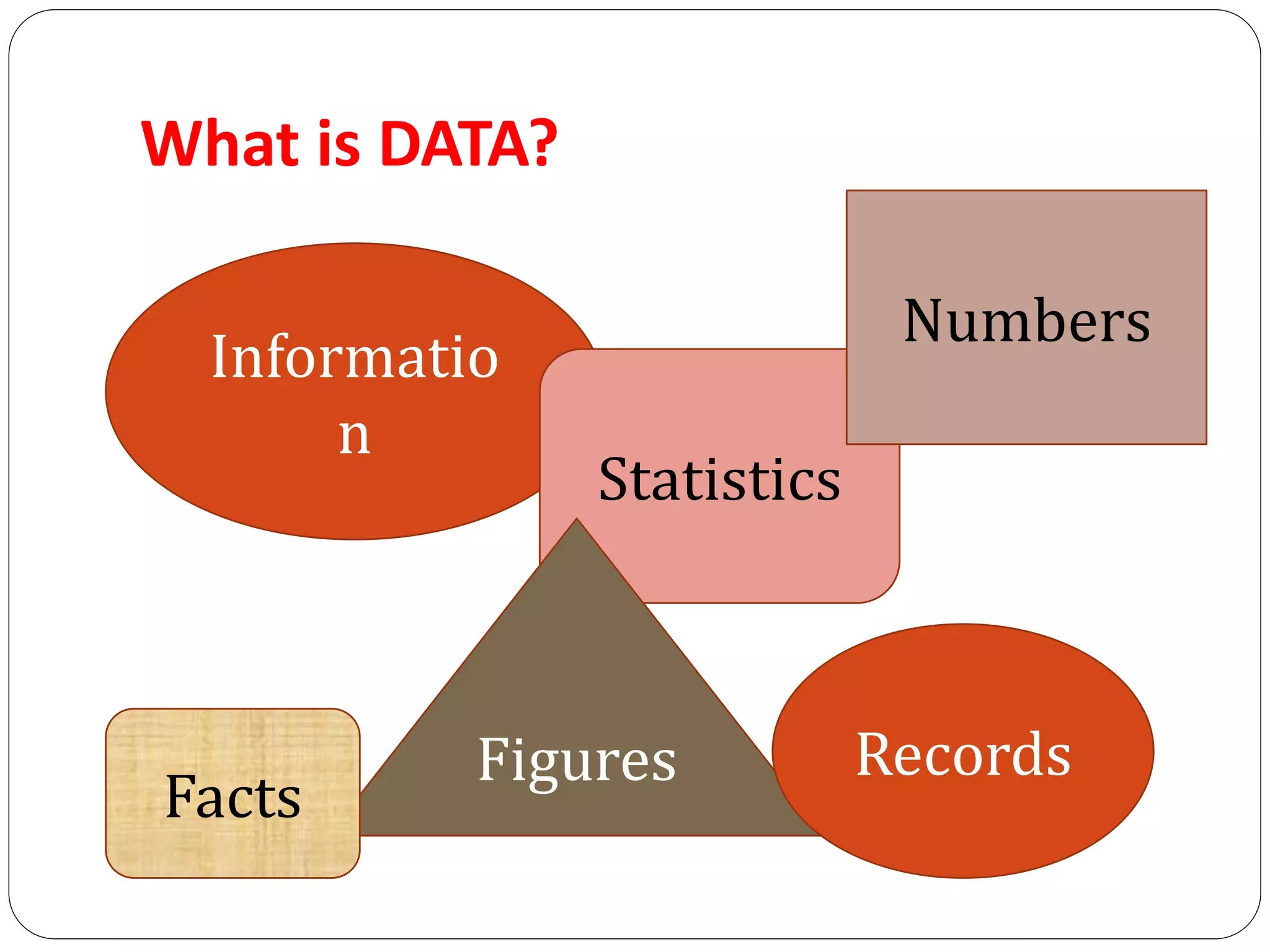
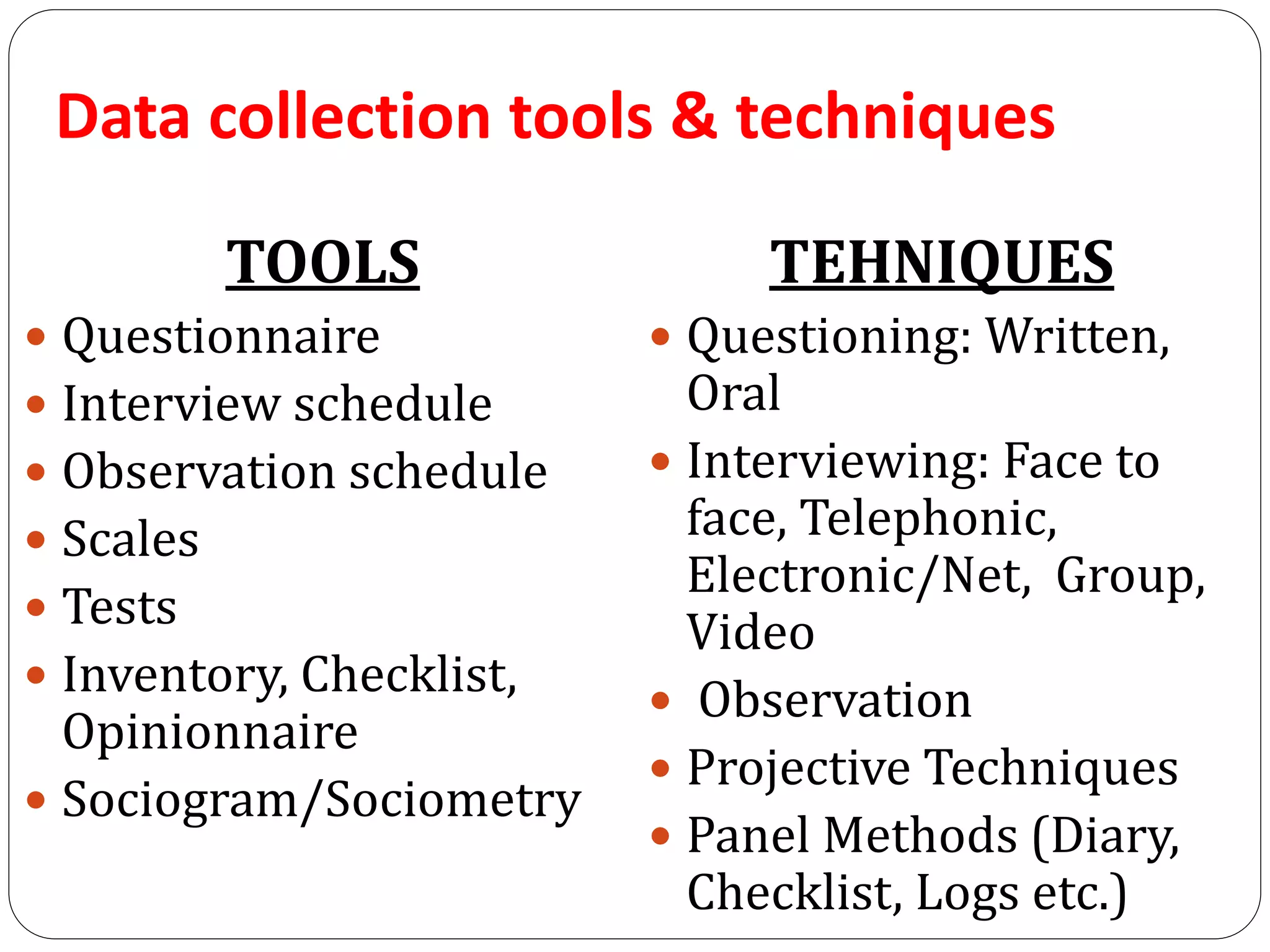
This document discusses data collection tools, techniques, and methods. It provides definitions of data and describes the different types of data. The key steps in data collection are identified as constructing tools, deciding on techniques, testing tools through pilot studies, finalizing tools and techniques, and actual data collection. Important factors that influence the choice of data collection methods are also outlined.