Embed presentation
Download to read offline

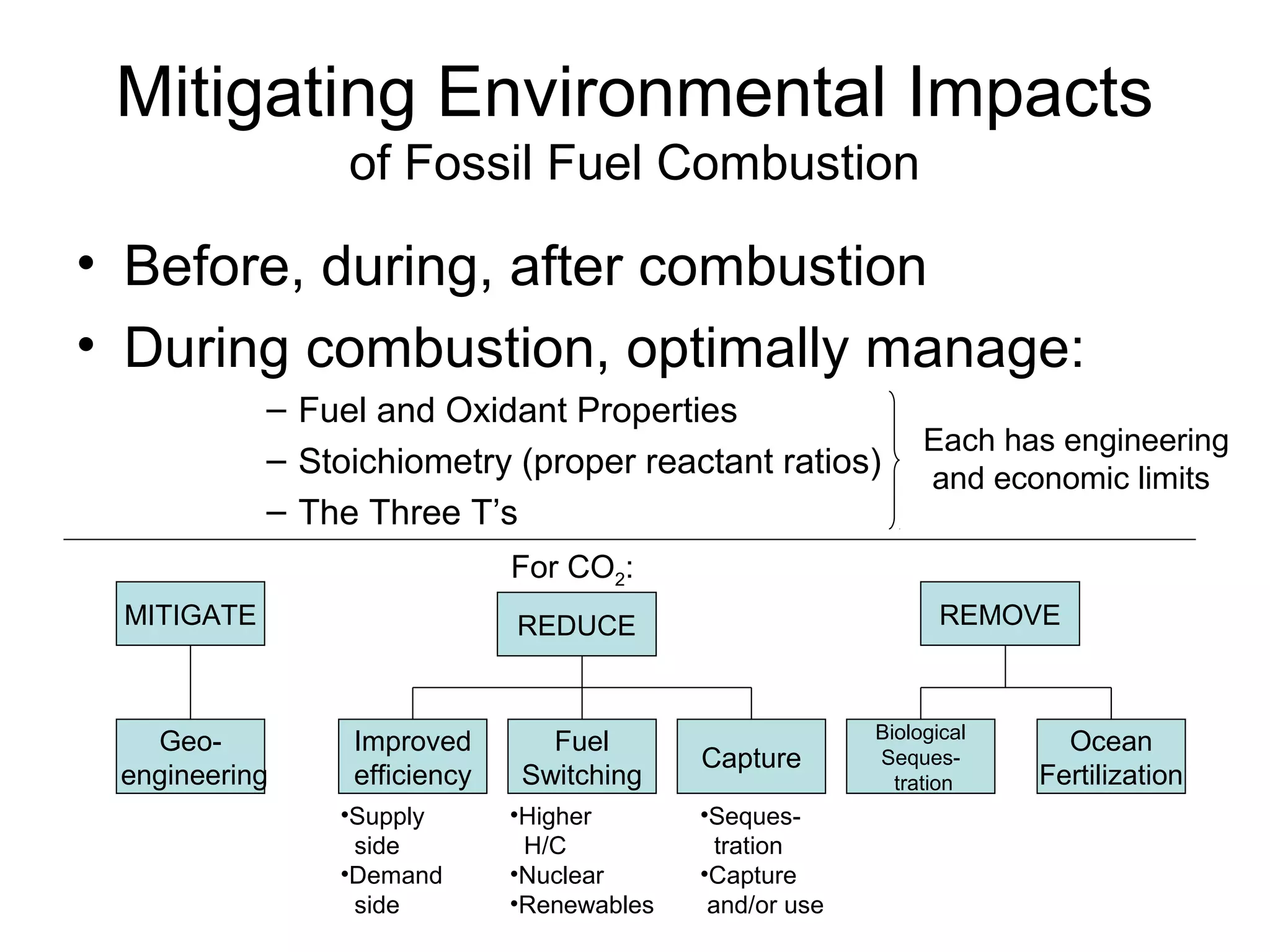






This document discusses mitigating environmental impacts and economic solutions to emissions from fossil fuel combustion. It describes strategies for reducing, improving efficiency, fuel switching, and capturing carbon dioxide emissions. It also compares carbon taxes and cap-and-trade programs, noting that cap-and-trade has precedent from the successful SO2 program that is projected to provide $100 billion in health benefits at a cost of $3 billion. Geoengineering approaches to altering the earth's reflectivity and emissivity are also briefly mentioned.






