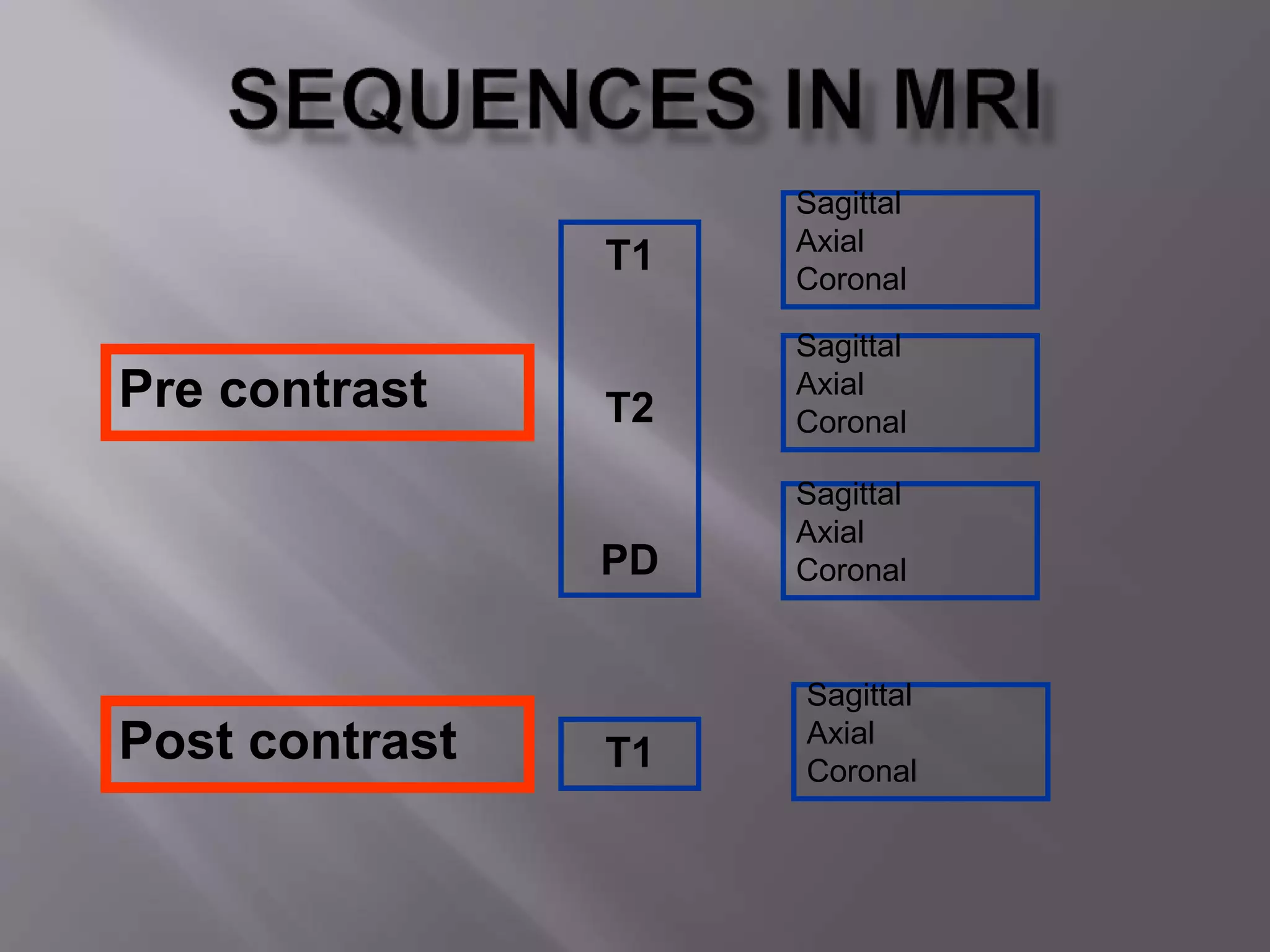
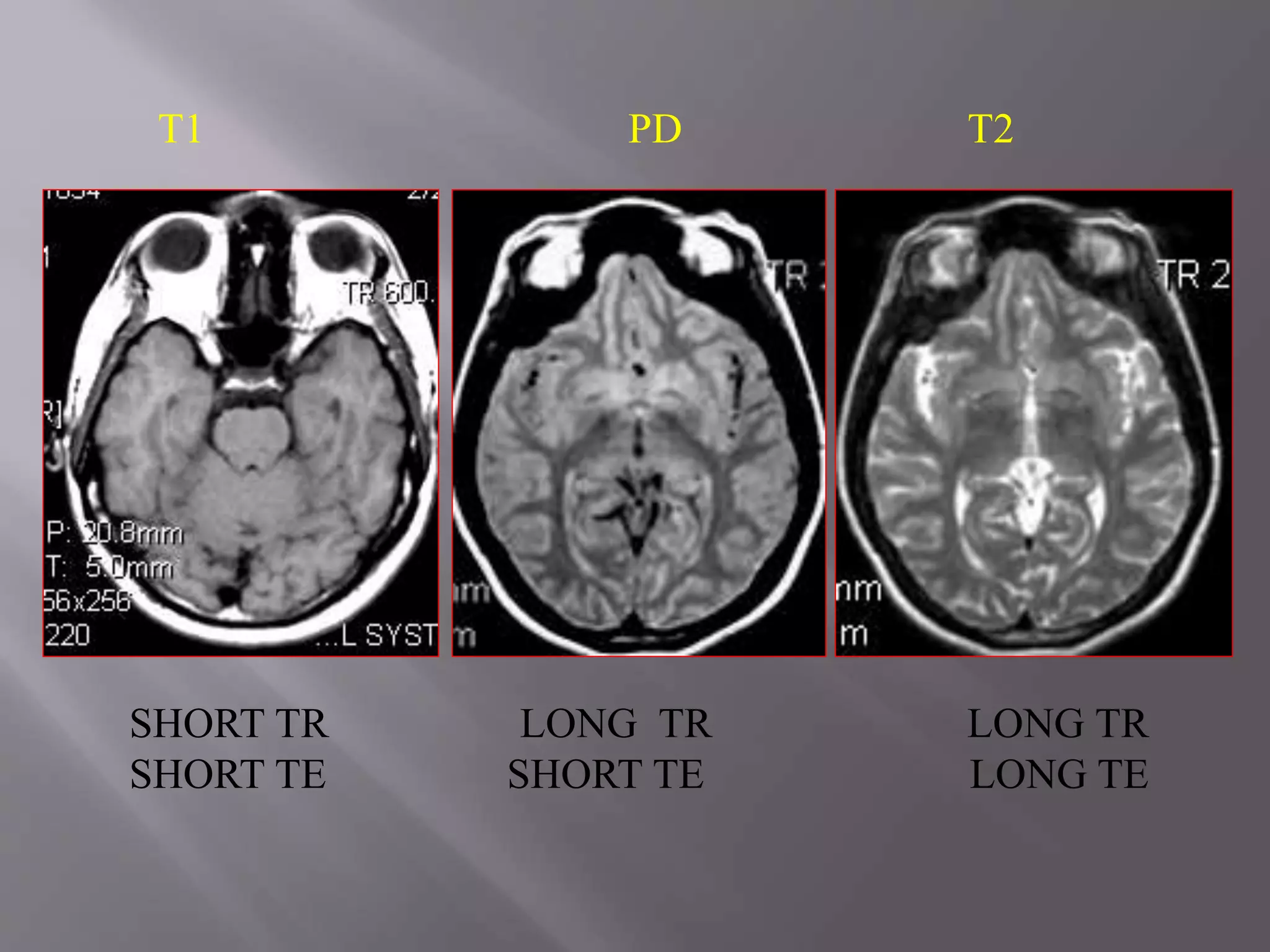
