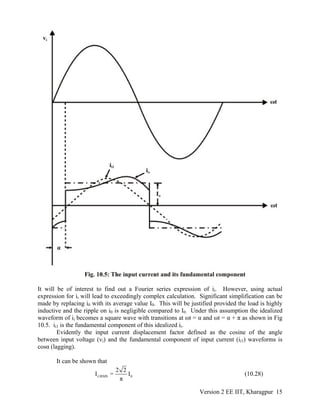
This document provides an overview of single phase fully controlled rectifiers. It begins by explaining the advantages of fully controlled rectifiers over uncontrolled rectifiers, namely the ability to control output voltage/current and allow bidirectional power flow. It then discusses the operation of a single phase fully controlled half-wave rectifier with resistive and resistive-inductive loads. The full bridge configuration is introduced as the most popular topology. Operation in both continuous and discontinuous conduction modes is analyzed for a full bridge supplying an R-L-E load. Key points like conduction periods, voltage waveforms, and the relationship between firing angle and output voltage/current are explained.




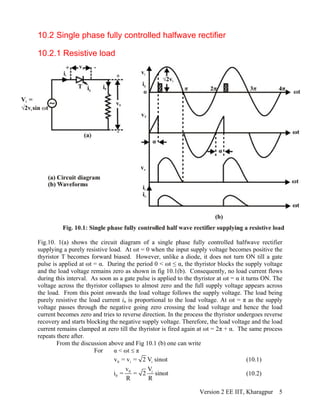




![The dc link voltage waveform shown next follows from this conduction diagram and the
conduction table shown in Fig 10.3(b). It is observed that the emf source E is greater than the dc
link voltage till ωt = α. Therefore, the load current i0 continues to fall till this point. However,
as T1T2 are fired at this point v0 becomes greater than E and i0 starts increasing through R-L and
E. At ωt = π – θ v0 again equals E. Depending upon the load circuit parameters io reaches its
maximum at around this point and starts falling afterwards. Continuous conduction mode will be
possible only if i0 remains greater than zero till T3T4 are fired at ωt = π + α where upon the same
process repeats. The resulting i0 waveform is shown below v0. The input ac current waveform ii
is obtained from i0 by noting that whenever T1T2 conducts ii = i0 and ii = - i0 whenever T3T4
conducts. The last waveform shows the typical voltage waveform across the thyristor T1. It is to
be noted that when the thyristor turns off at ωt = π + α a negative voltage is applied across it for a
duration of π – α. The thyristor must turn off during this interval for successful operation of the
converter.
It is noted that the dc voltage waveform is periodic over half the input cycle. Therefore,
it can be expressed in a Fourier series as follows.
[
α
0 OAV an bn
n=1
v = V + v cos2nωt + v sin2nωt∑ ] (10.16)
Where
π+α
OAV 0 iα
1 2 2
V = v dωt = V cosα
π π∫ (10.17)
π
an 0 i0
2 2 2 cos(2n +1)α cos(2n -1)α
v = v cos2nωt dωt = V -
π π 2n +1 2n -1
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ⎥⎣ ⎦∫ (10.18)
π
bn 0 i0
2 2 2 sin(2n +1)α sin(2n -1)α
v = v sin2nωt dωt = V -
π π 2n +1 2n -1
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ⎥⎣ ⎦∫ (10.19)
Therefore the RMS value of the nth harmonic
2 2
OnRMS an bn
1
V = v + v
2
(10.20)
RMS value of v0 can of course be completed directly from.
