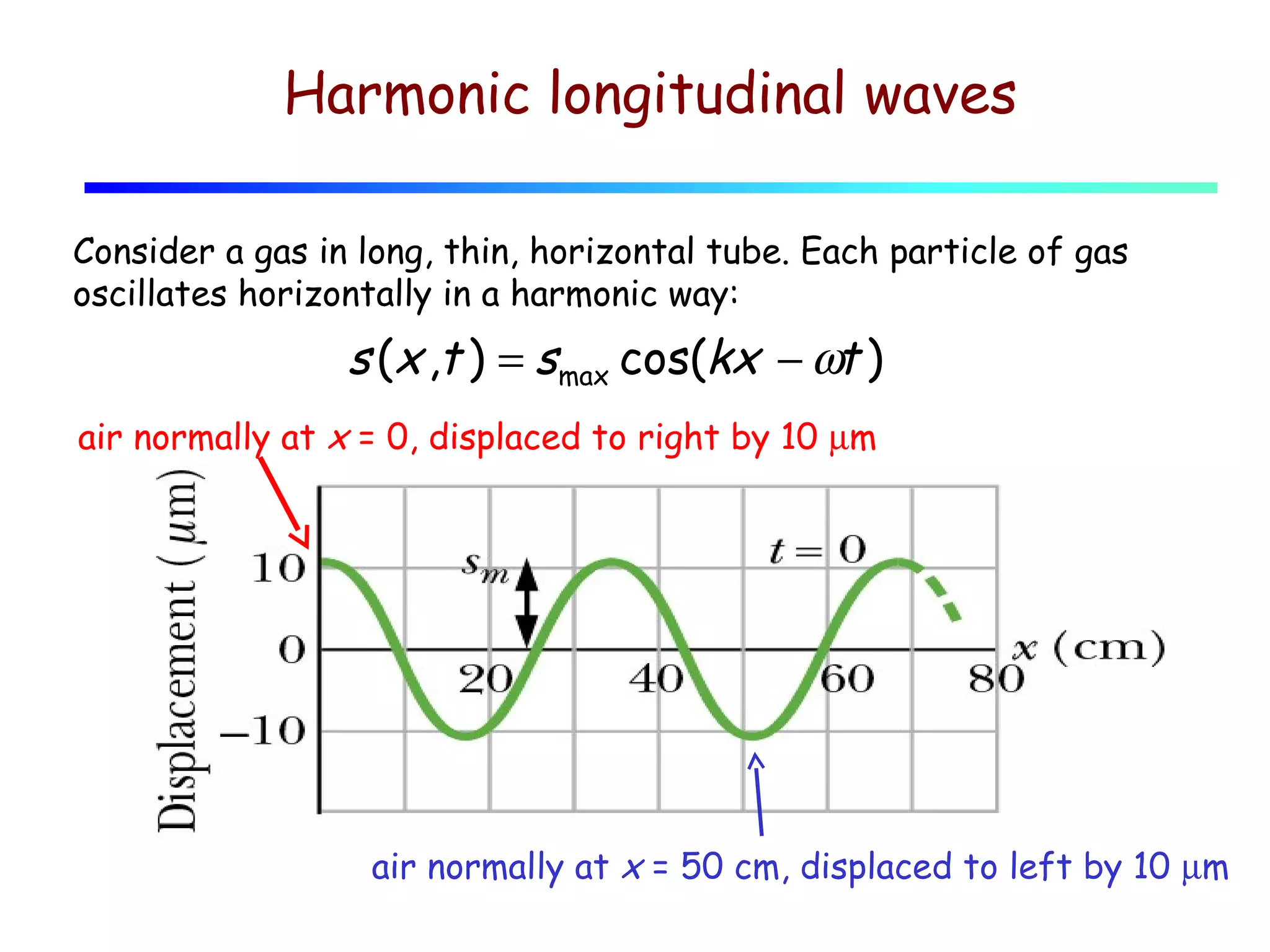
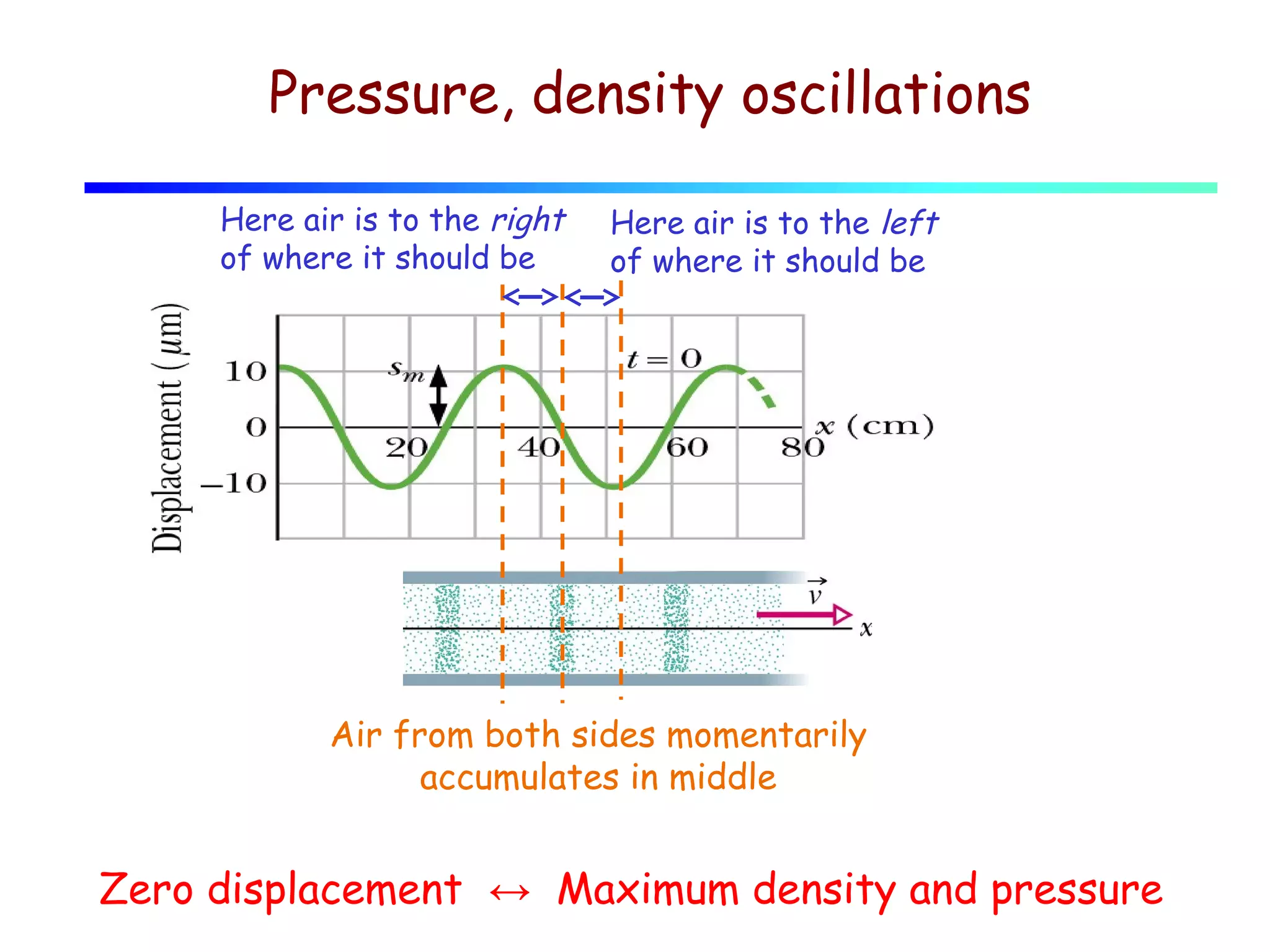
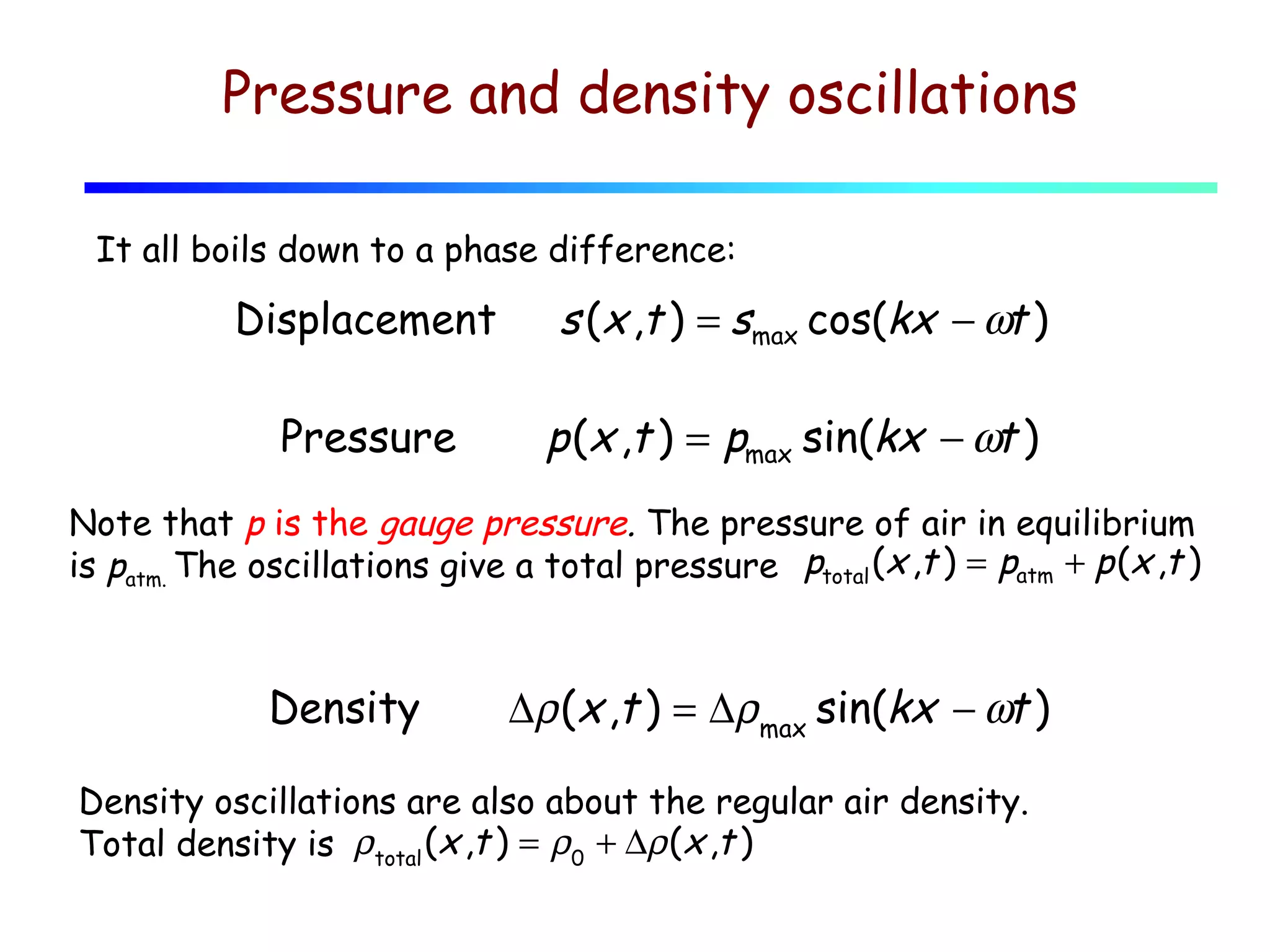