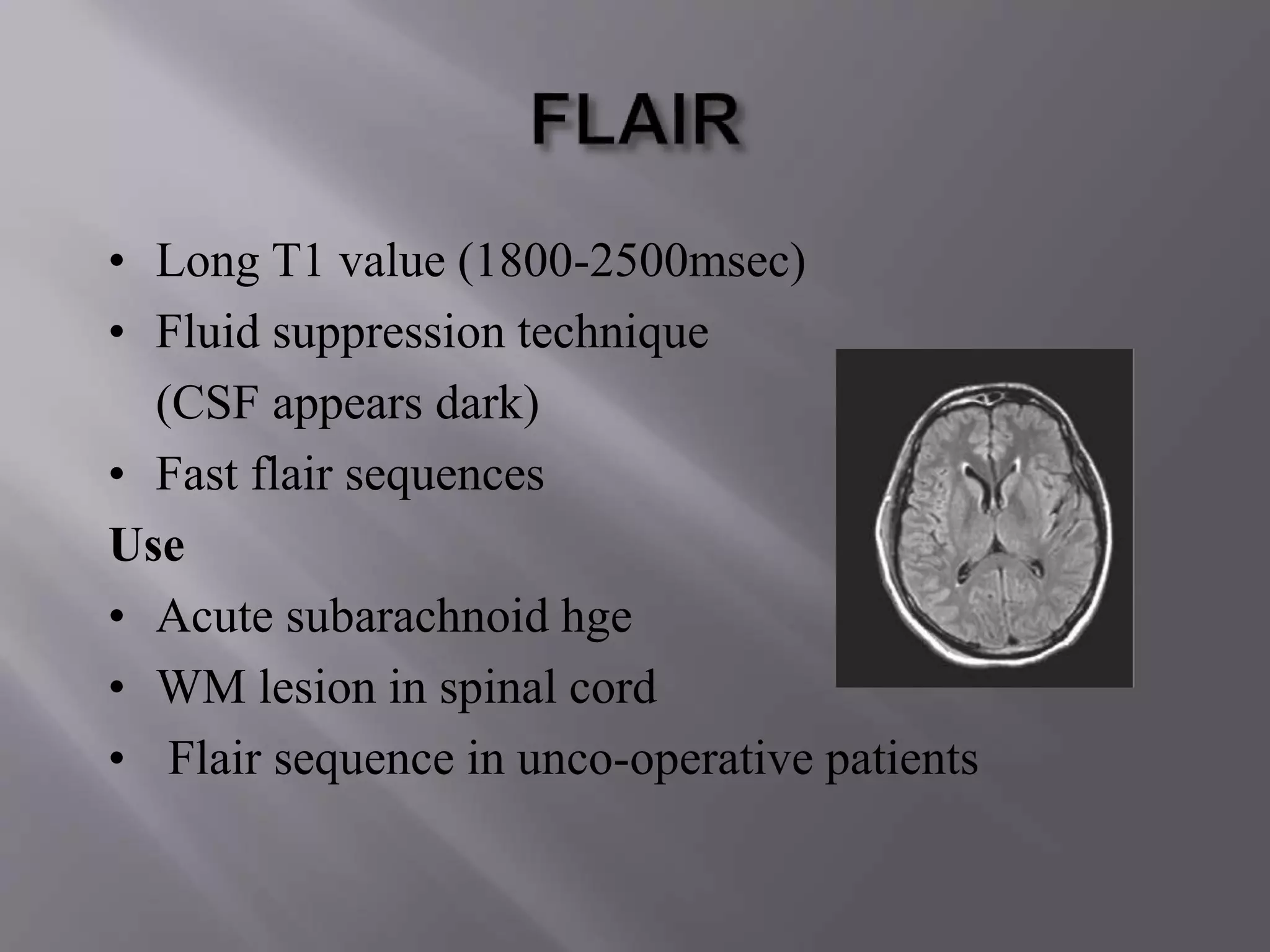
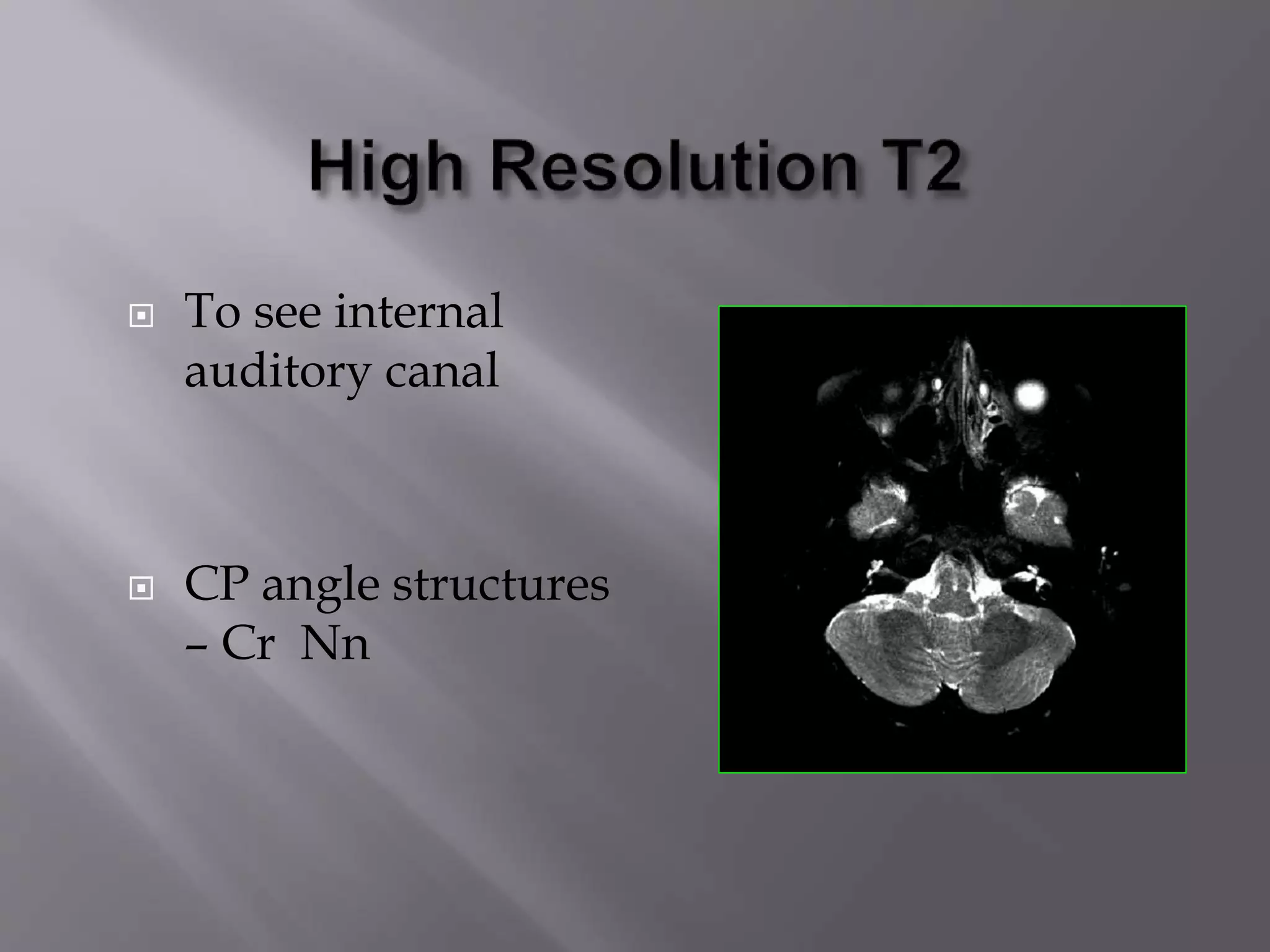