π+α
2
ORMS 0 iα
1
V = v dωt = V
π ∫ (10.21)
Fourier series expression of v0 is important because it provides a simple method of estimating
individual and total RMS harmonic current injected into the load as follows:
The impedance offered by the load at nth harmonic frequency is given by
2
nZ = R + (2nωL)2
(10.22)
1
α 2
2onRMS
onRMS OHRMS onRMS
n=1n
V
I = ; I = I
Z
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣ ⎦
∑ (10.23)
From (10.18) – (10.23) it can be argued that in an inductive circuit IonRMS → 0 as fast as 1/n2
. So
in practice it will be sufficient to consider only first few harmonics to obtain a reasonably
accurate estimate of IOHRMS form equation 10.23. This method will be useful, for example, while
calculating the required current derating of a dc motor to be used with such a converter.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-10dkpeeenptel-151126034631-lva1-app6892/85/controlled-Full-Bridge-Rectifier-13-320.jpg)



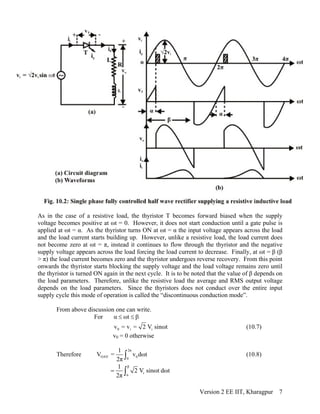
![π+α β π+α
OAV 0 i iα α β
1 1
V = v dωt = 2V sinωt dωt + 2V sinθ dωt
π π
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ⎥⎣ ⎦∫ ∫ ∫ (10.33)
Or [i
OAV
2V
V = cosα -cosβ + sinθ(π + α -β)
π
] (10.34)
OAV OAV i
OAV
V - E V - 2Vsinθ
I = =
R Zcosφ
(10.35)
Or [i
OAV
2V
I = cosα -cosβ +sinθ(α -β)
π Zcosφ
] (10.36)
It is observed that the performance of the converter is strongly affected by the value of β. The
value of β in terms of the load parameters (i.e, θ, φ and Z) and α can be found as follows.
In the interval α ωt β≤ ≤
o
o i
di
L + Ri + E = 2Vsinωt
dt
(10.37)
0 ωt=α
i = 0
From which the solution of i0 can be written as
( )
( )
{ }
ωt-α-
ωt-αi tanφ -
tanφ0
2V sinθ
i = sin(φ -α)e - + sin(ωt -φ)
1-eZ cosφ
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣ ⎦
(10.38)
Now 0 ωt=β
i = 0
α-β
α-βtanφ
tanφ
sinθ
sin(φ -α)e - + sin(β -φ) = 0
1-ecosφ
⎡ ⎤∴
⎣ ⎦
(10.39)
Given φ, α and θ, the value of β can be found by solving equation 10.39.
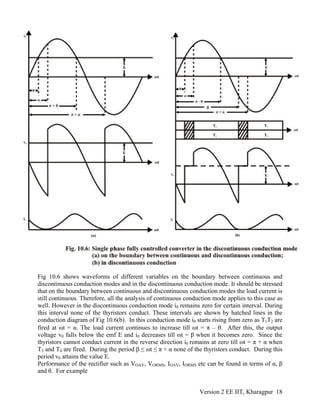
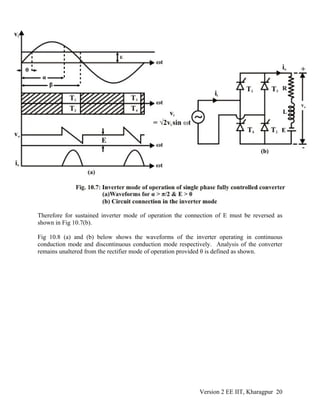
10.3.3 Inverter Mode of operation
The expression for average dc voltage from a single phase fully controlled converter in
continuous conduction mode was
0 i
2 2
V = V cosα
π
(10.40)
For α < π/2, Vd > 0. Since the thyristors conducts current only in one direction I0 > 0 always.
Therefore power flowing to the dc side P = V0I0 > 0 for α < π/2. However for α > π/2, V0 < 0.
Hence P < 0. This may be interpreted as the load side giving power back to the ac side and the
converter in this case operate as a line commutated current source inverter. So it may be
tempting to conclude that the same converter circuit may be operated as an inverter by just
increasing α beyond π/2. This might have been true had it been possible to maintain continuous
conduction for α < π/2 without making any modification to the converter or load connection. To
supply power, the load EMF source can be utilized. However the connection of this source in
Fig 10.3 is such that it can only absorb power but can not supply it. In fact, if an attempt is made
to supply power to the ac side (by making α > π/2) the energy stored in the load inductor will be
exhausted and the current will become discontinuous as shown in Fig 10.7 (a).