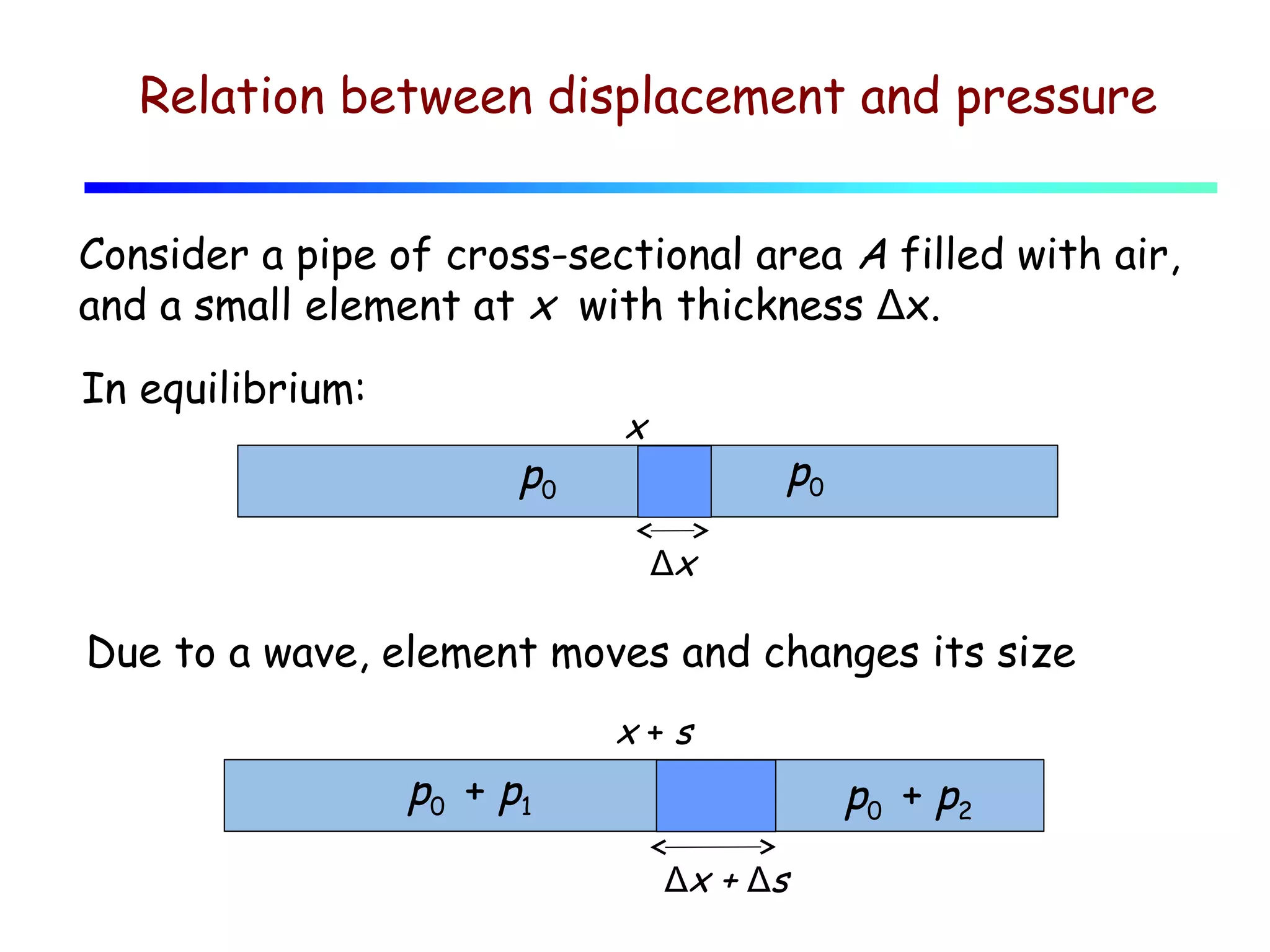
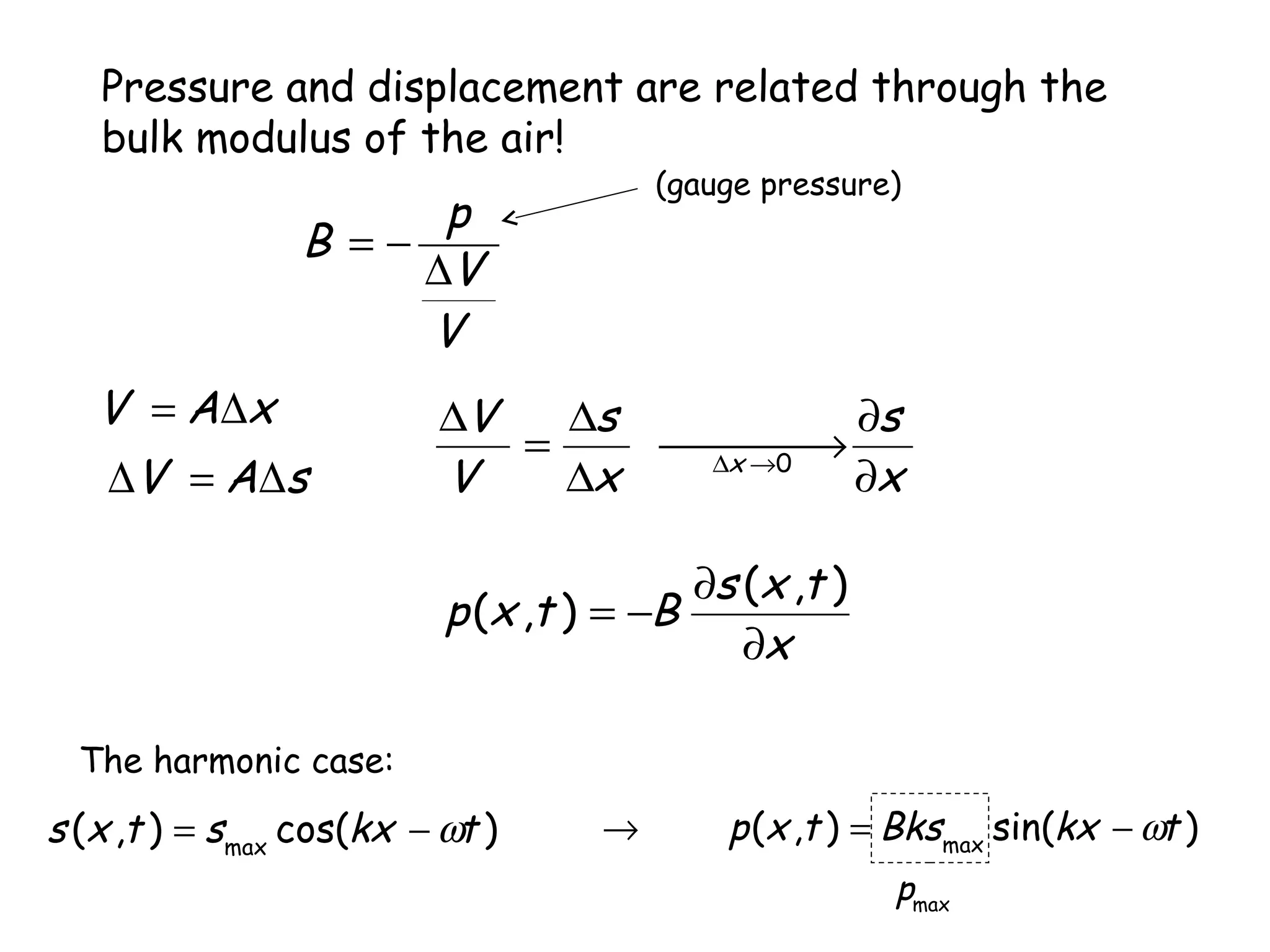