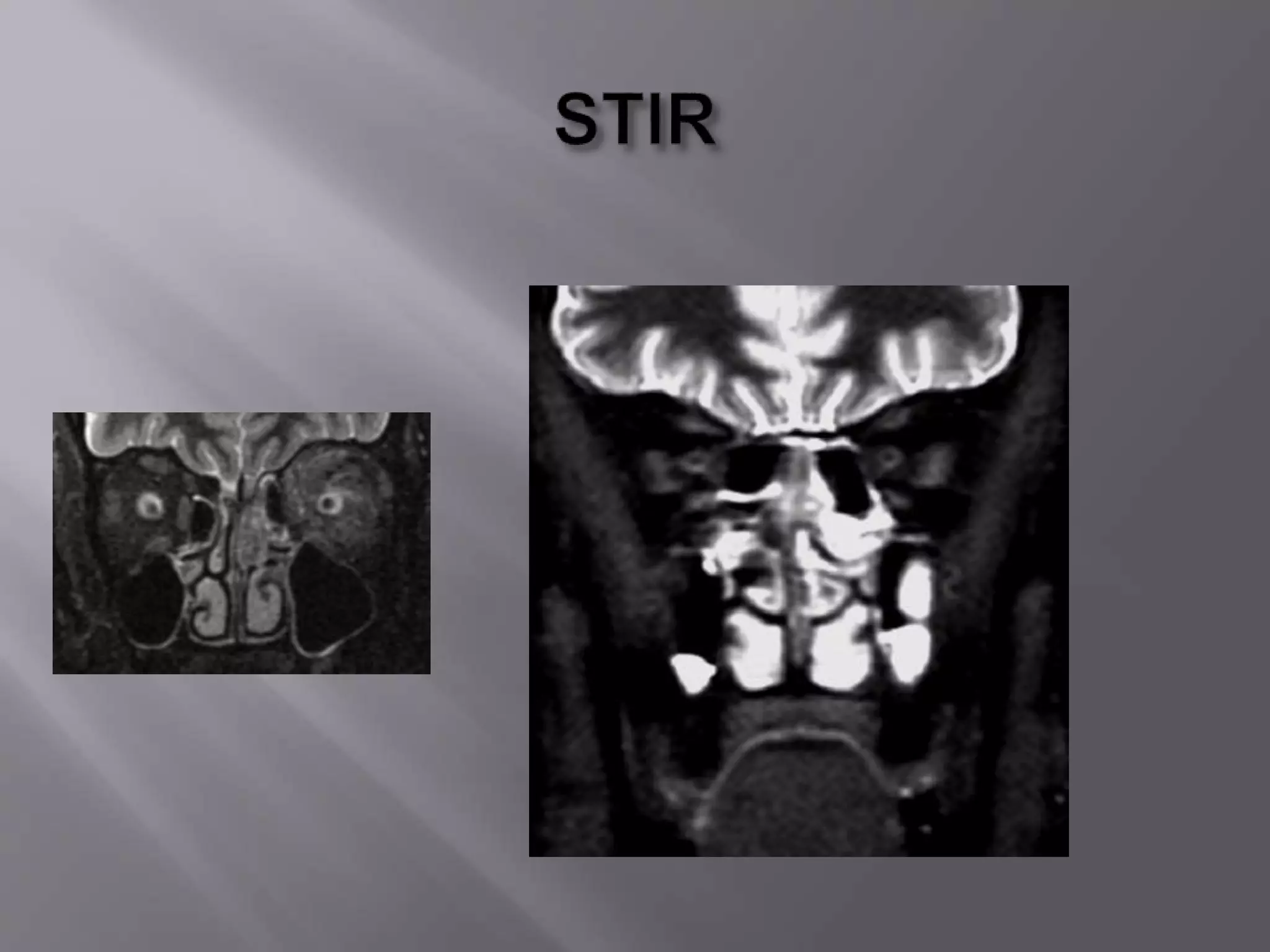
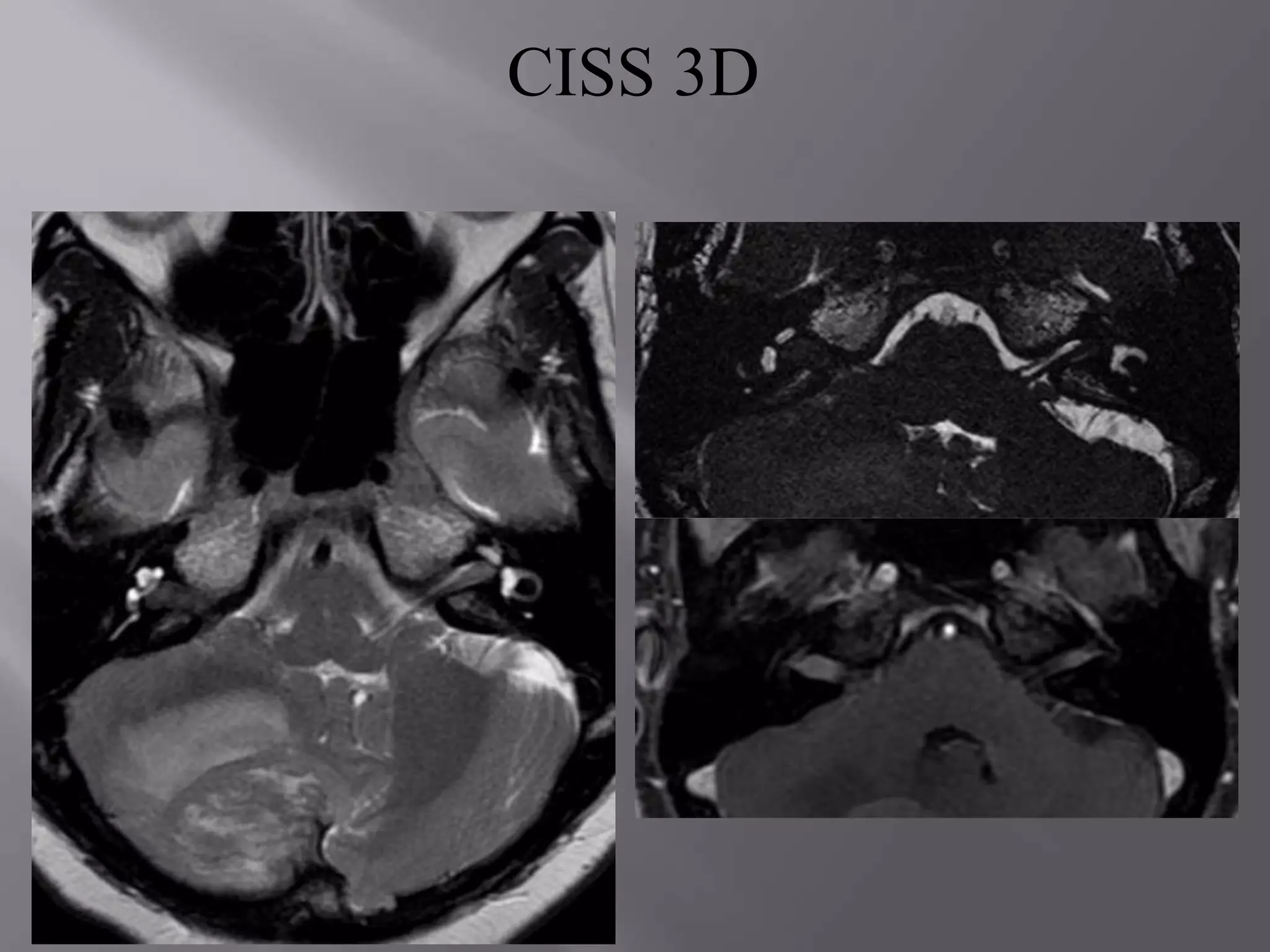