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-10dkpeeenptel-151126034631-lva1-app6892/85/controlled-Full-Bridge-Rectifier-19-320.jpg)


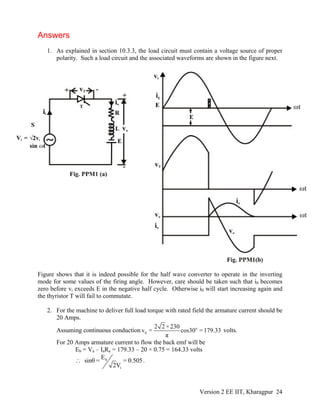
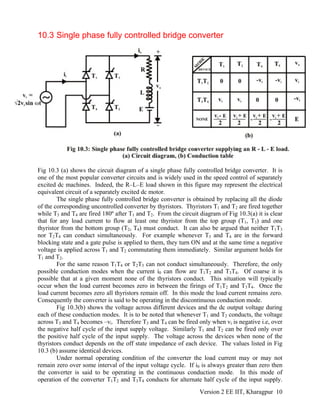
![For the given machine, oa
a
ωL
tan = = 20.944, = 87.266
R
φ φ .
Now from equation (10.32)
-π/tanφ
2sin(φ -α)
-sin(φ -α) =11.2369.
1-e
and
sinθ
=10.589
cosφ
∴ the conduction is continuous.
At 1500 RPM the back emf is 220 – 20 × 0.75 = 205 volts.
∴The speed at which the machine delivers rated torques
is r
164.33
N = ×1500 =1202 RPM
205
.
3. To maintain constant load torque equal to the rated value the armature voltage should be
a a a brated rated
rated
N
V = r I + E
N
N
= 0.75× 20 + 205× = 0.137 N +15 V
1500
In a fully controlled converter operating in the continuous conduction mode
a i
2 2
V = V cosα = 207.073 cosα
π
- 4
cosα = 6.616 × 10 N + 0.0724∴
Now the power factor from equation 10.31 is
- 42 2
pf = cosα = 5.9565 × 10 N + 0.0652
π
This gives the input power factor as a function of speed.
4. At 2000 RPM, b
2000
E = × 205 = 273.33 volts
1500
o ob
i
E
sinθ = = 0.84, = 87.266 , α = 30
2V
∴ φ
From equation 10.32 it can be shown that the conduction will be discontinuous.
Now from equation 10.39
( ) ( ) ( )
α -β
tanφ sinθ sinθ
+sin φ-αsin - + e =α -φ α -β
cosφ cosφ
⎡ ⎤
⎡ ⎤⎣ ⎦ ⎢ ⎥
⎣ ⎦
or [ ] ( ).0477(α -β) o
e - sin =17.6157.266 + α -β17.61+.8412 ⎡ ⎤⎣ ⎦
( ).0477(α -β) o
18.4515 e - sin =17.61+ 57.266α -β⎡ ⎤⎣ ⎦
Solving which β ≈ 140°
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-10dkpeeenptel-151126034631-lva1-app6892/85/controlled-Full-Bridge-Rectifier-25-320.jpg)
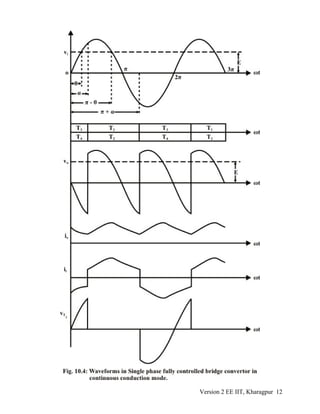
![∴ from equation 10.36
[ ]i
oav
2V
I = = 2.676 Ampscosα -cosβ +sinθ(α -β)
πZcosφ
∴ the load torque should be
2.676
×100 =13.38%
20
of the full load torque.
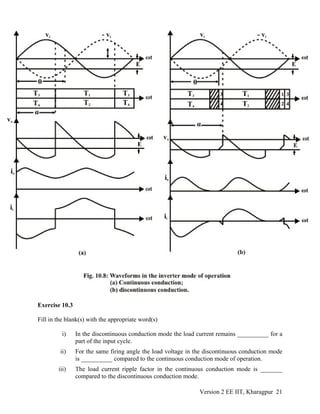
5. Referring to Fig 10.8 (a) let there be a commutation failure of T1 at ωt = α. In that case
the conduction mode will be T3 T2 instead of T1 T2 and v0 will be zero during that period.
As a result average value of V0 will be less negative and the average armature current
will increase. However the converter will continue to operate in the inverter mode and
the motor will be braked.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-10dkpeeenptel-151126034631-lva1-app6892/85/controlled-Full-Bridge-Rectifier-26-320.jpg)