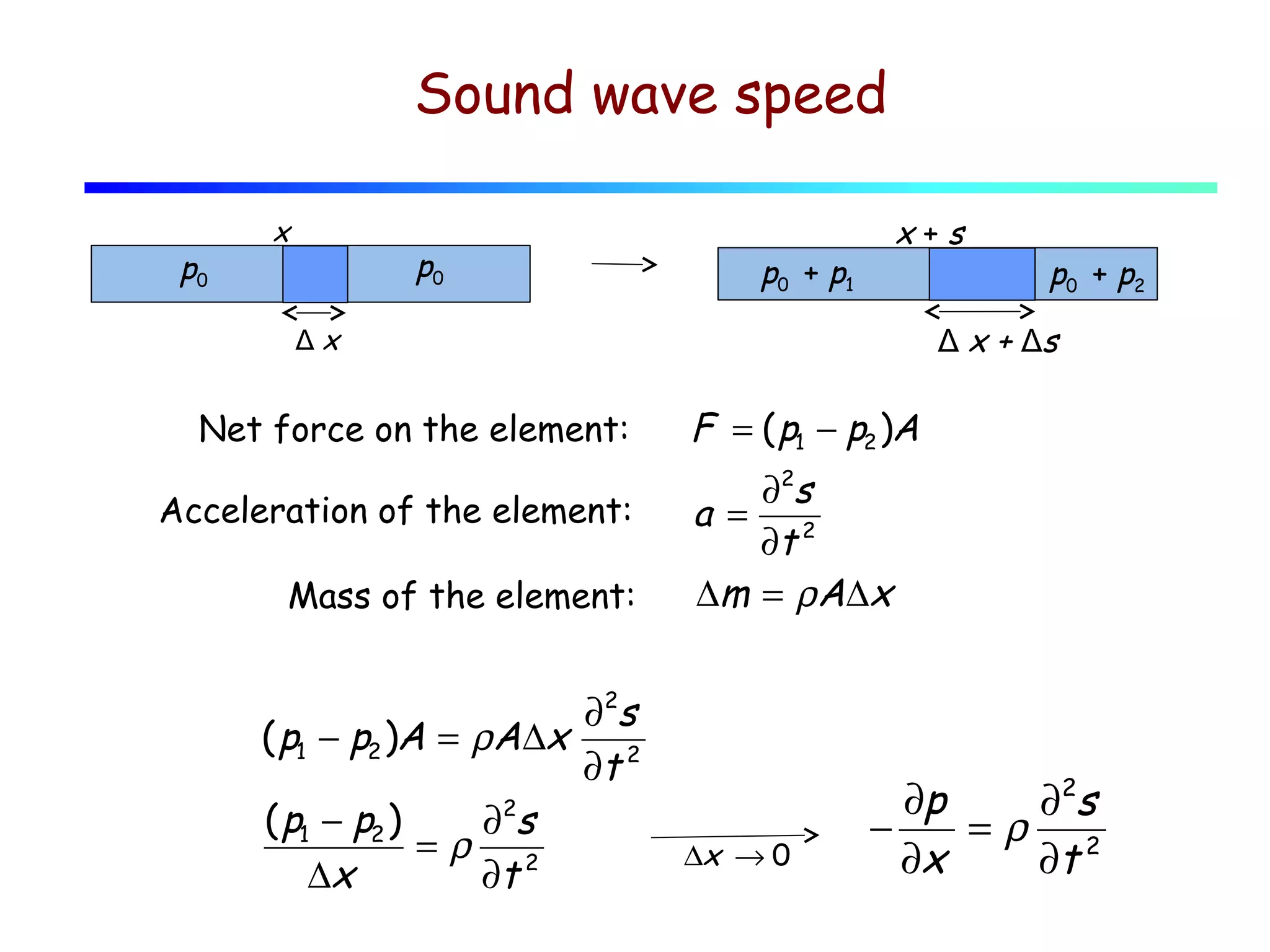
1) Sound waves propagate as periodic longitudinal oscillations of