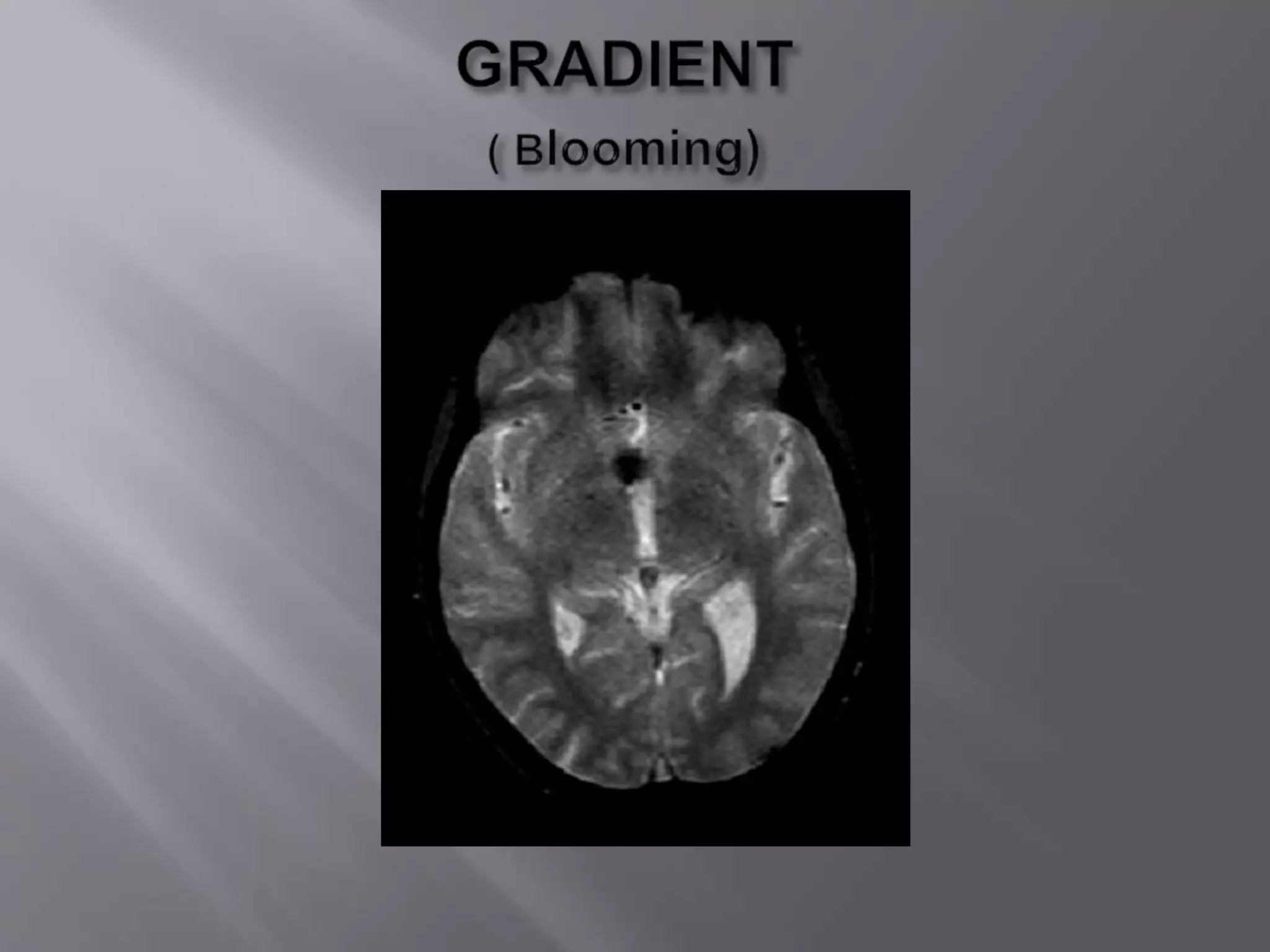
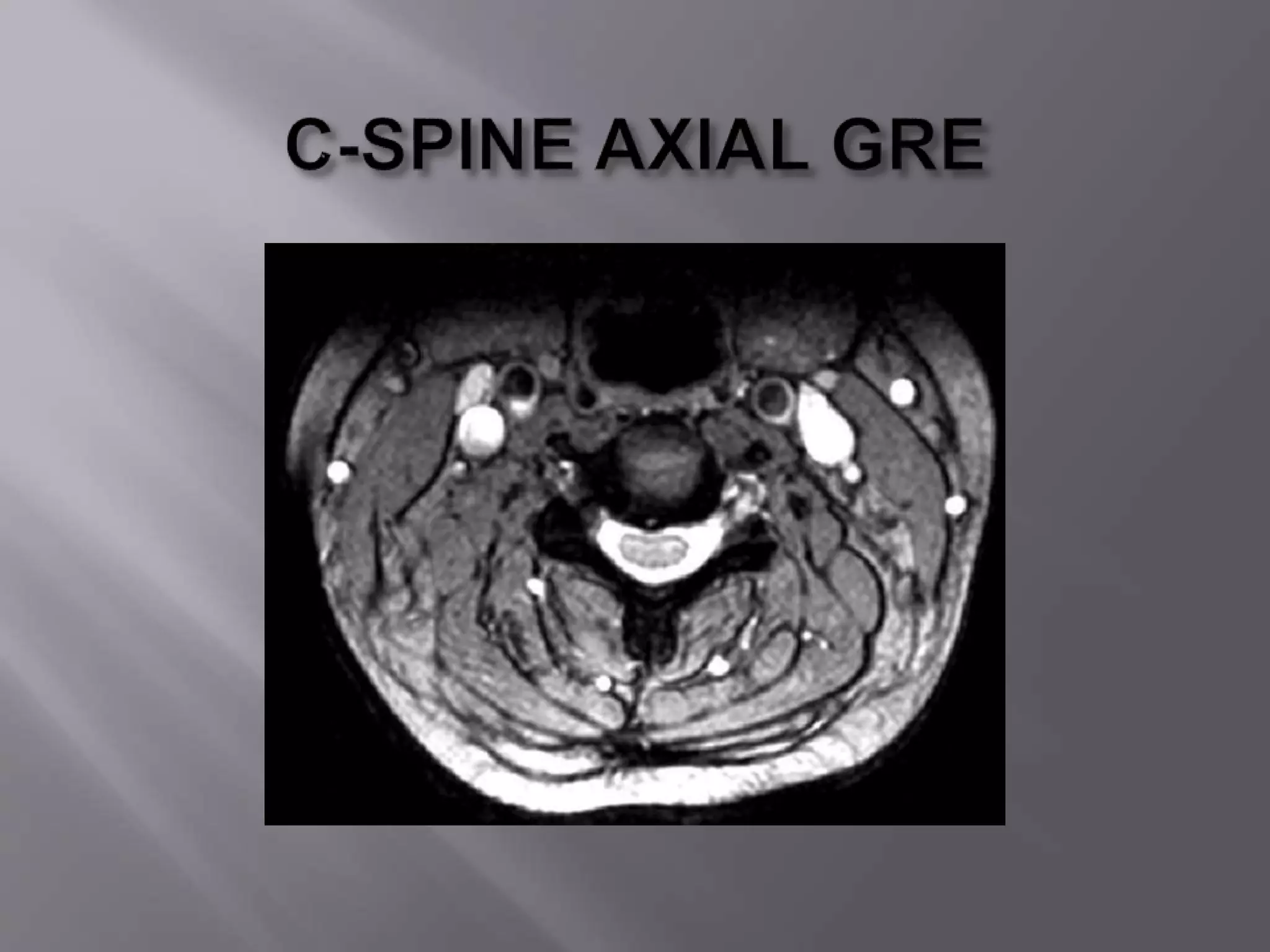
