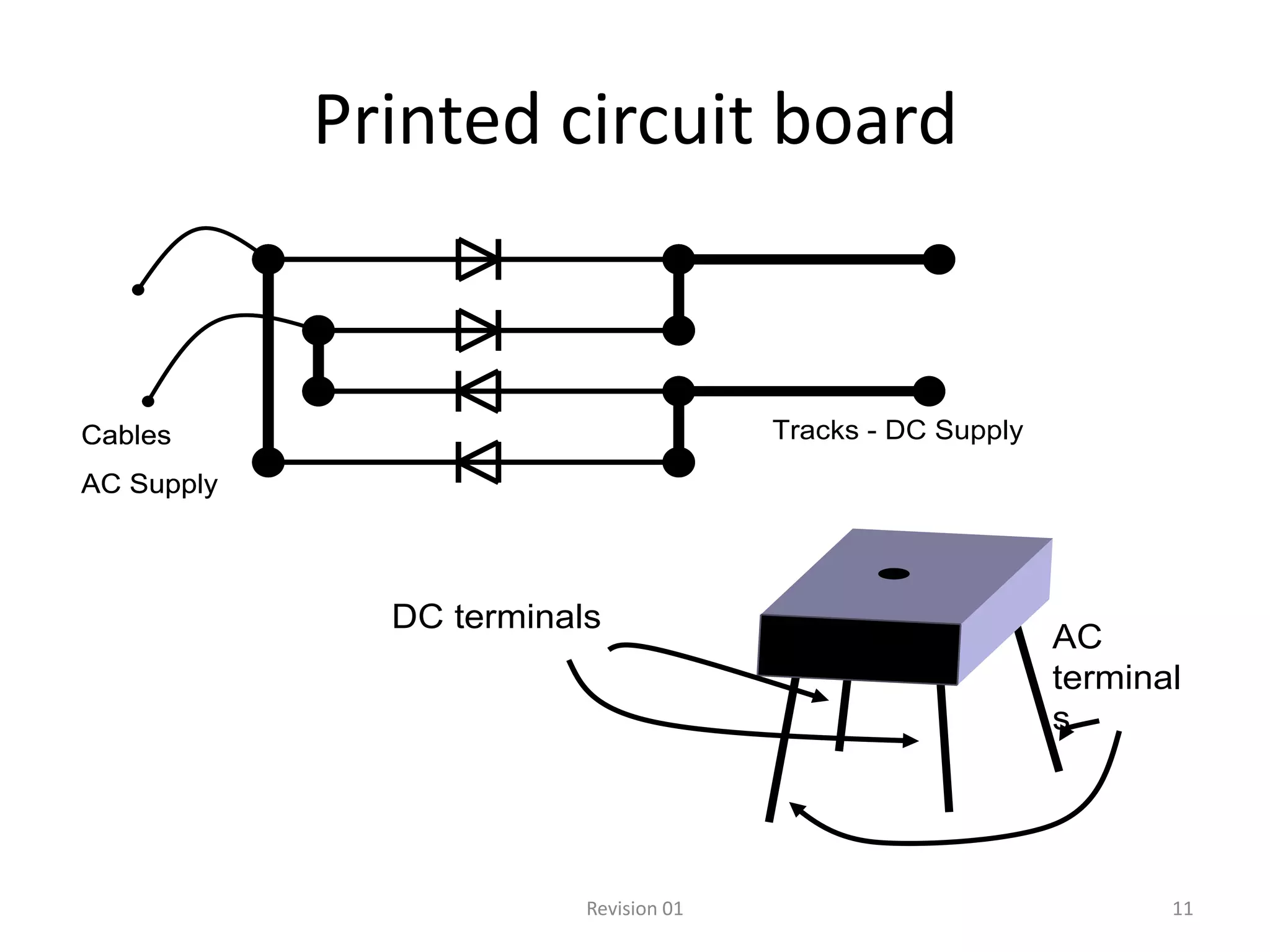
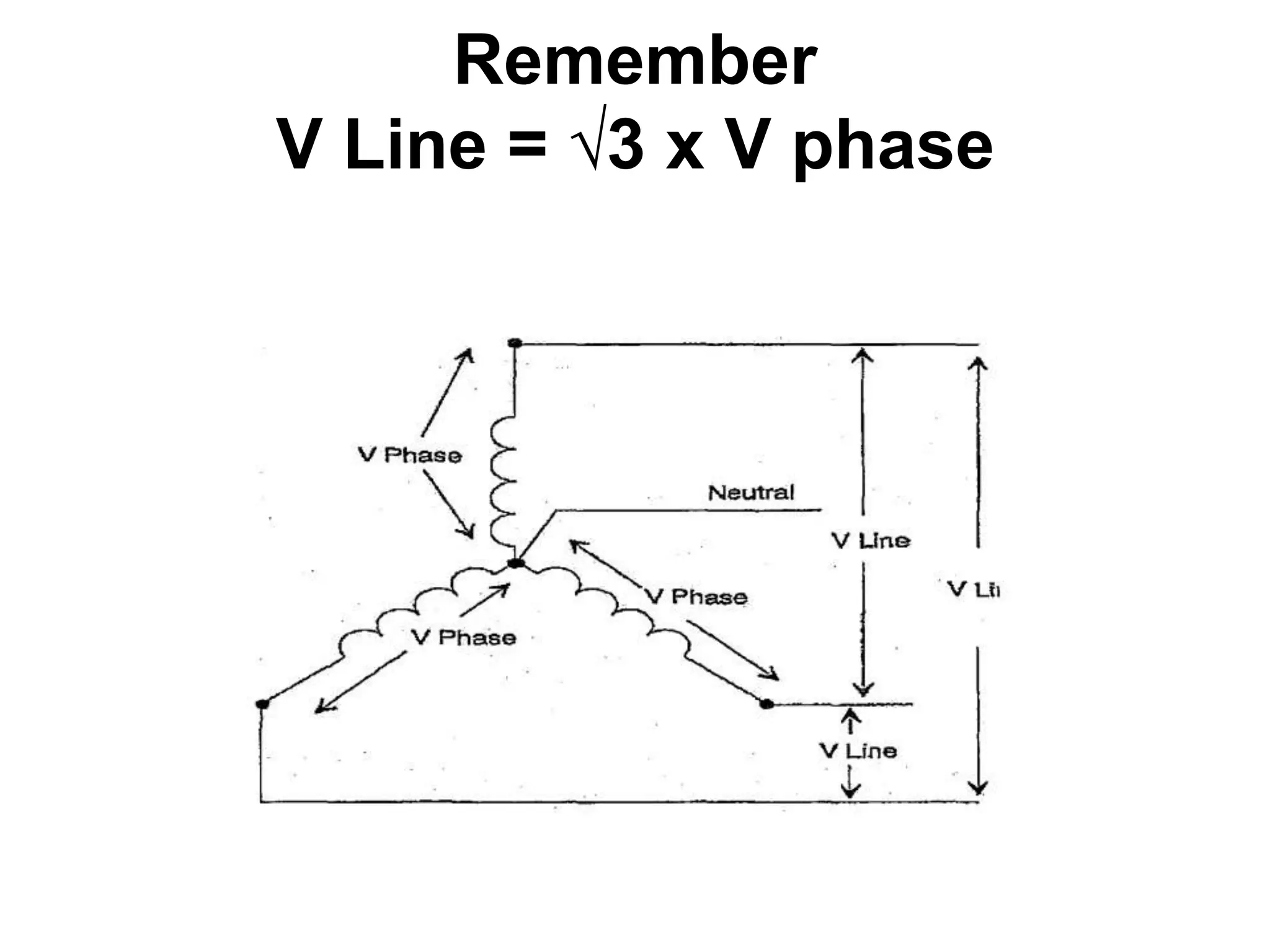
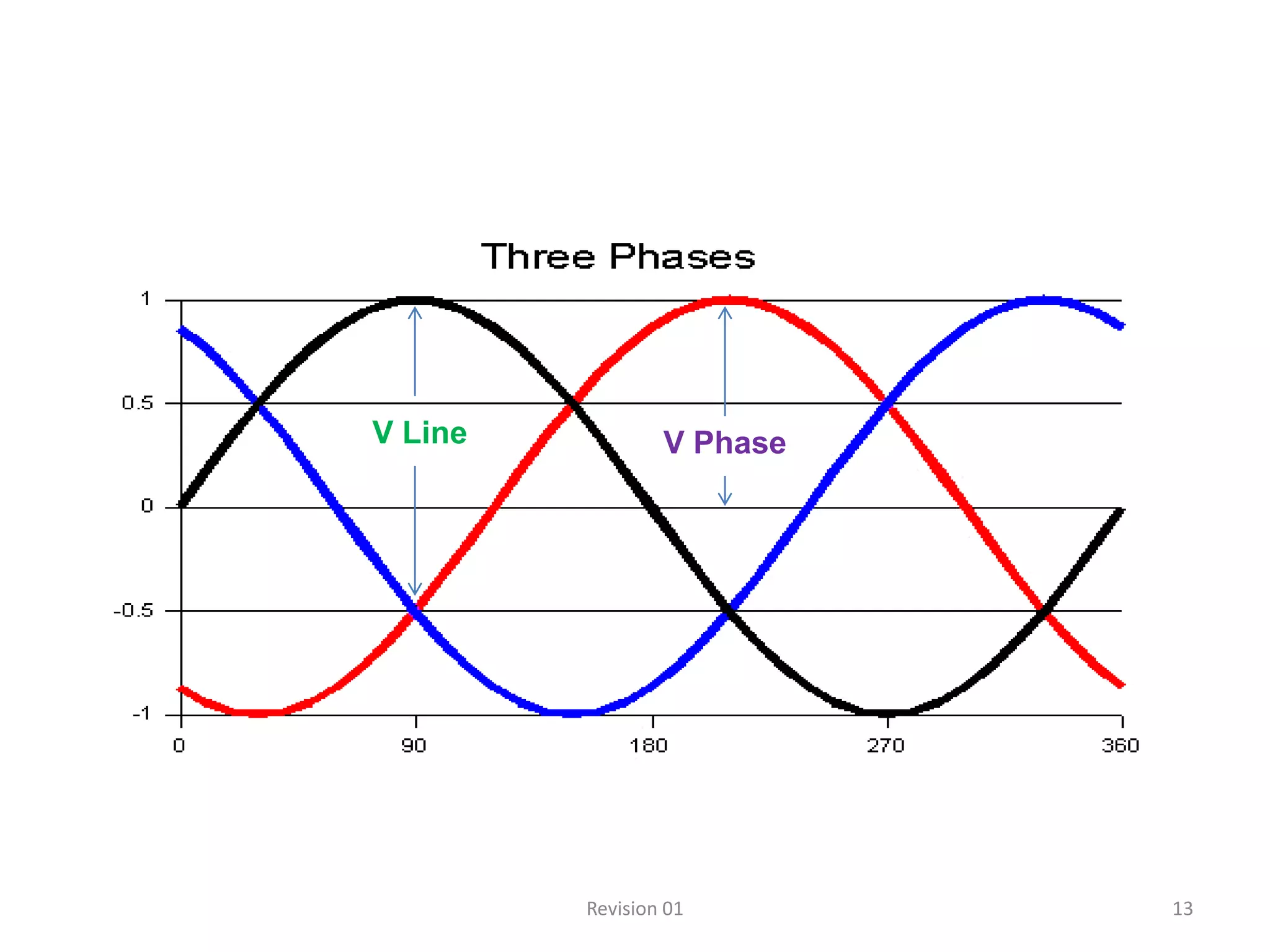