particles in a medium, causing oscillations in pressure and density around the equilibrium values.
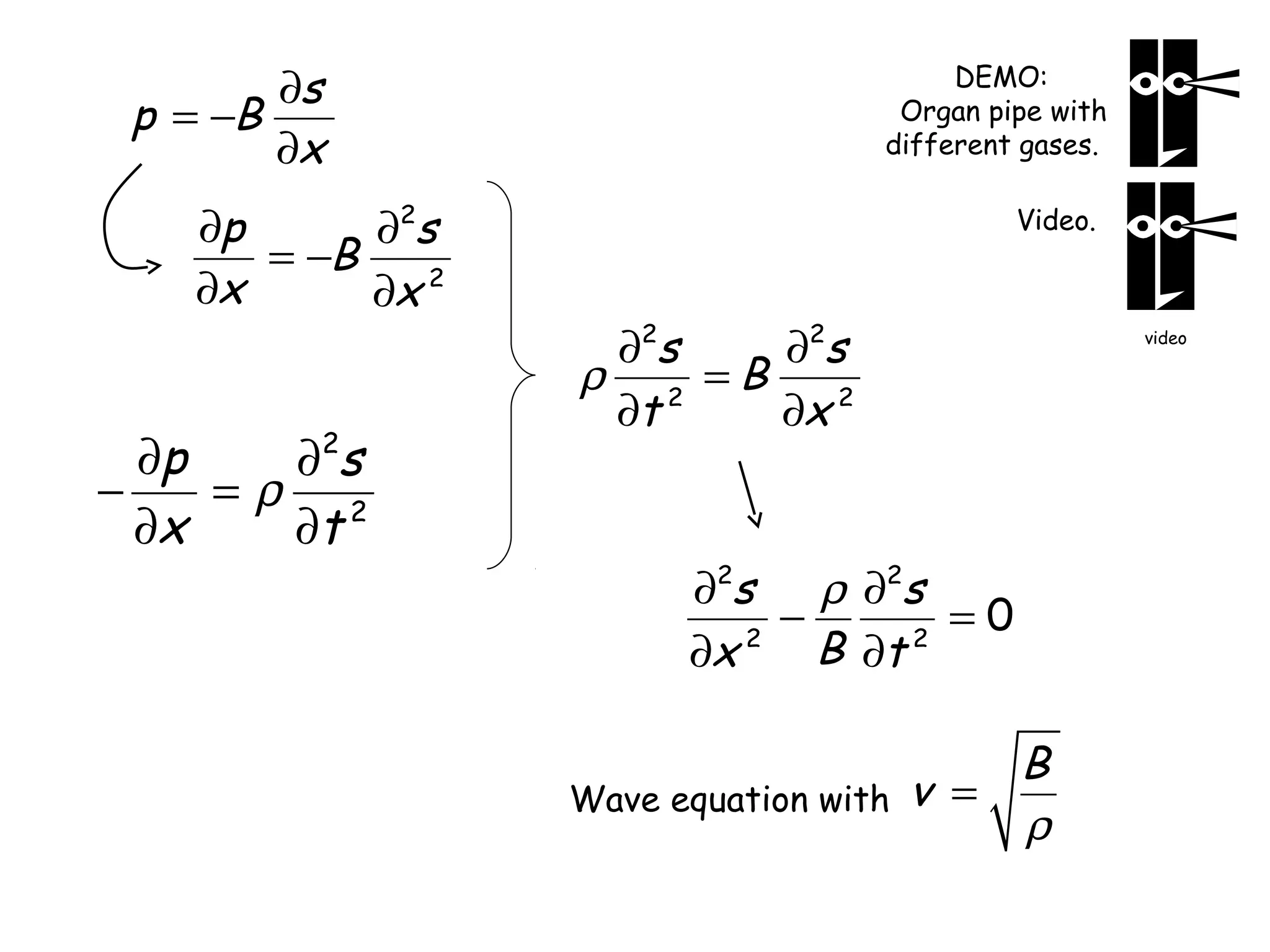
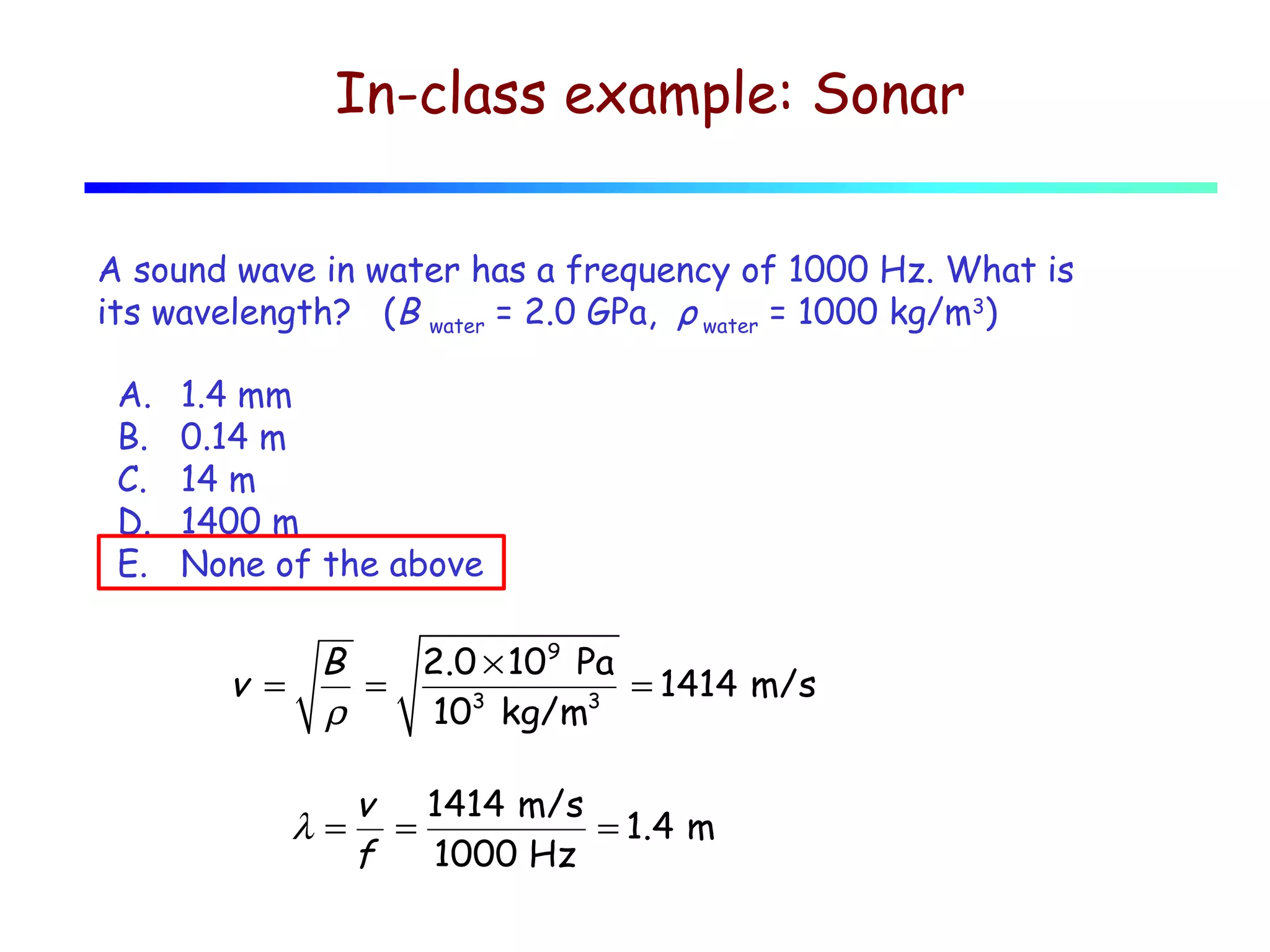
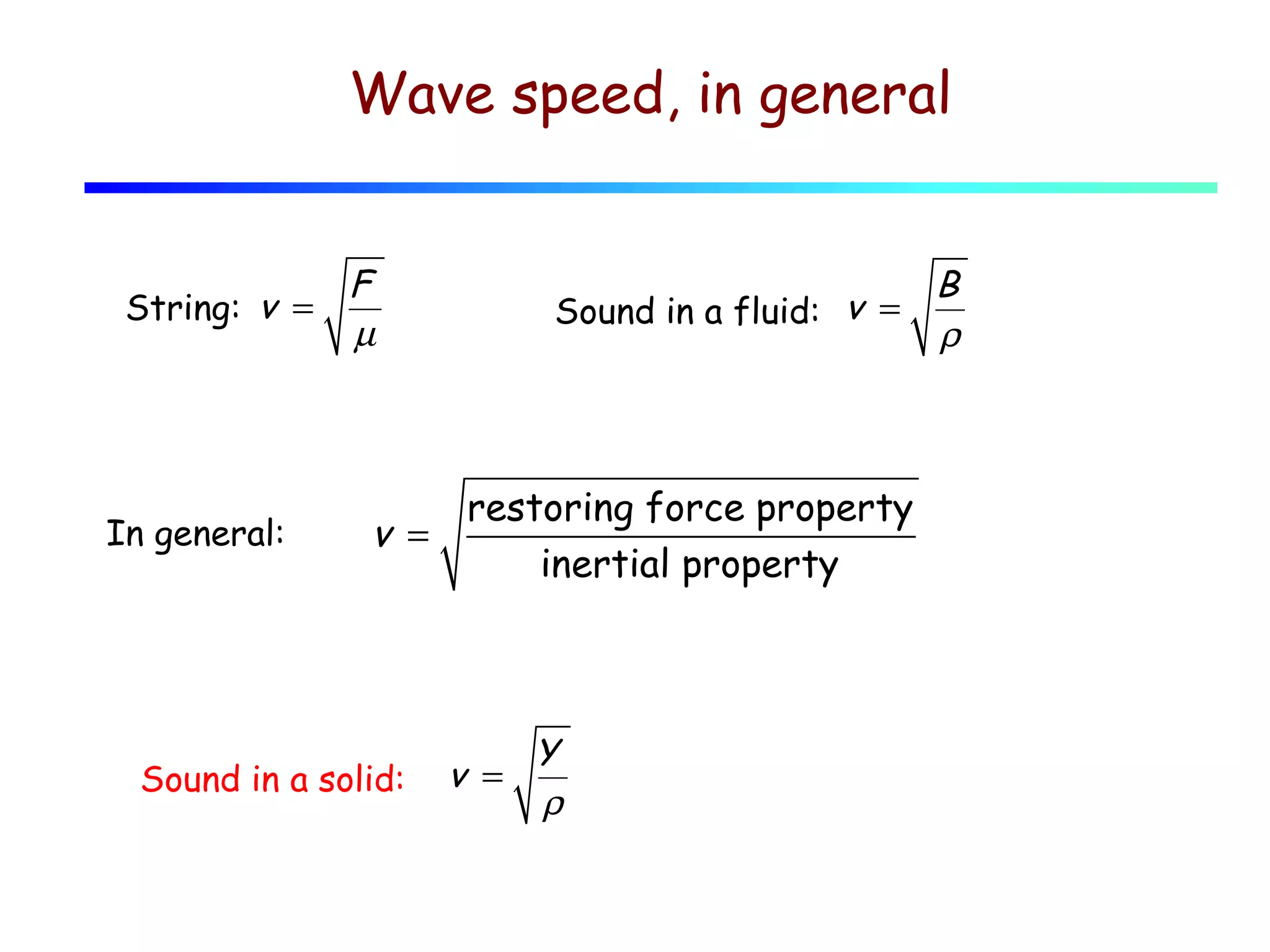