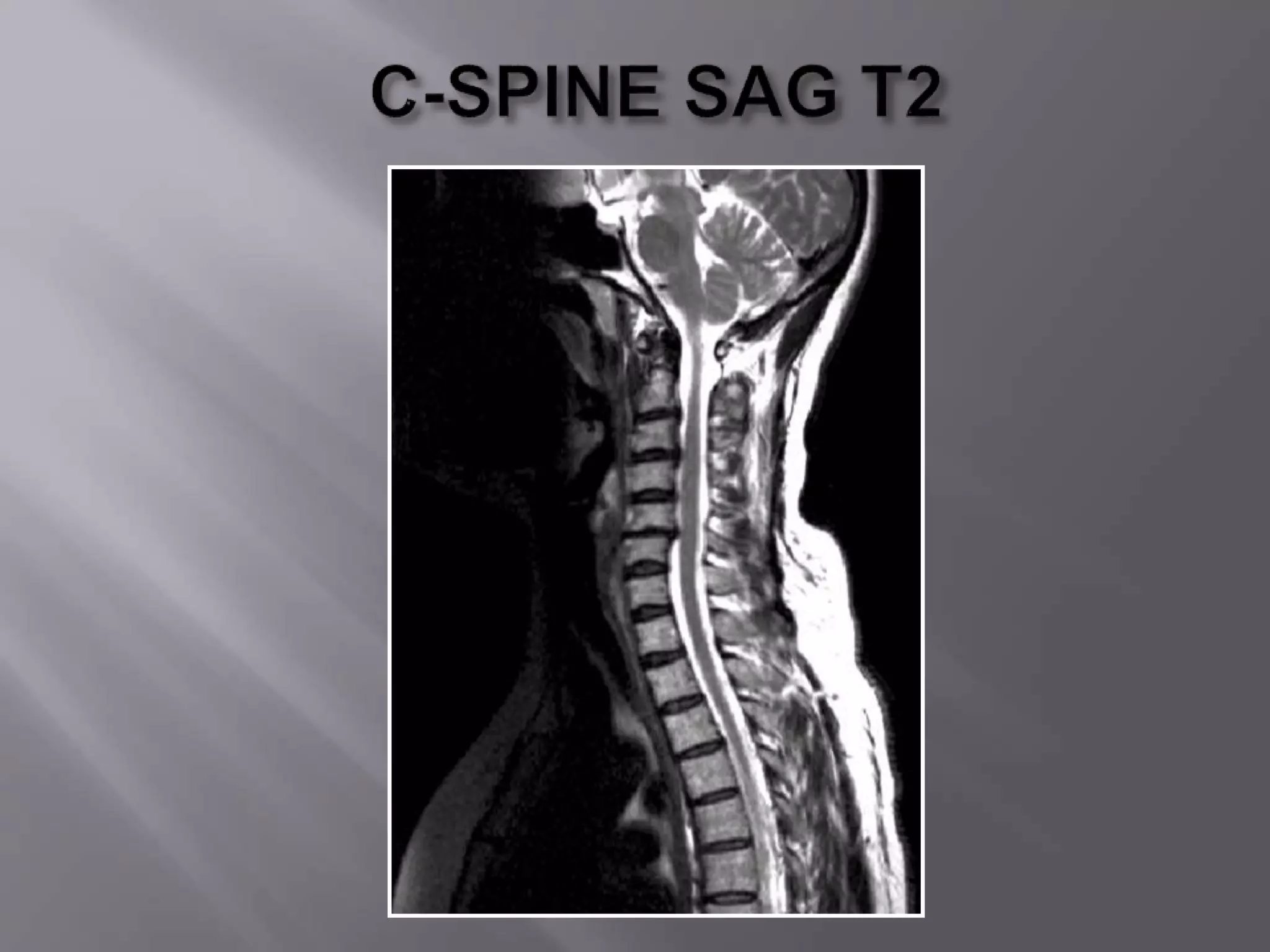
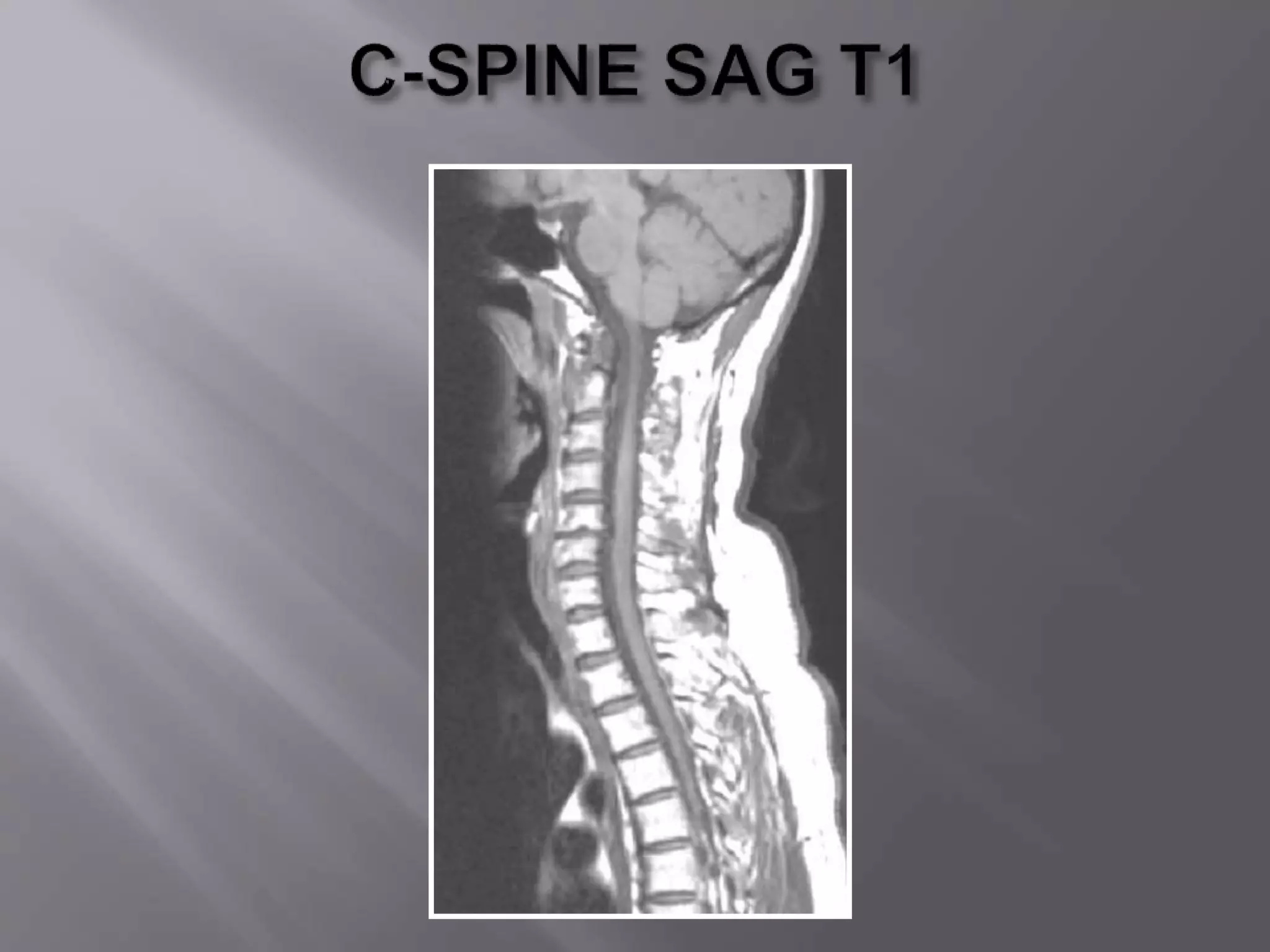
