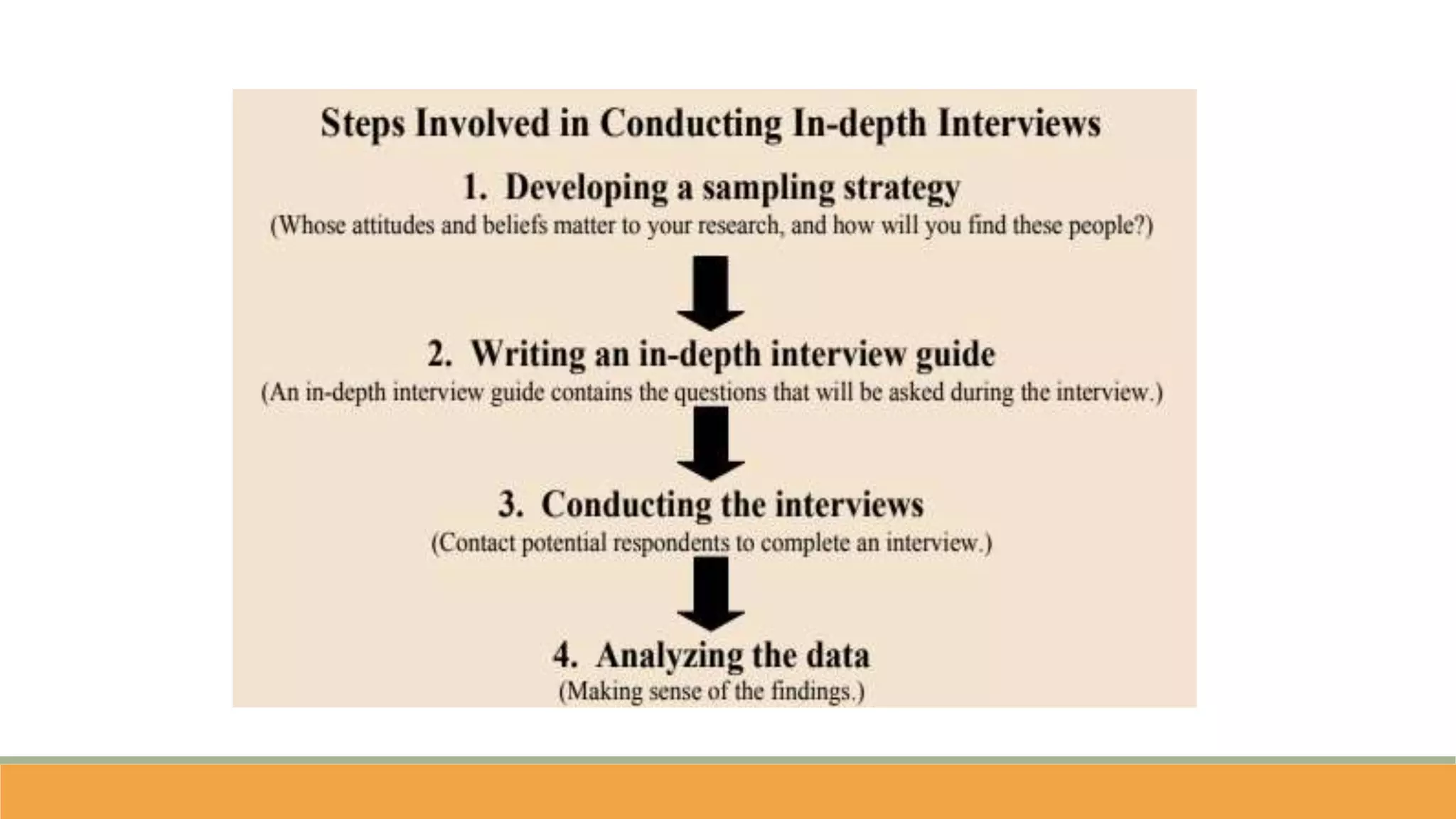
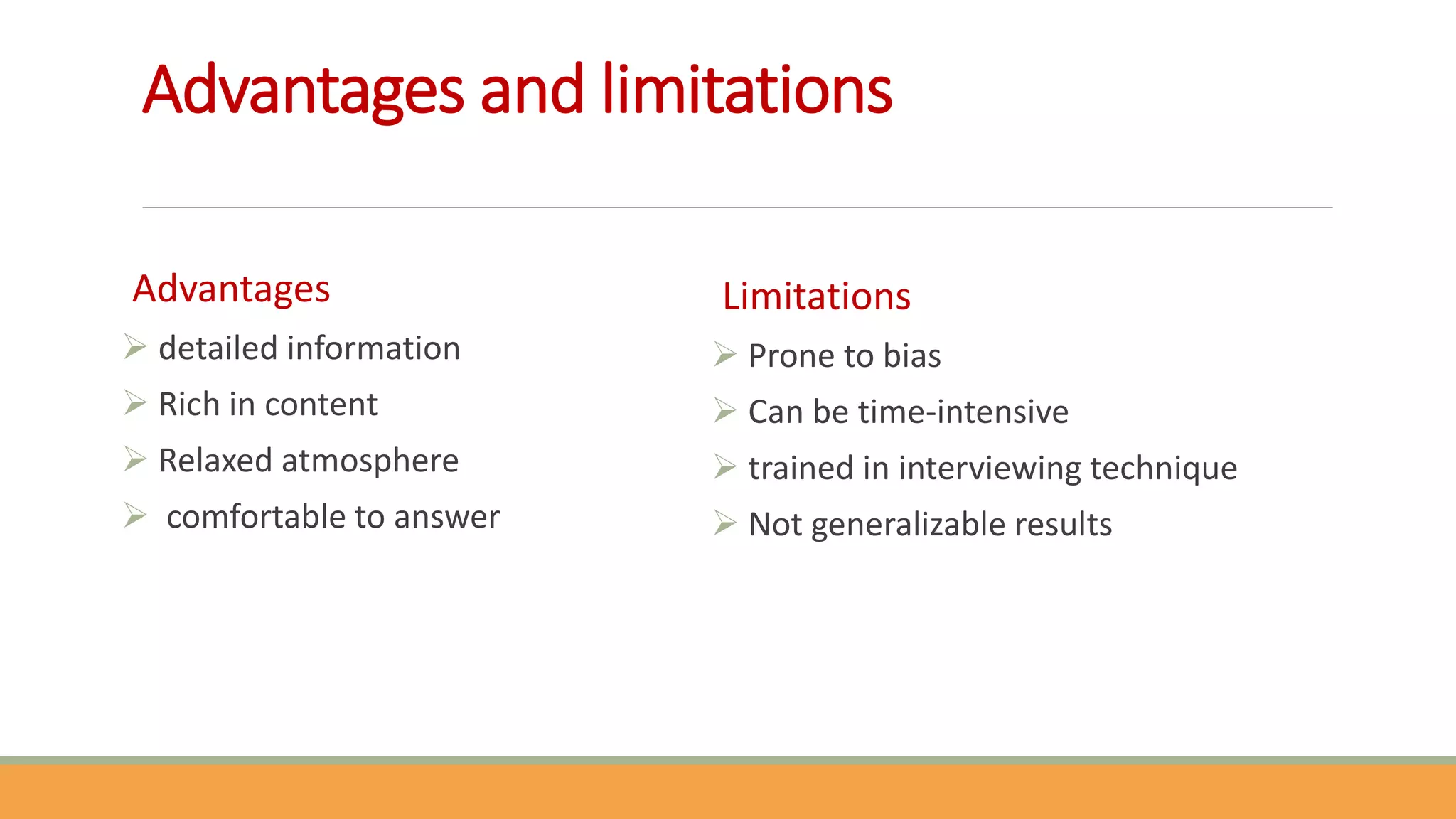
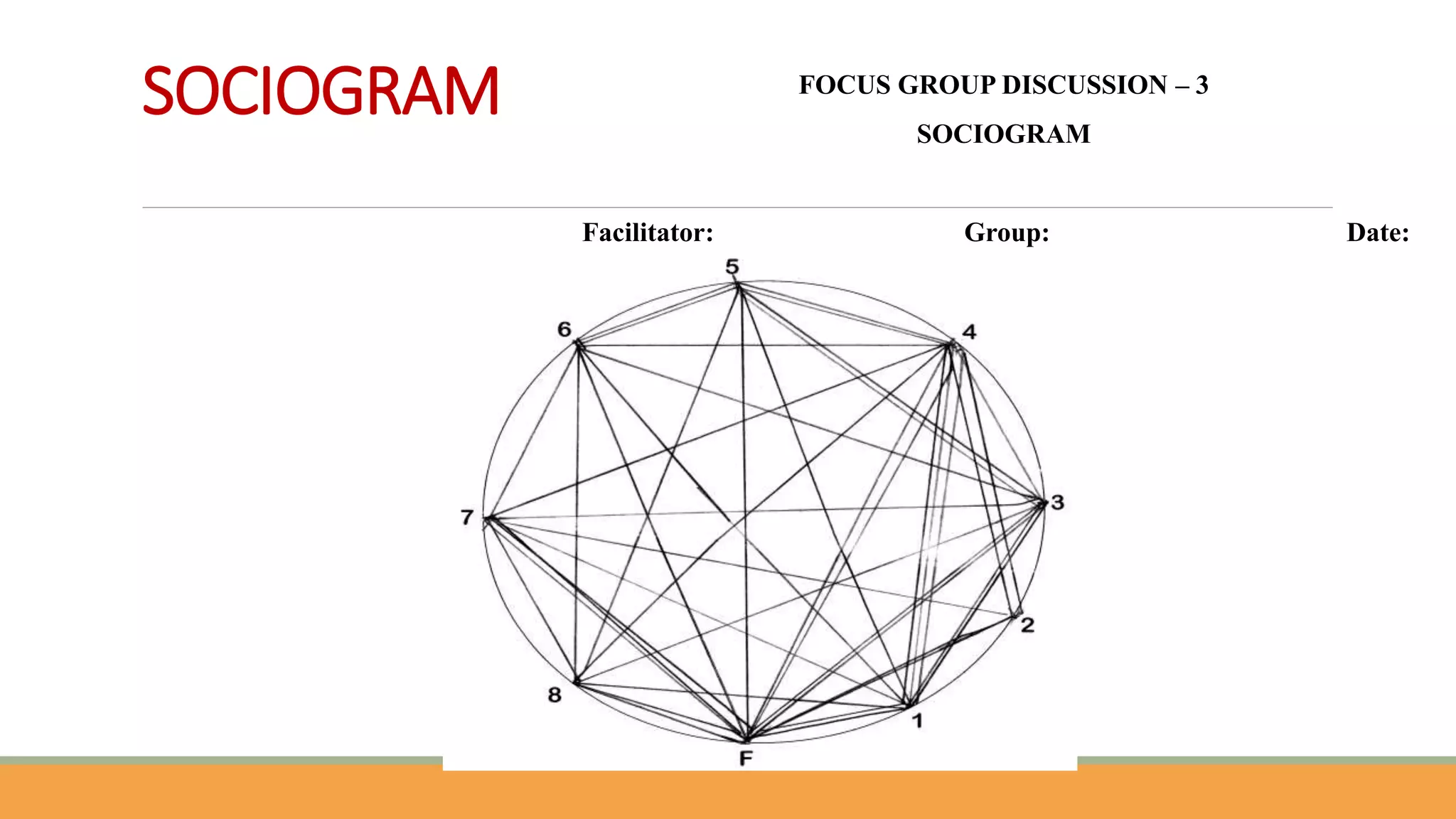
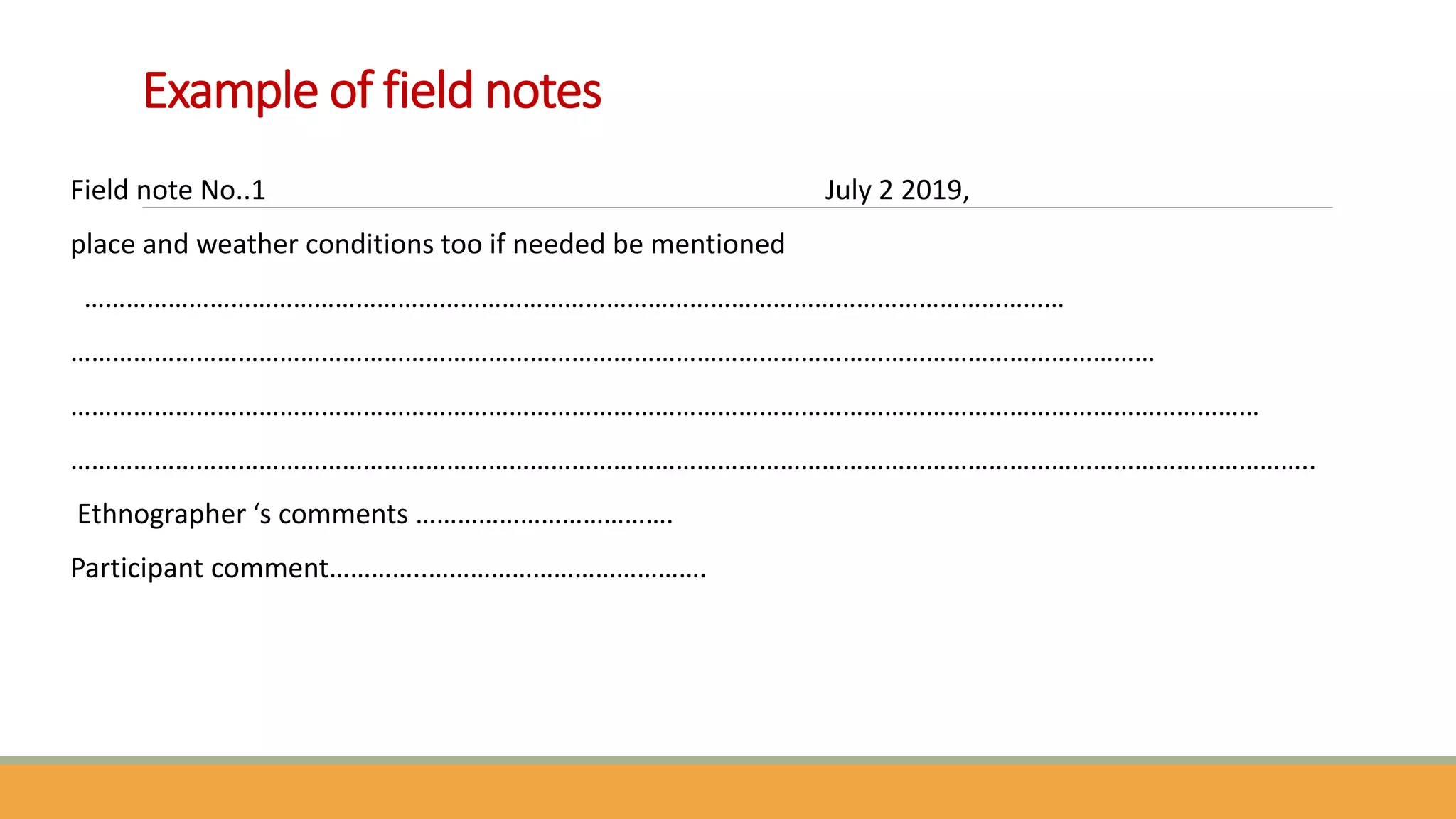
The document discusses qualitative research methods, focusing on how to generate qualitative data through various approaches like in-depth interviews, focus group discussions, and observations. It highlights the importance of understanding social phenomena and the complexities of human behavior, emphasizing rich, detailed information while noting the limitations of bias and time consumption. Ethical considerations in data collection, including informed consent and confidentiality, are also addressed.