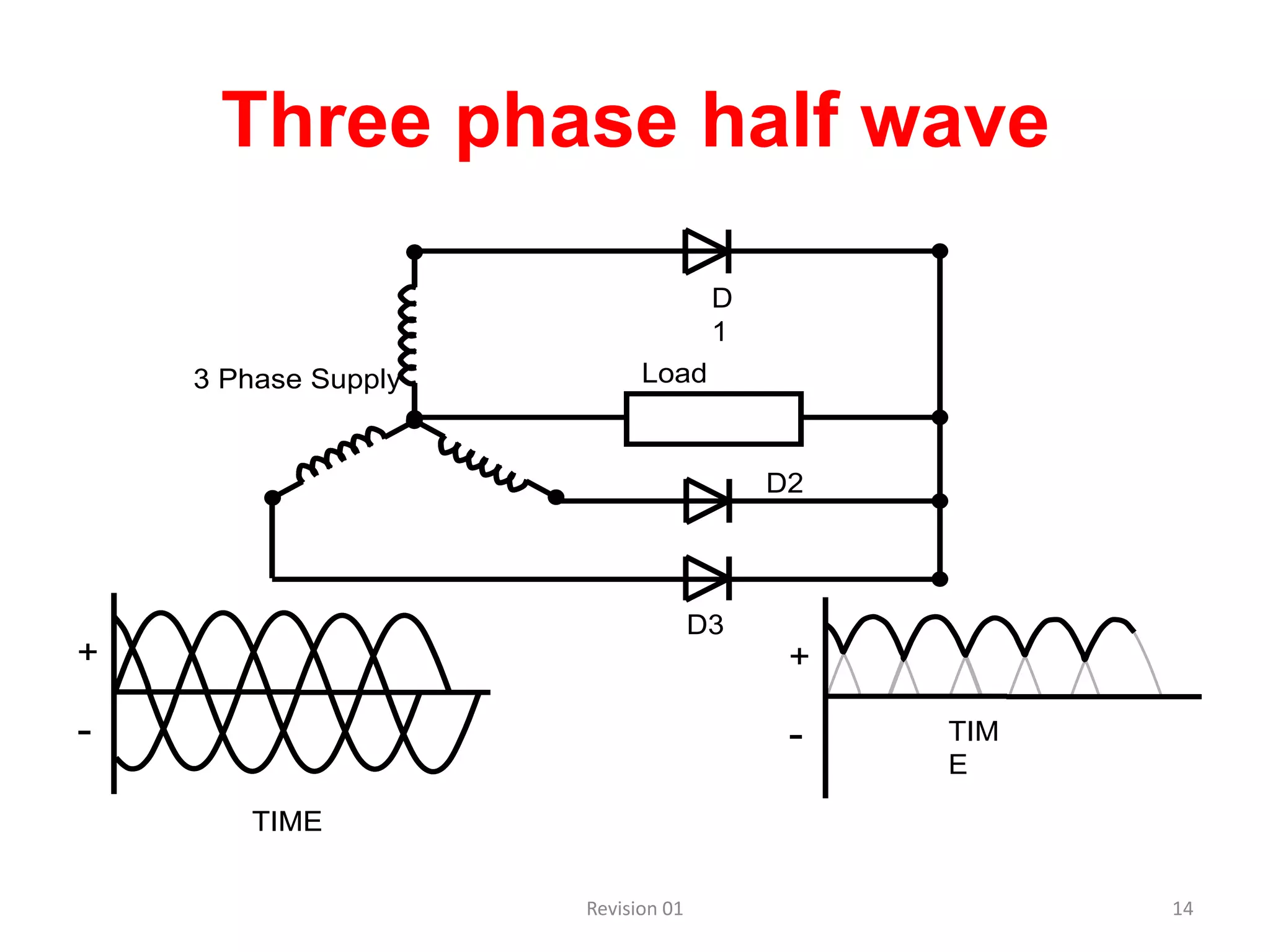
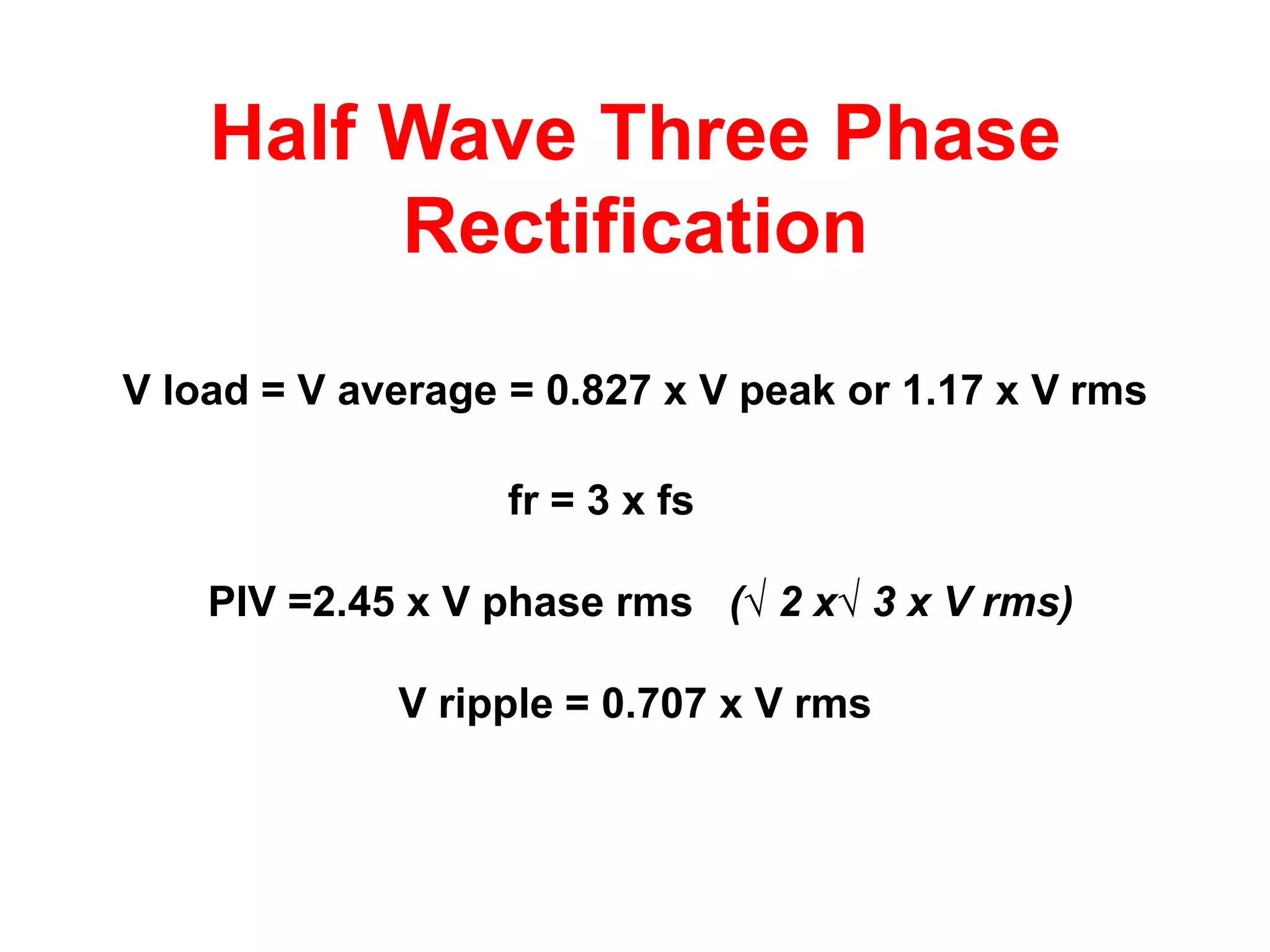