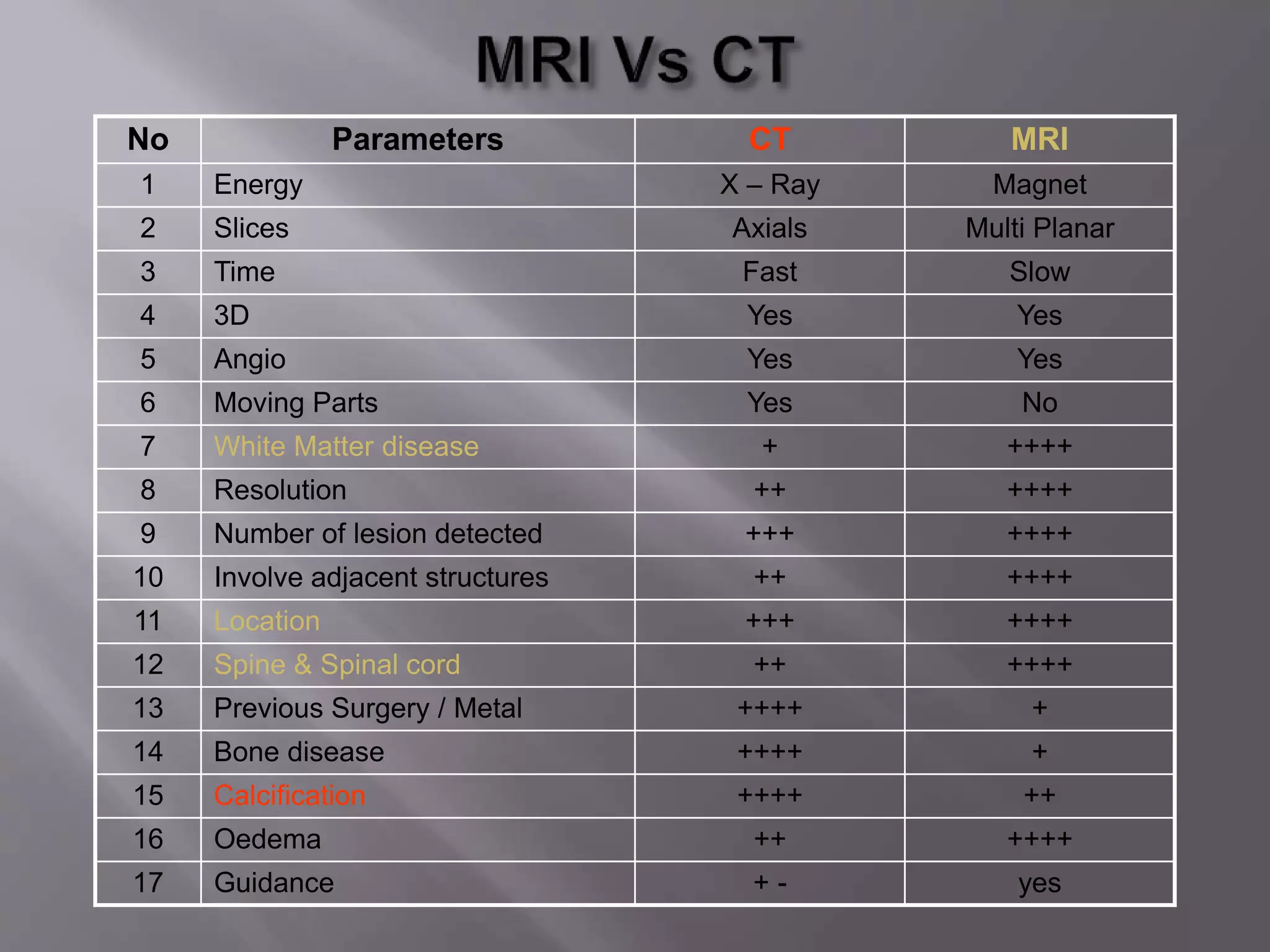
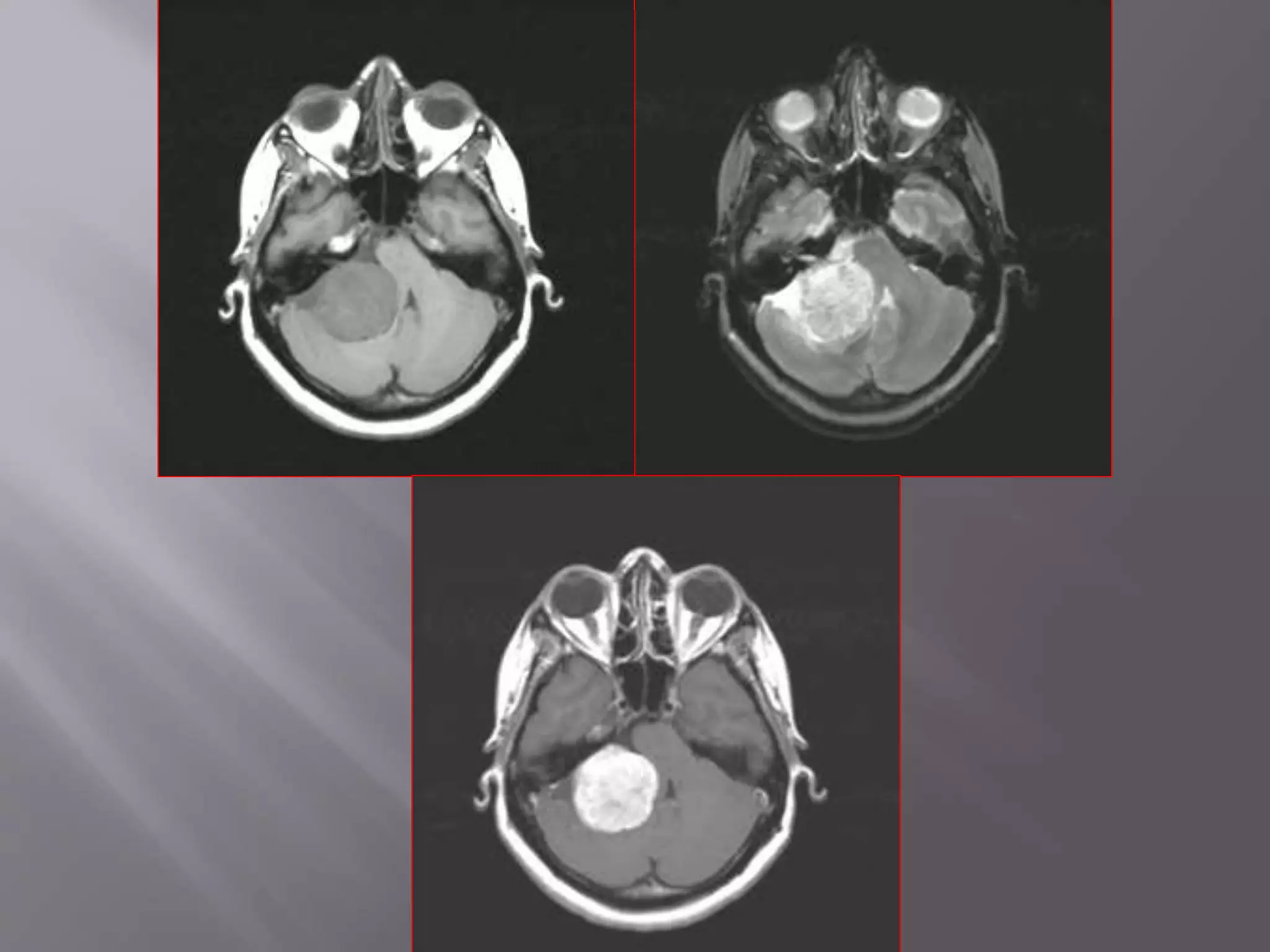
