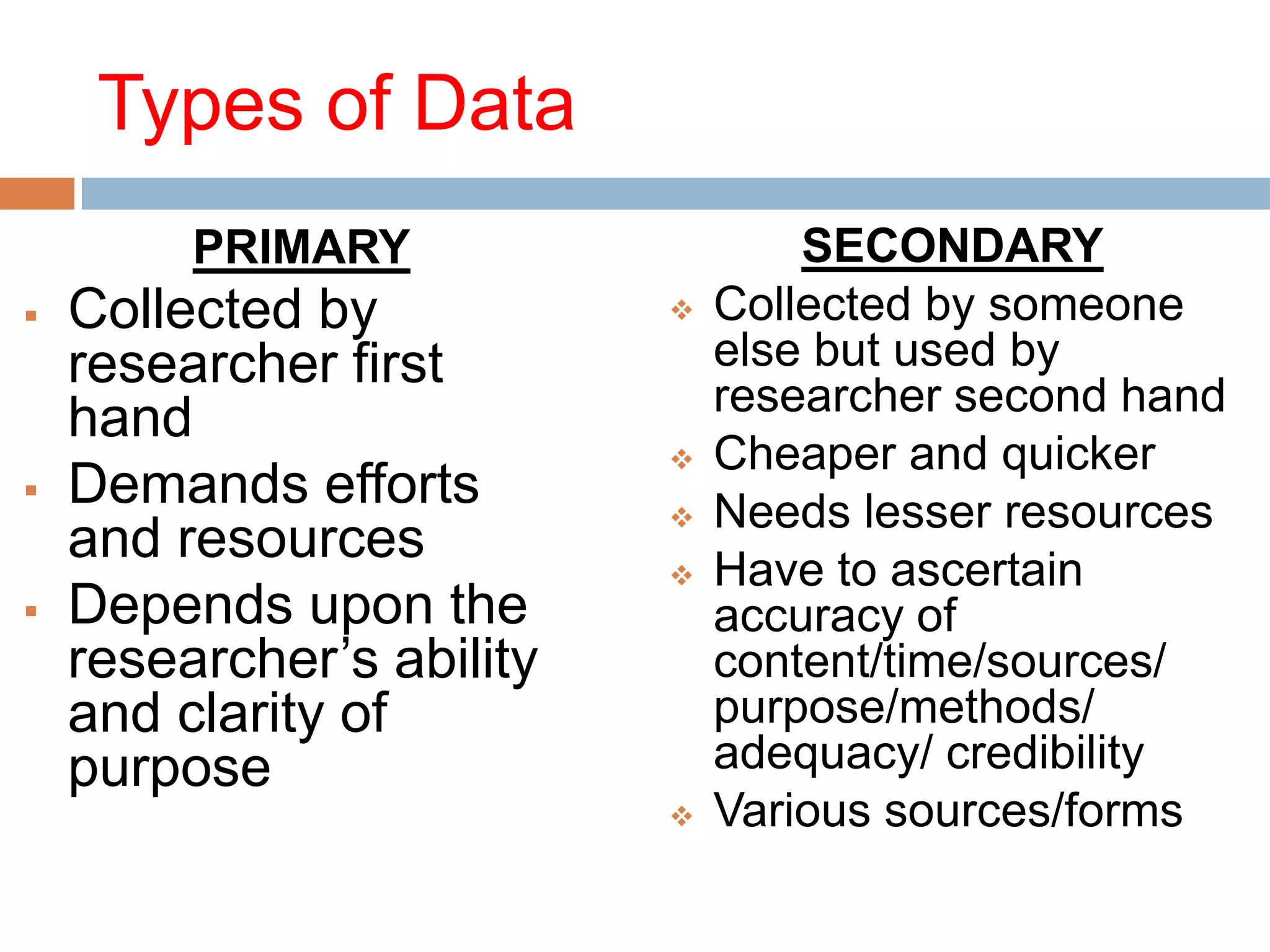
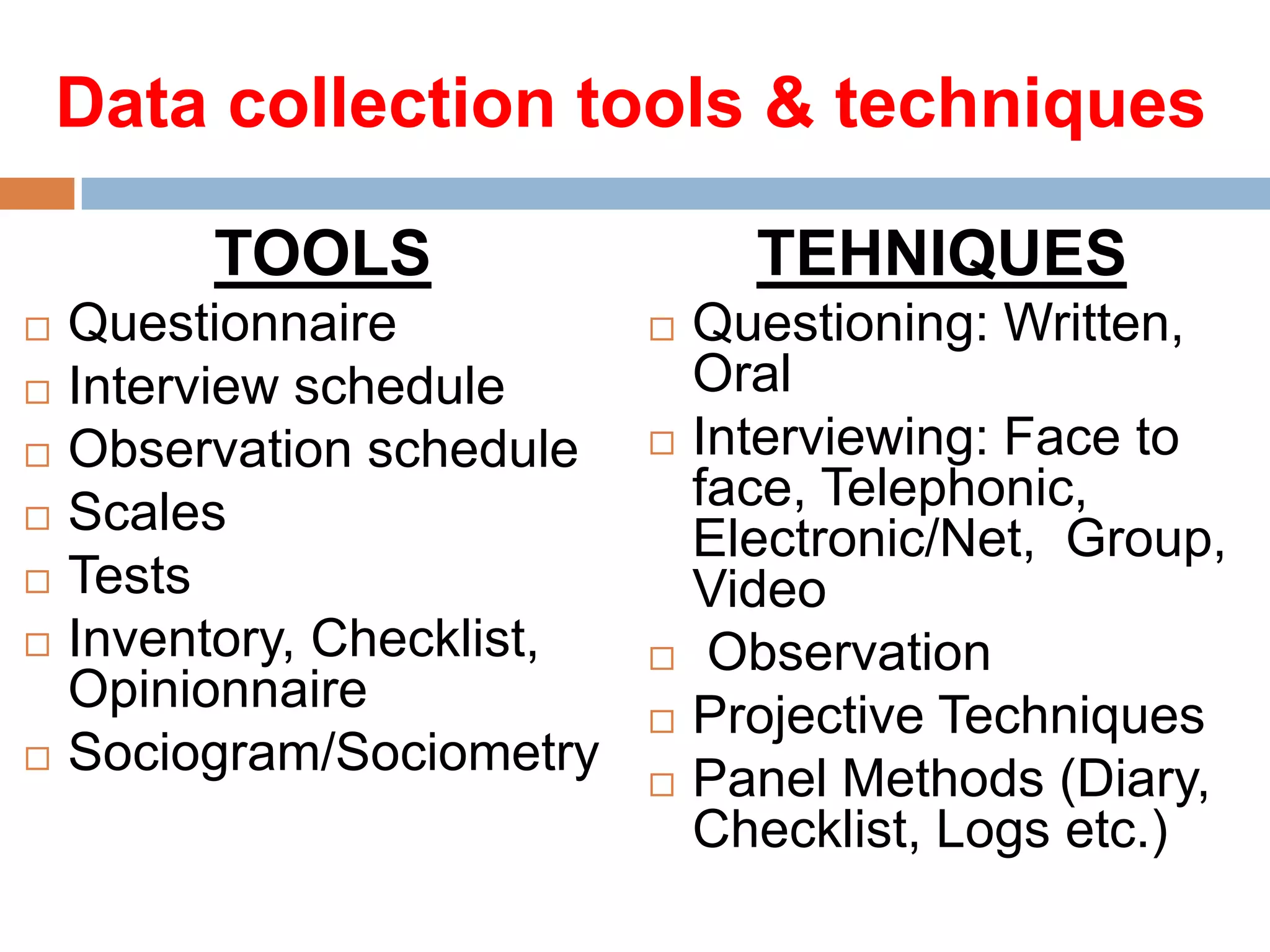
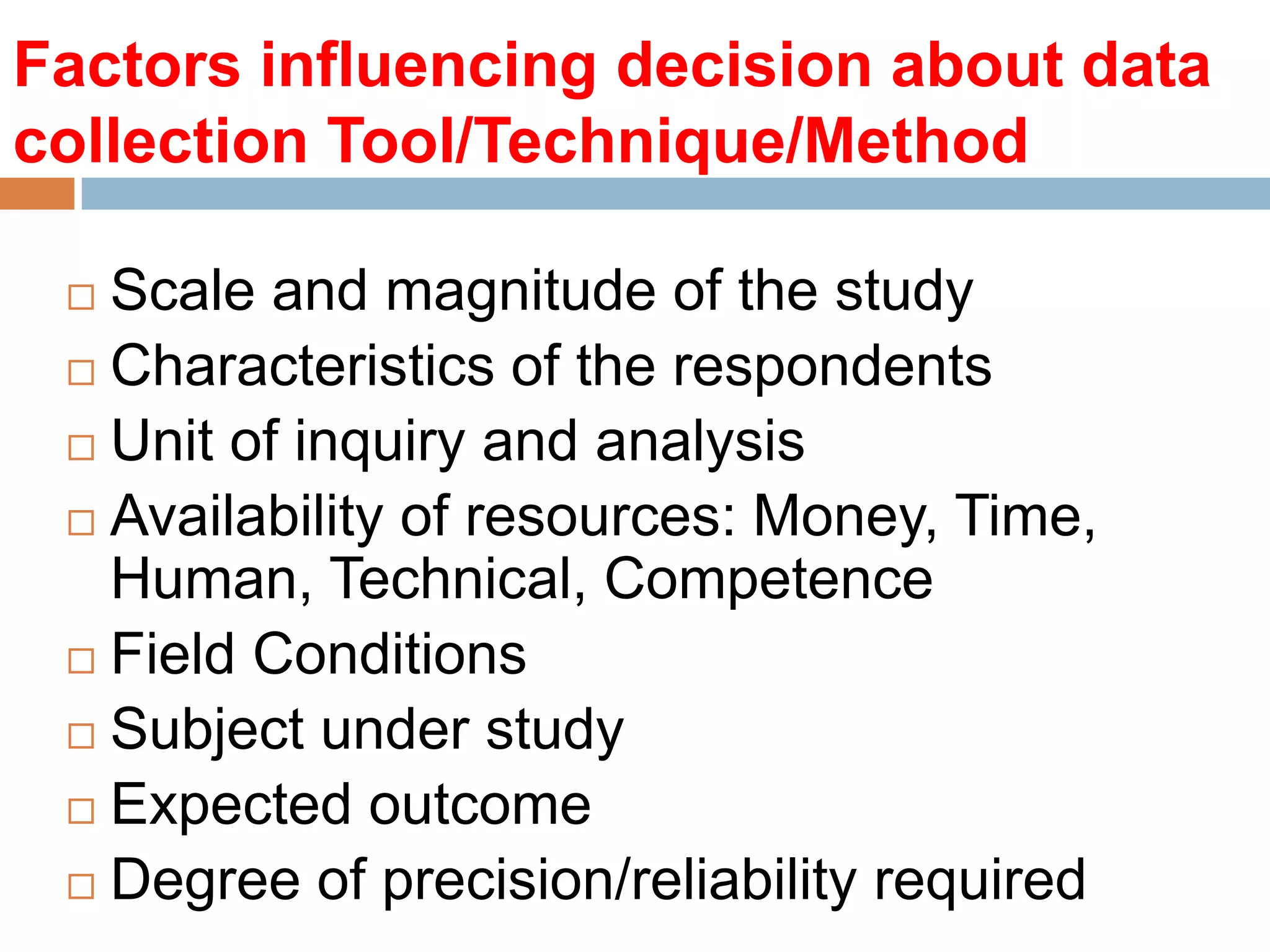
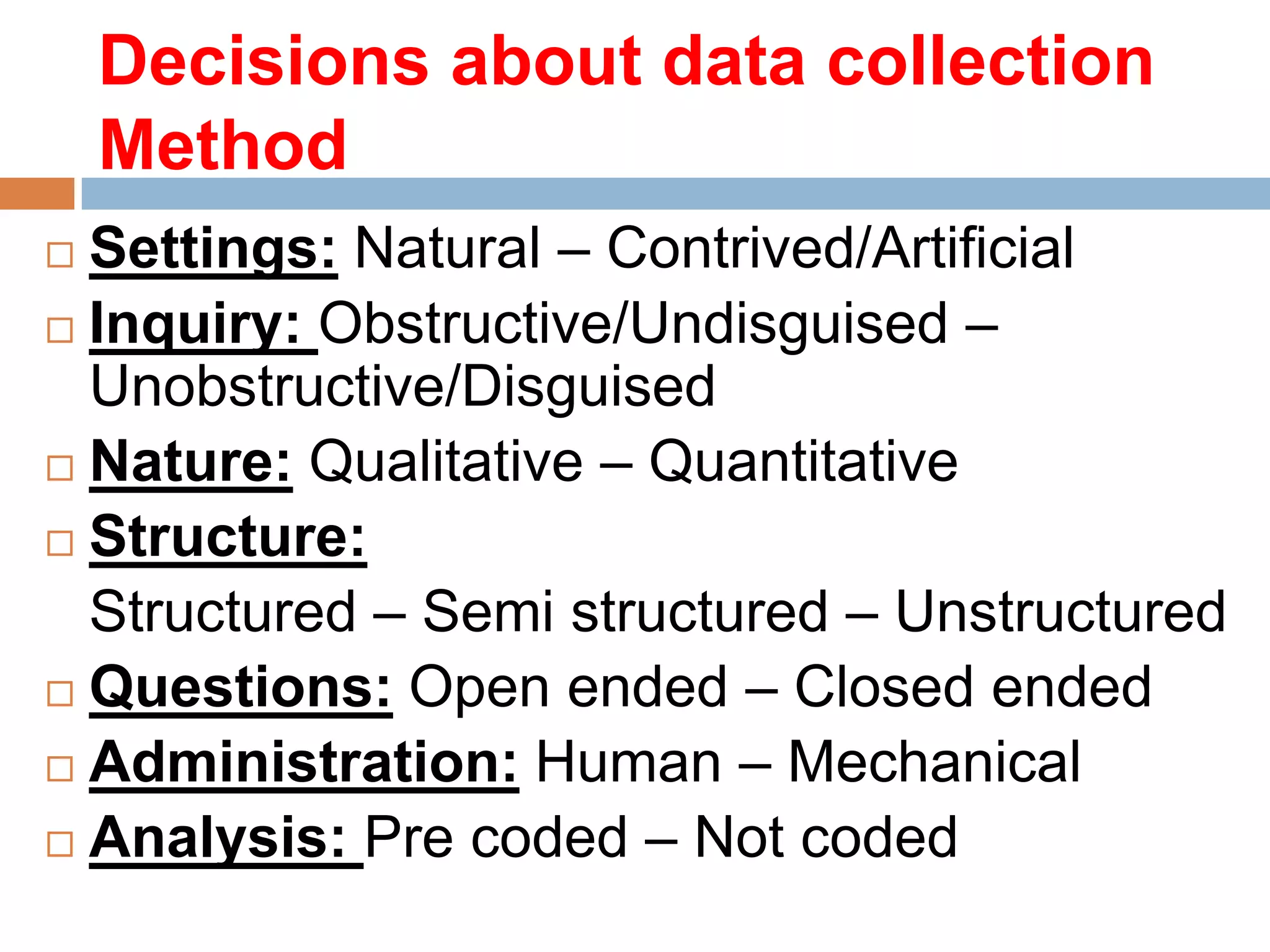
The document discusses various aspects of data collection, including definitions of data, types of data (primary and secondary), and steps involved in collecting data effectively. It outlines tools and techniques for data collection, the factors influencing the choice of these methods, and highlights the importance of clarity in research objectives and tools used. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for proper communication and understanding in survey design to ensure accurate data gathering.