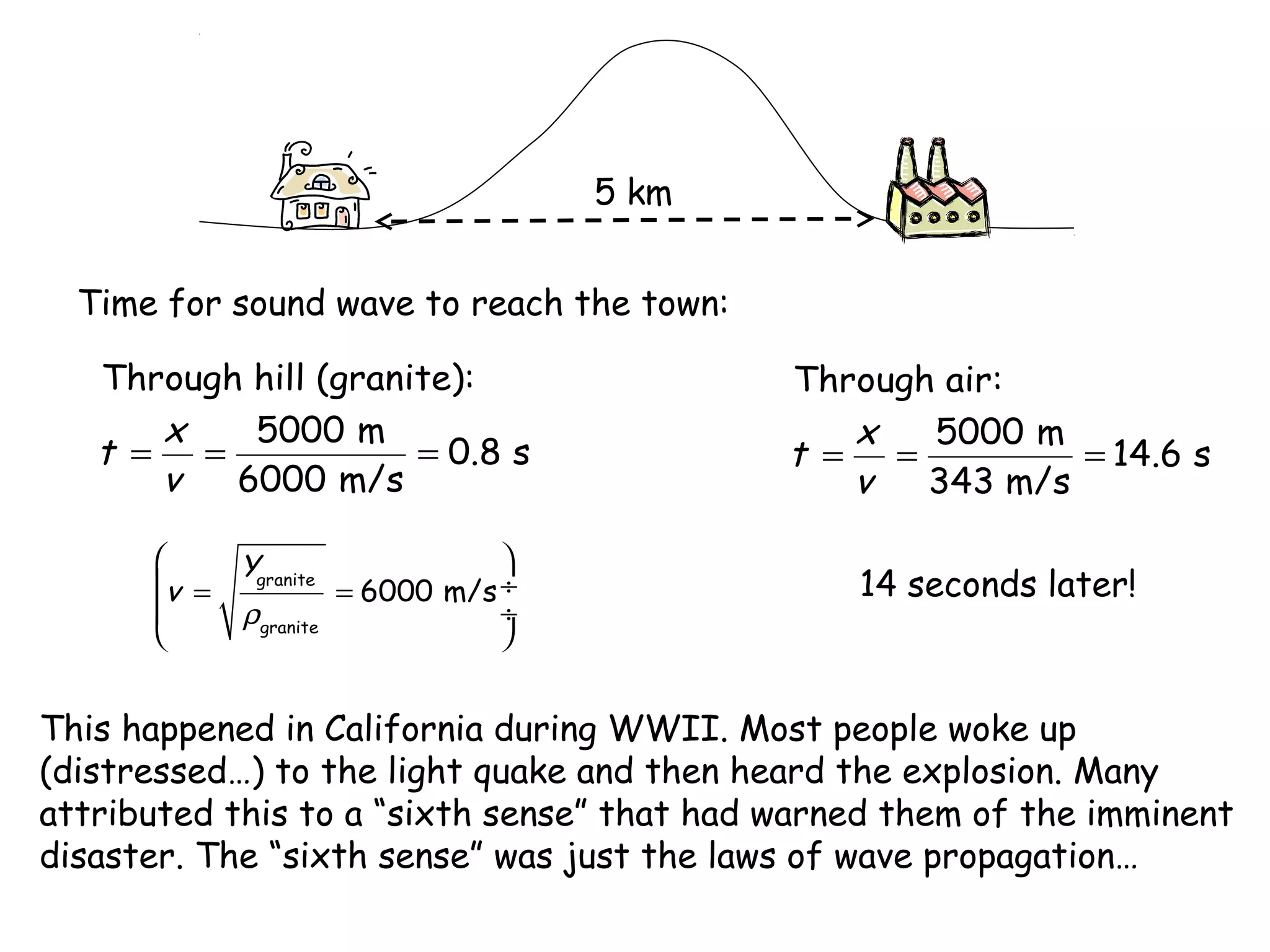
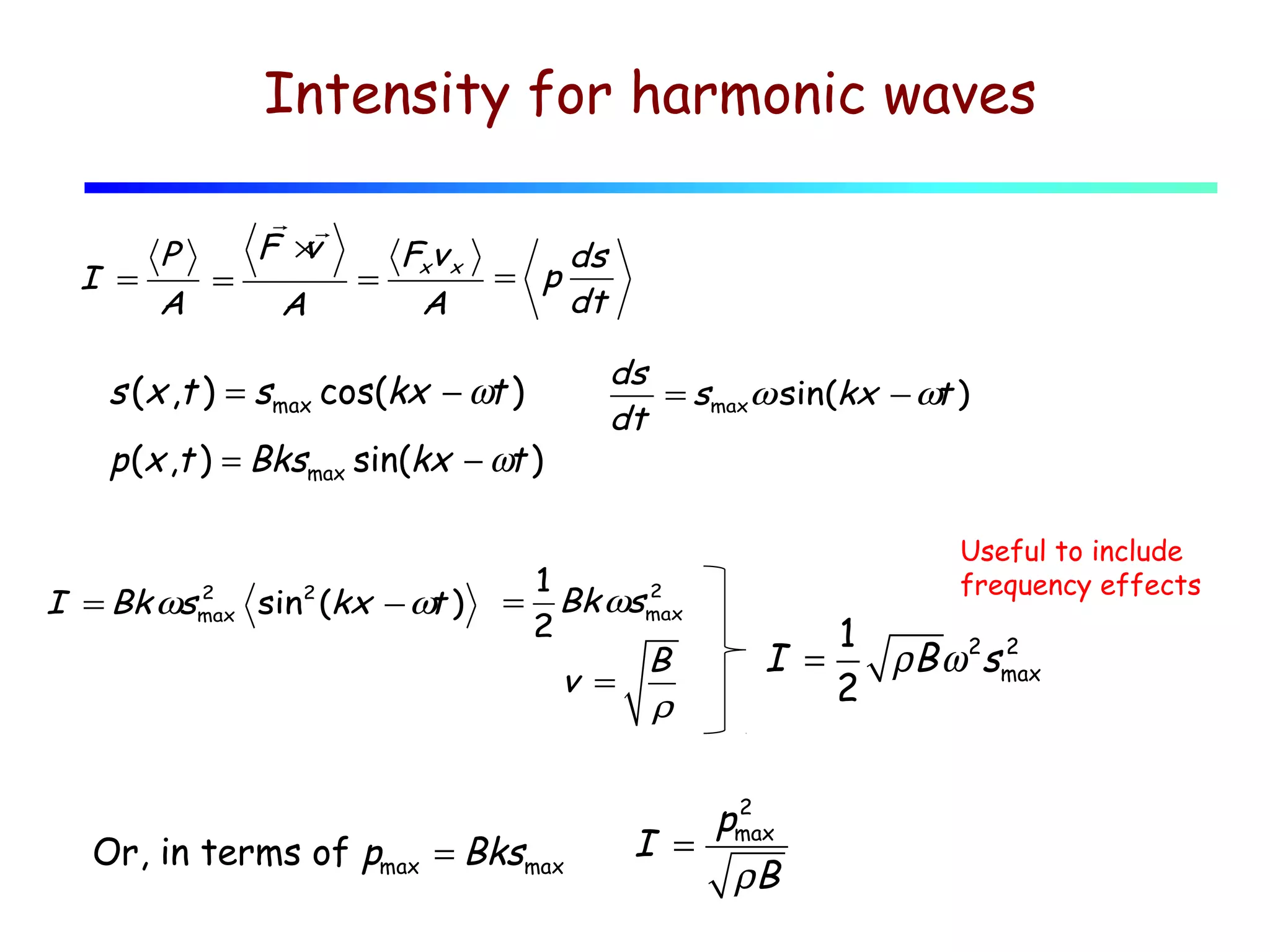
2) The speed of sound in a medium depends on its bulk modulus and density, following the equation v = √(B/ρ).