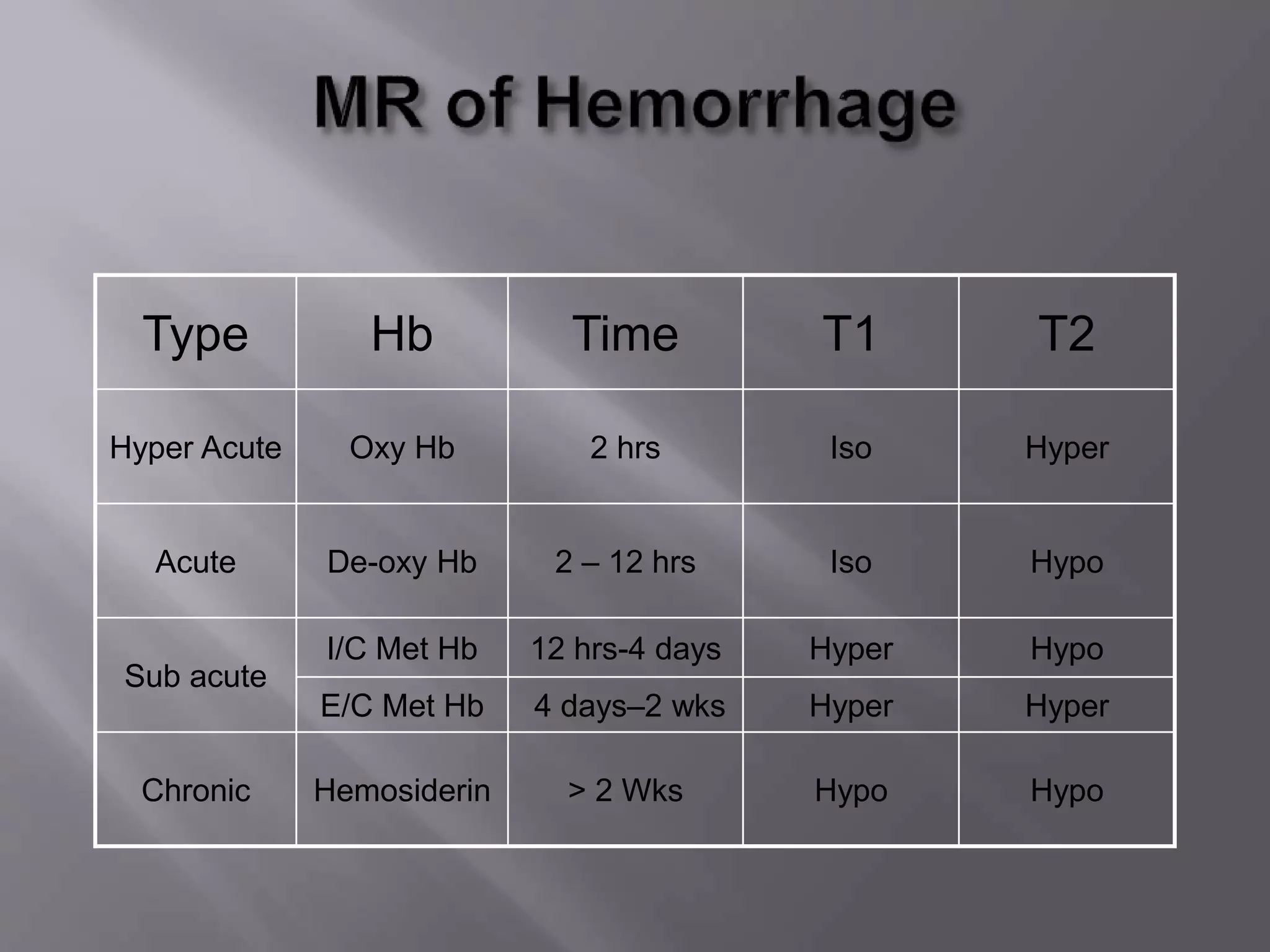
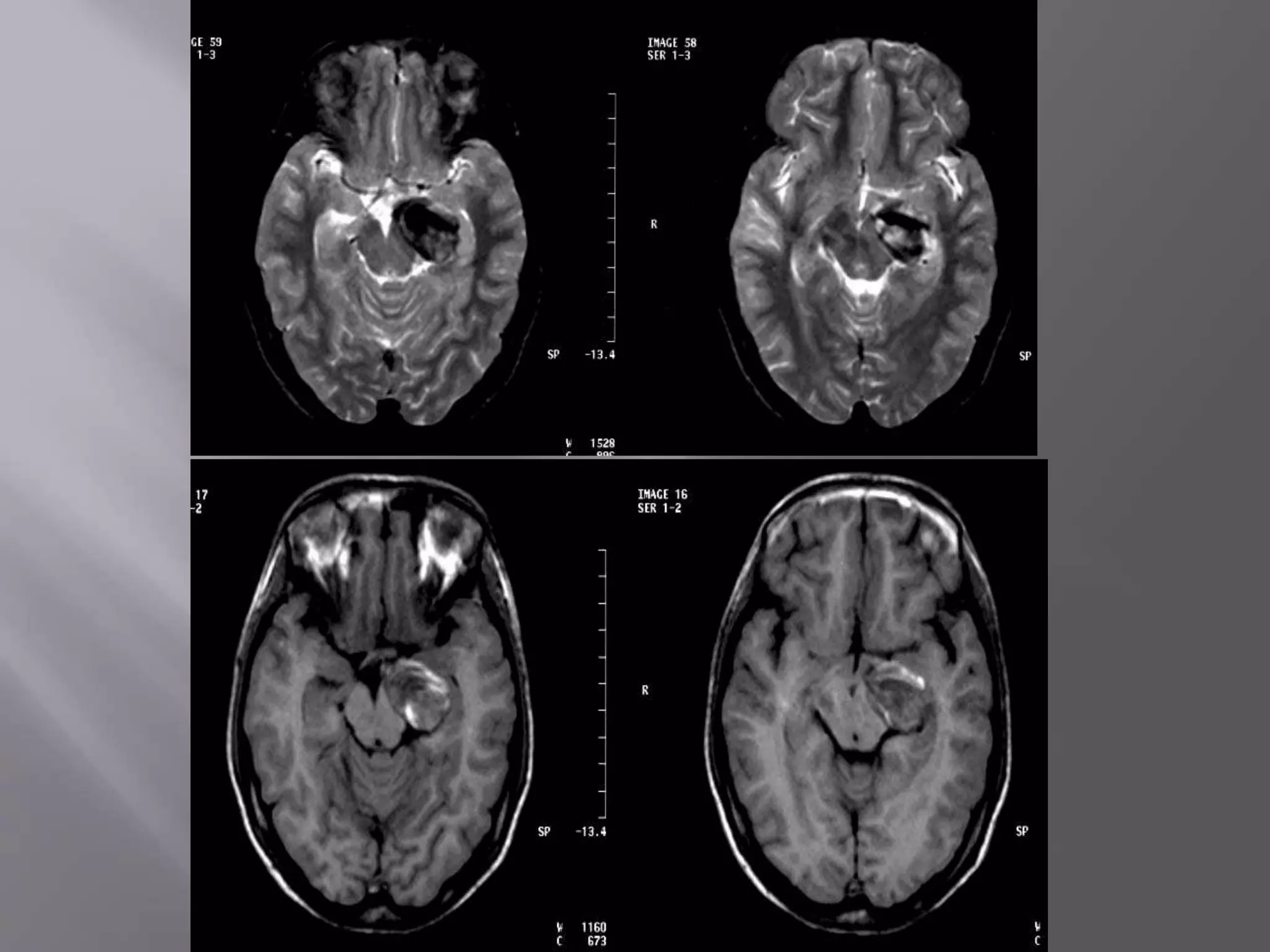
