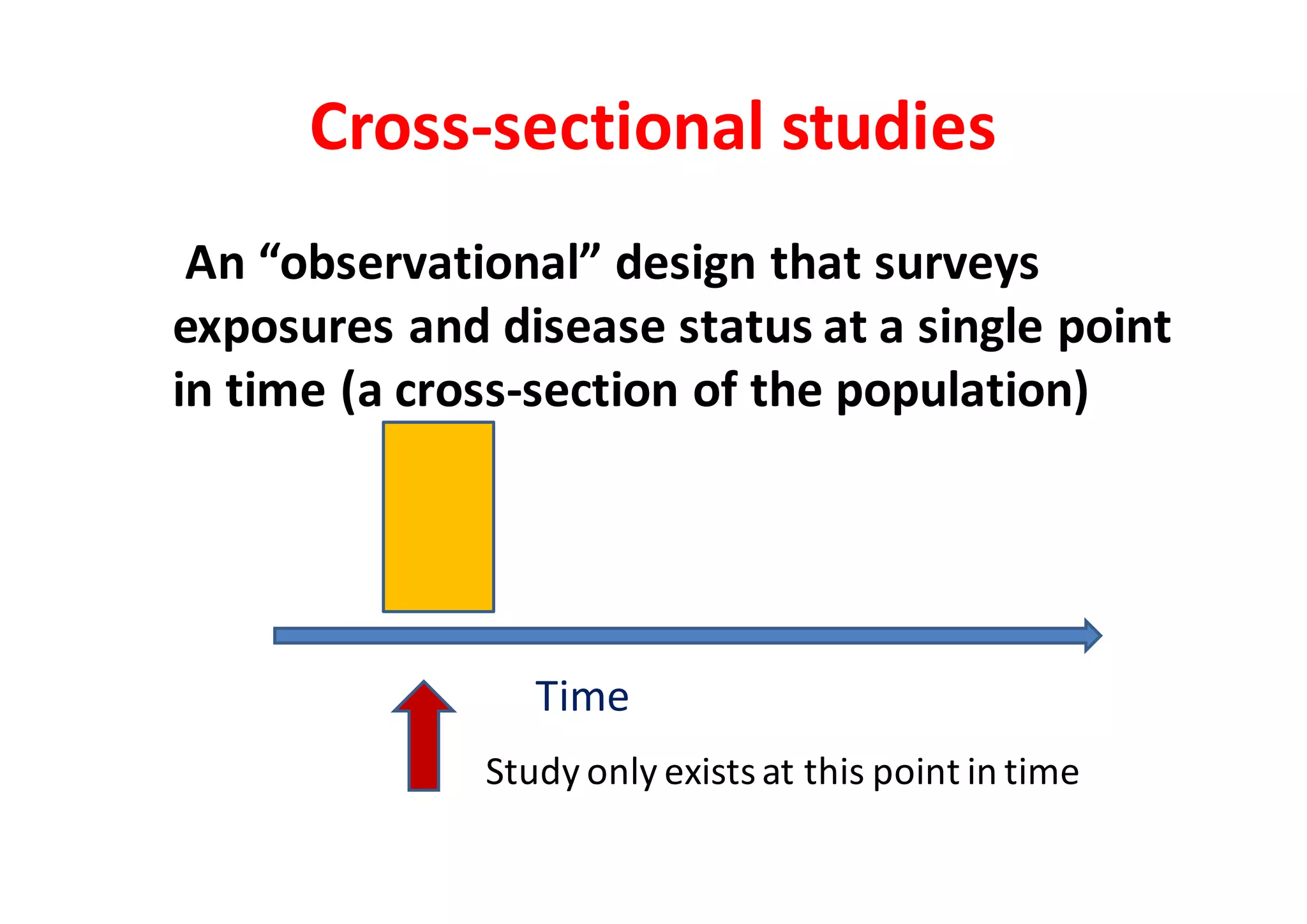
This document describes different types of epidemiological study designs, including observational studies like cross-sectional, case-control, cohort, and experimental studies like randomized controlled trials. It provides details on descriptive versus analytical epidemiology and cross-sectional studies specifically. Cross-sectional studies measure prevalence at a single point in time by surveying exposures and disease status simultaneously in a population cross-section. They are useful for assessing disease burden, comparing prevalence between populations, and examining trends over time.