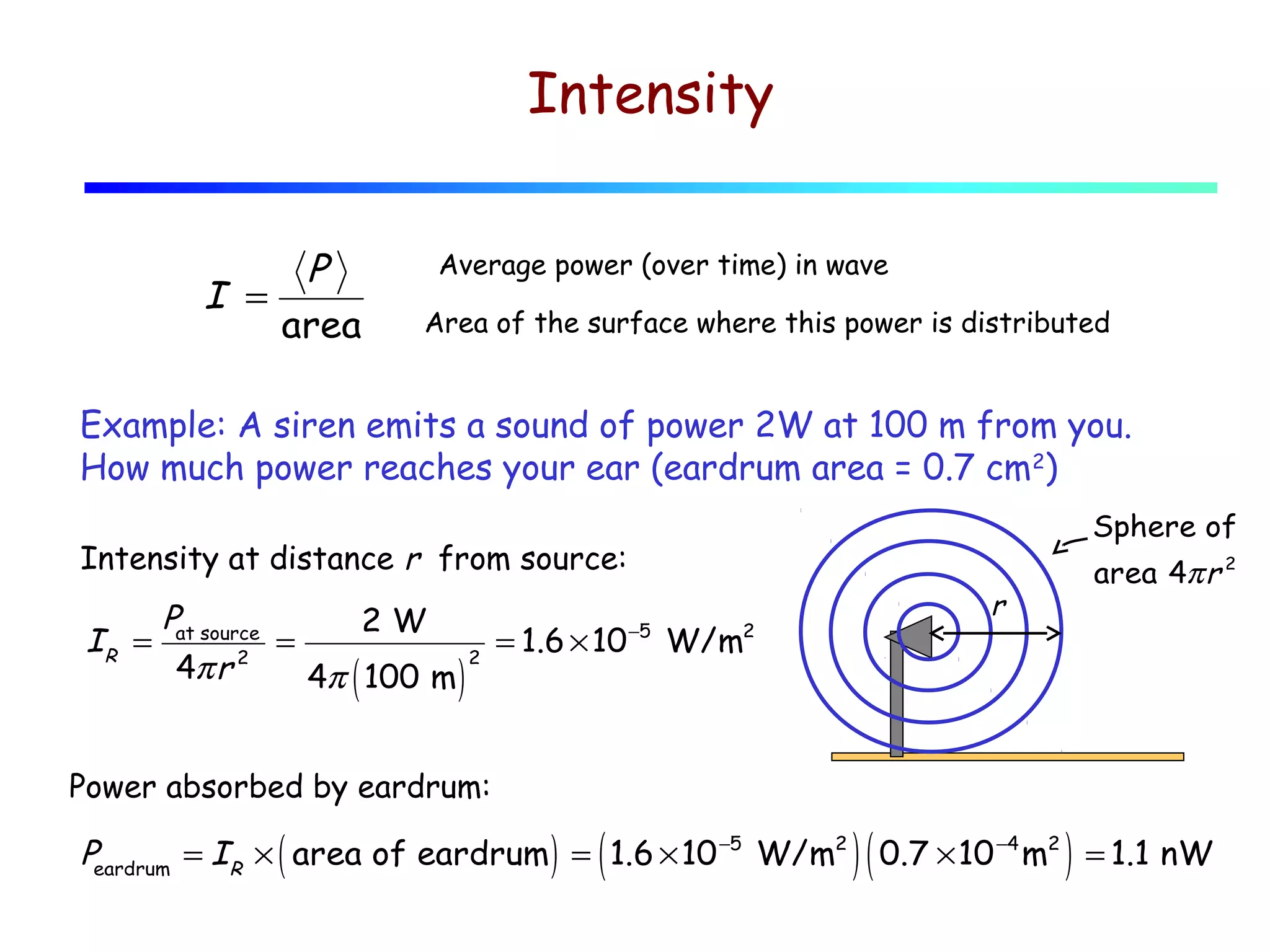
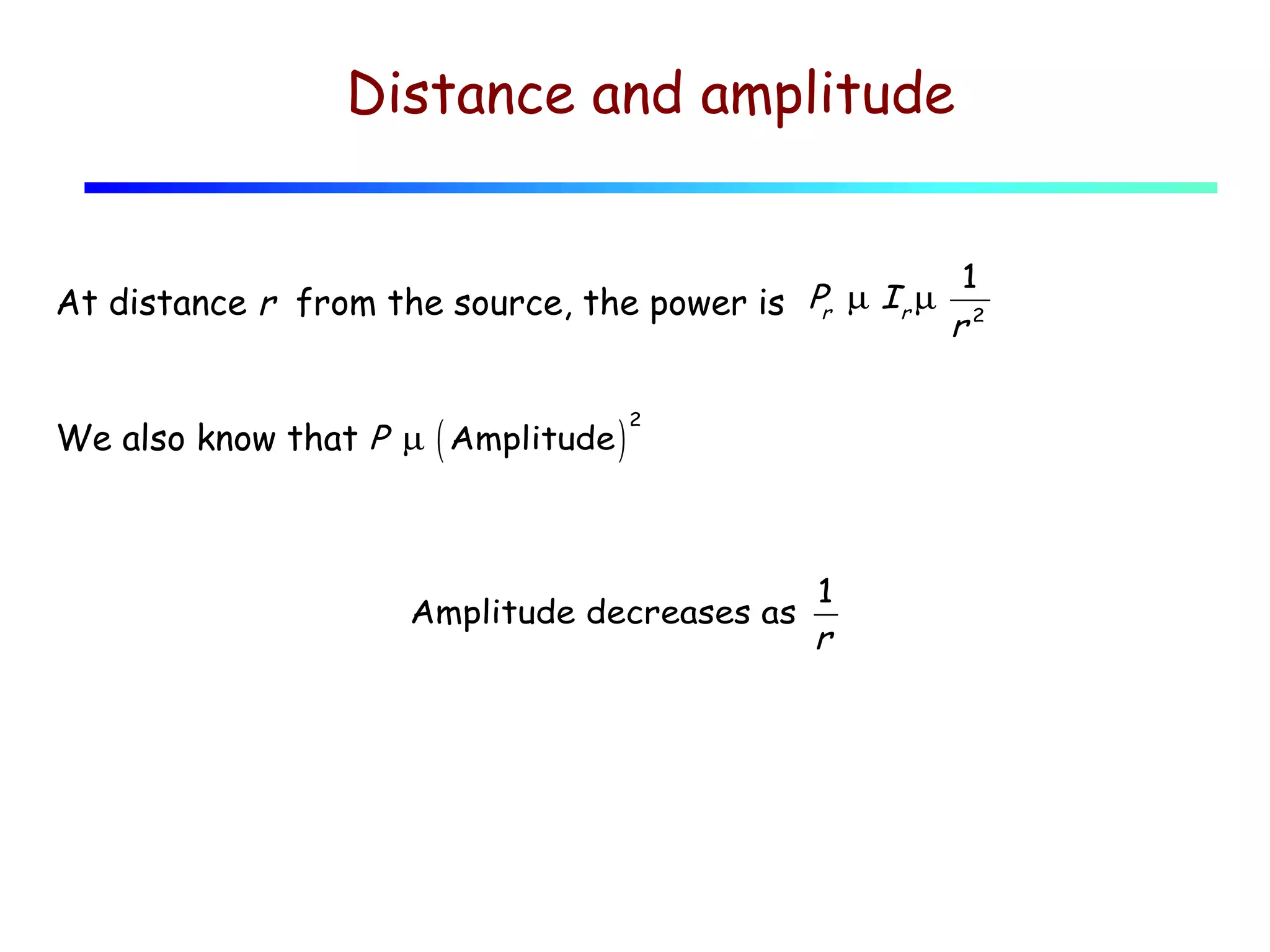
3) Sound intensity decreases with the square of the distance from the source, following the inverse square law. It can be calculated from the sound pressure or particle displacement using equations provided.