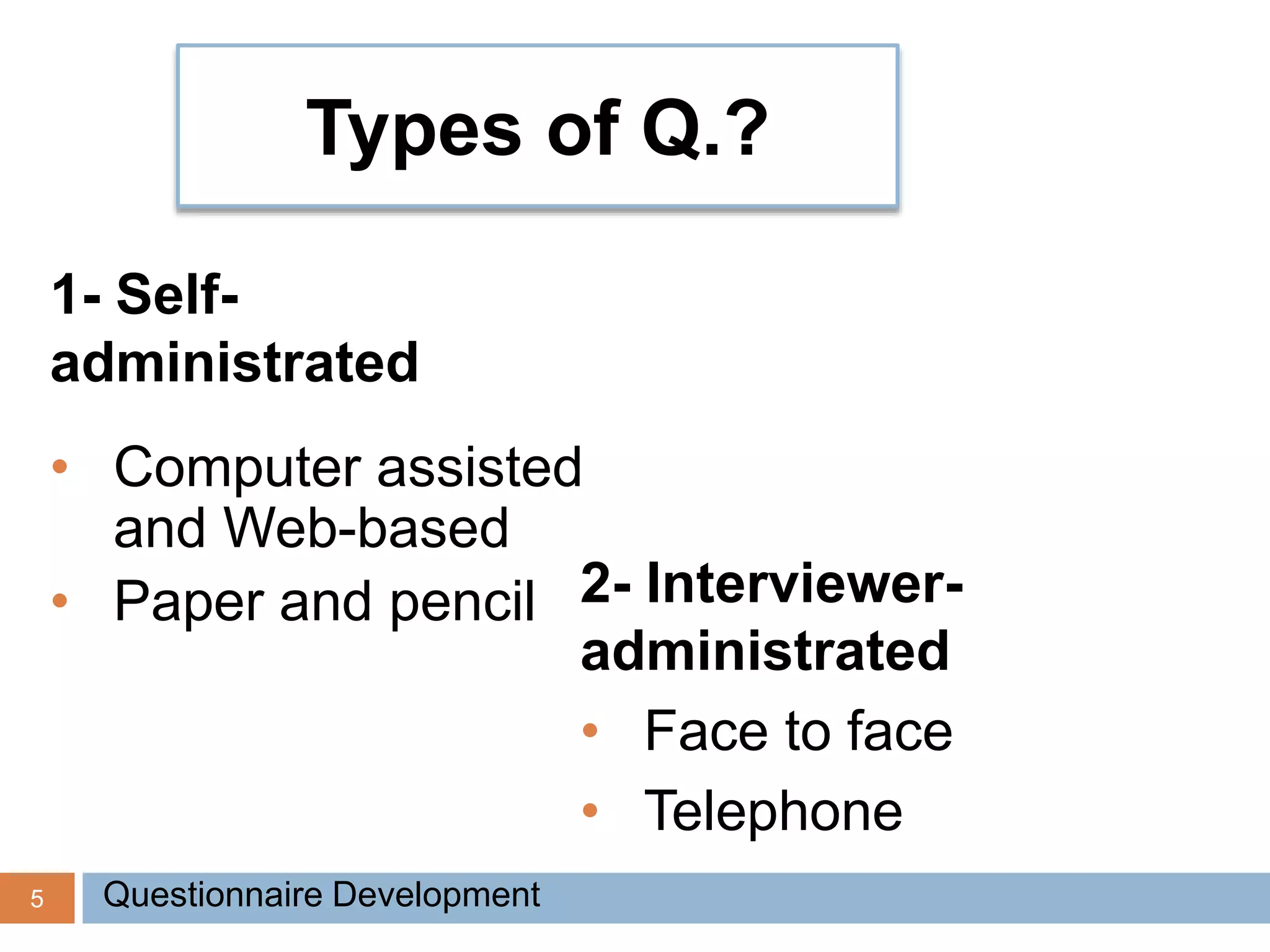
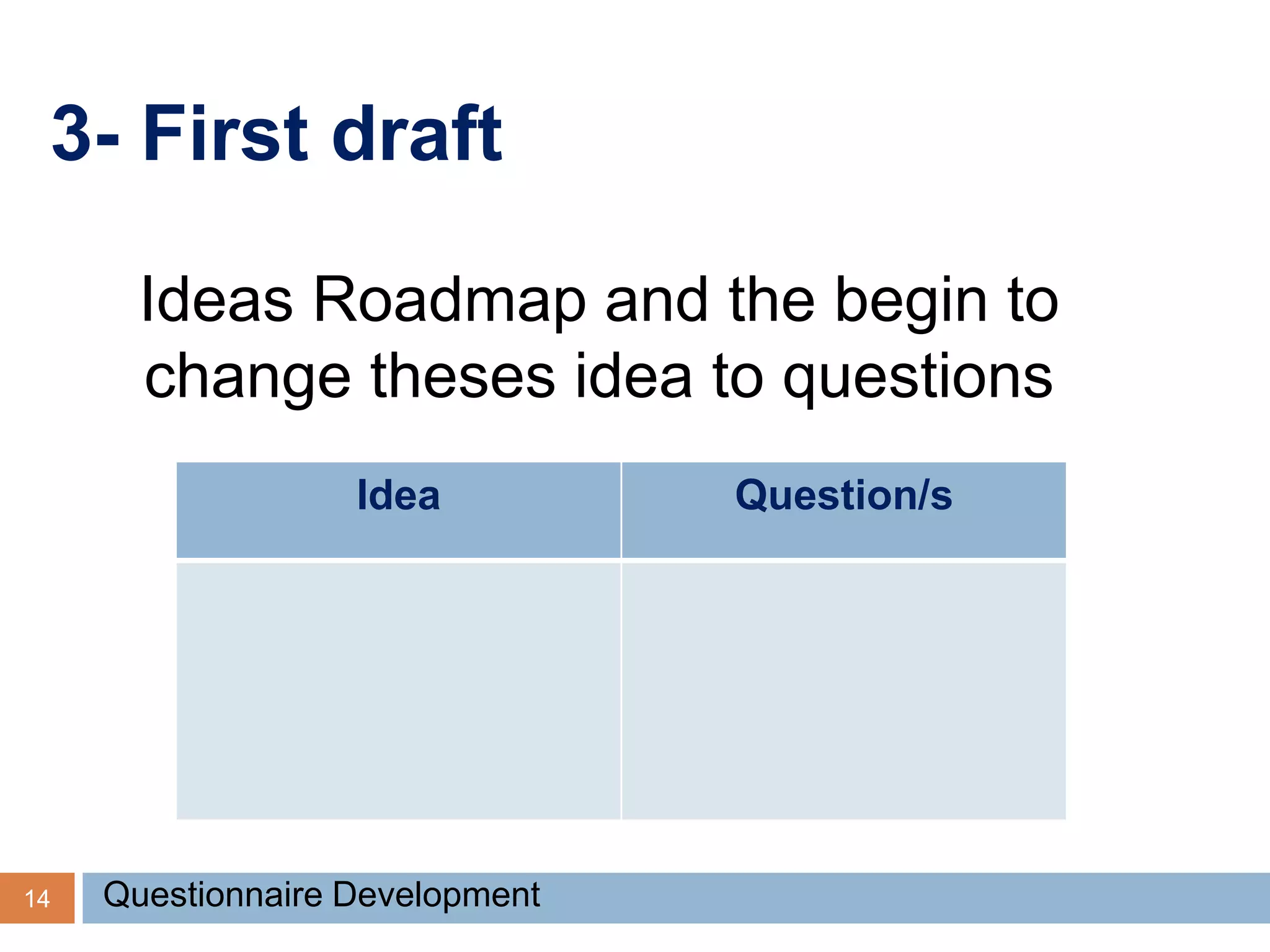
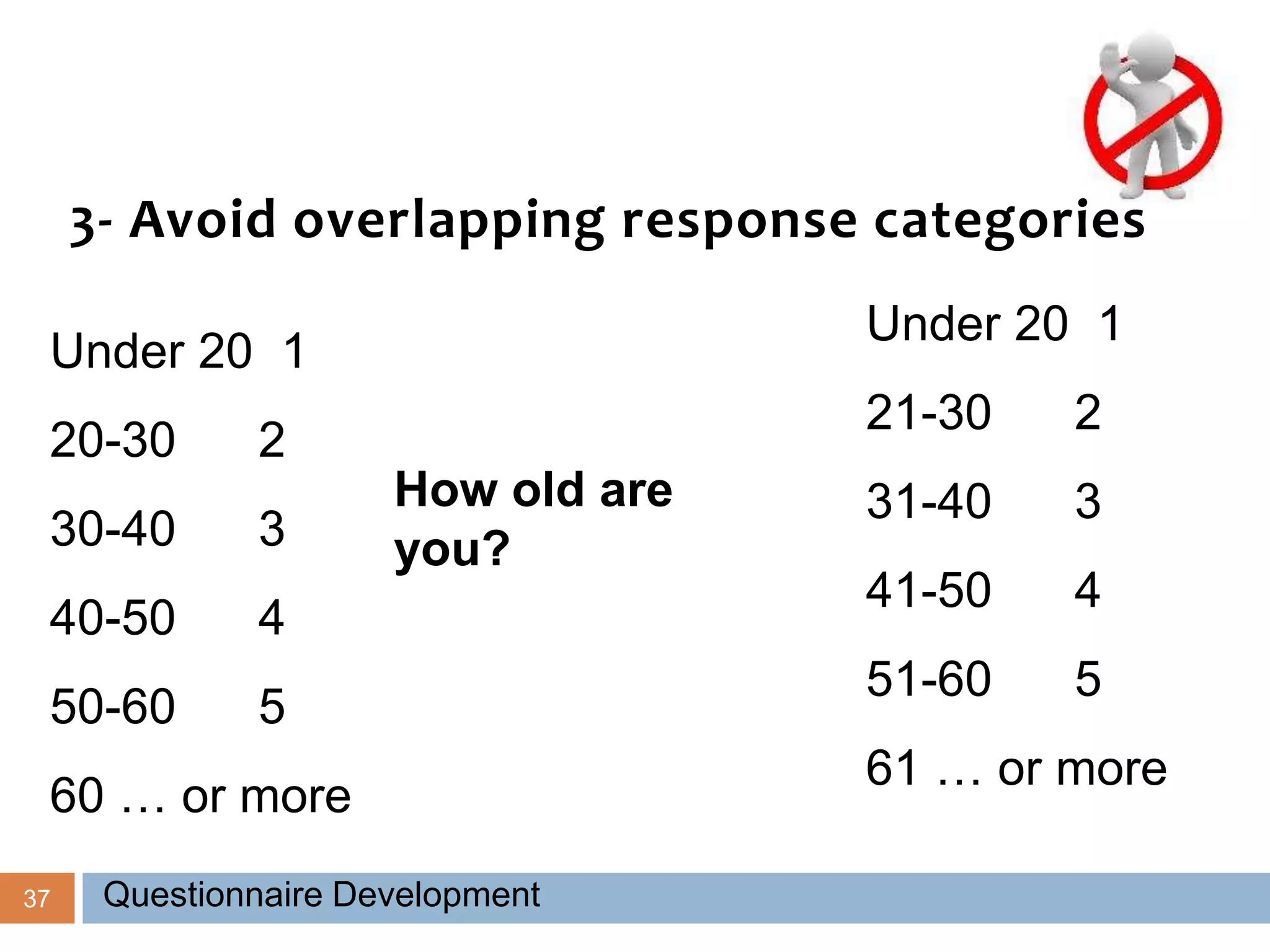
This document discusses the process of developing and validating a questionnaire. It begins by defining what a questionnaire is and noting that developing a good questionnaire takes significant time and effort, often involving multiple drafts. It then covers types of questionnaires, advantages and disadvantages of self-administered versus interviewer-administered questionnaires, and key steps in the development process including formulating objectives, conducting a literature review, designing initial drafts, and pre-testing drafts. The document provides guidance on question wording and types, testing questionnaires, and ensuring reliability and validity. It concludes by discussing important elements of covering letters.