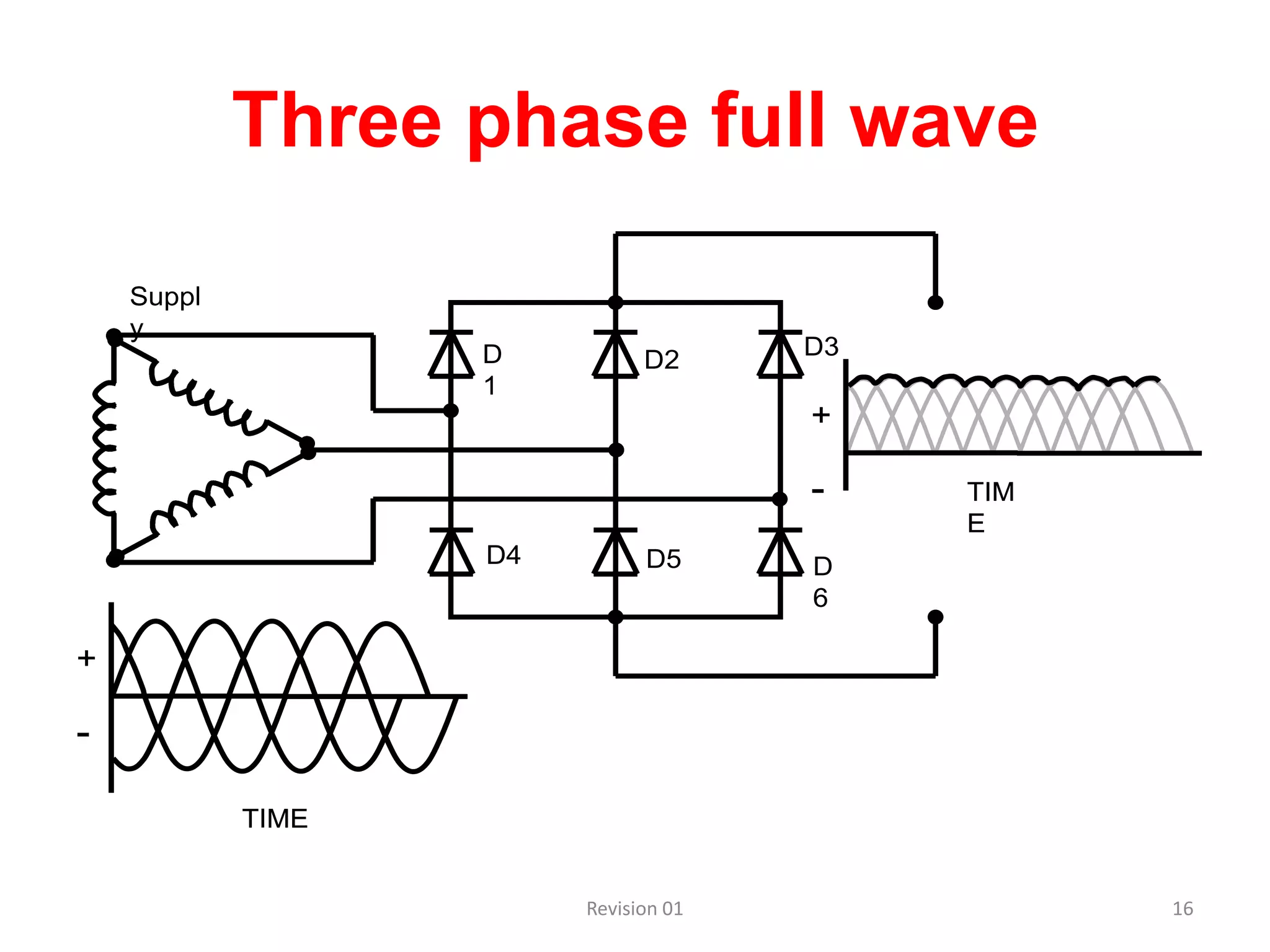
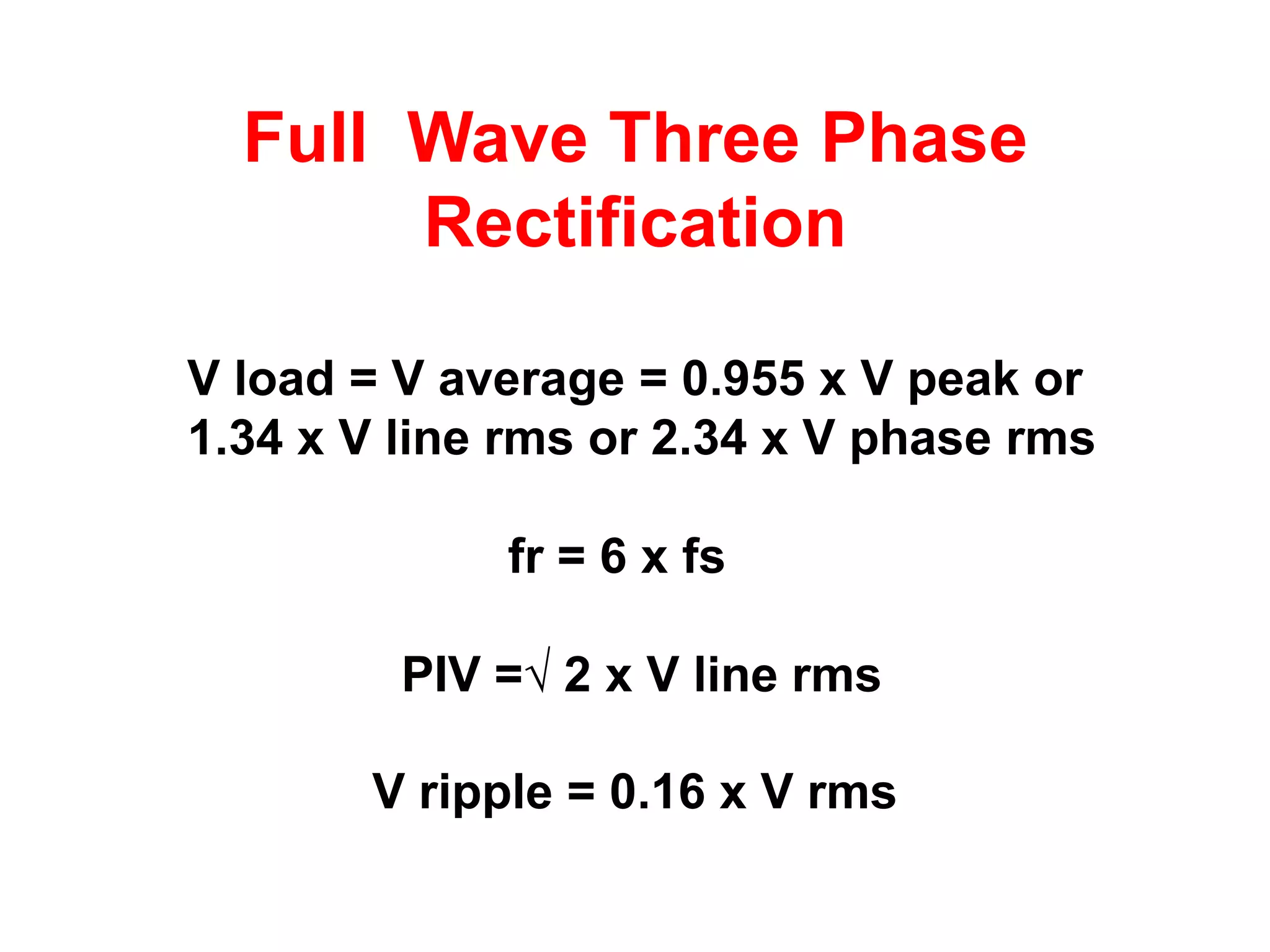
DC power supplies work by taking an AC voltage from a transformer, rectifying it using diodes to convert it to DC, filtering it using capacitors to smooth the output, and regulating it using integrated circuits to maintain a steady voltage level. Common rectification methods include half-wave and full-wave rectification using either single-phase or three-phase inputs. The rectification process converts the AC voltage to a pulsing DC voltage that is then filtered and regulated.