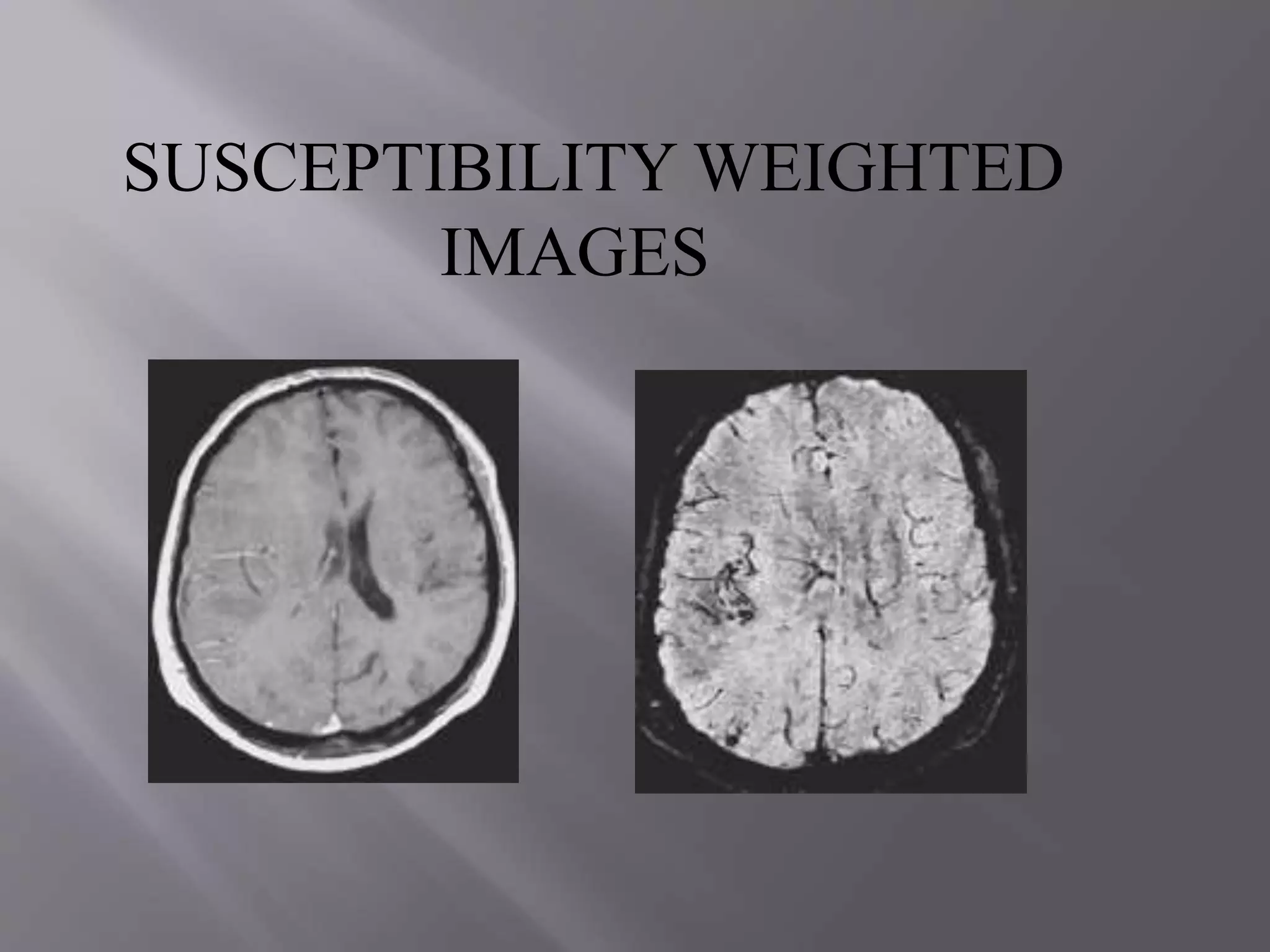
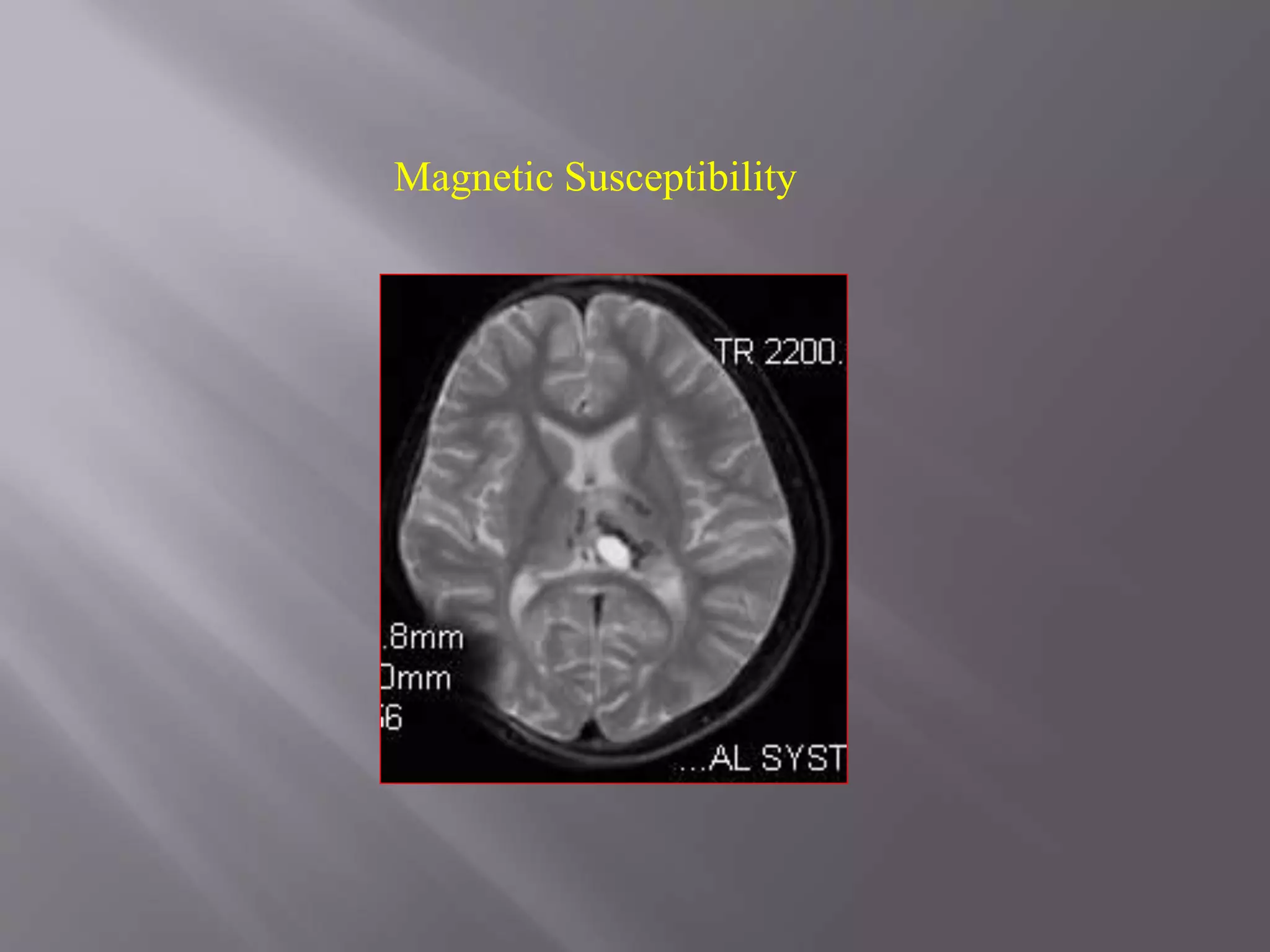
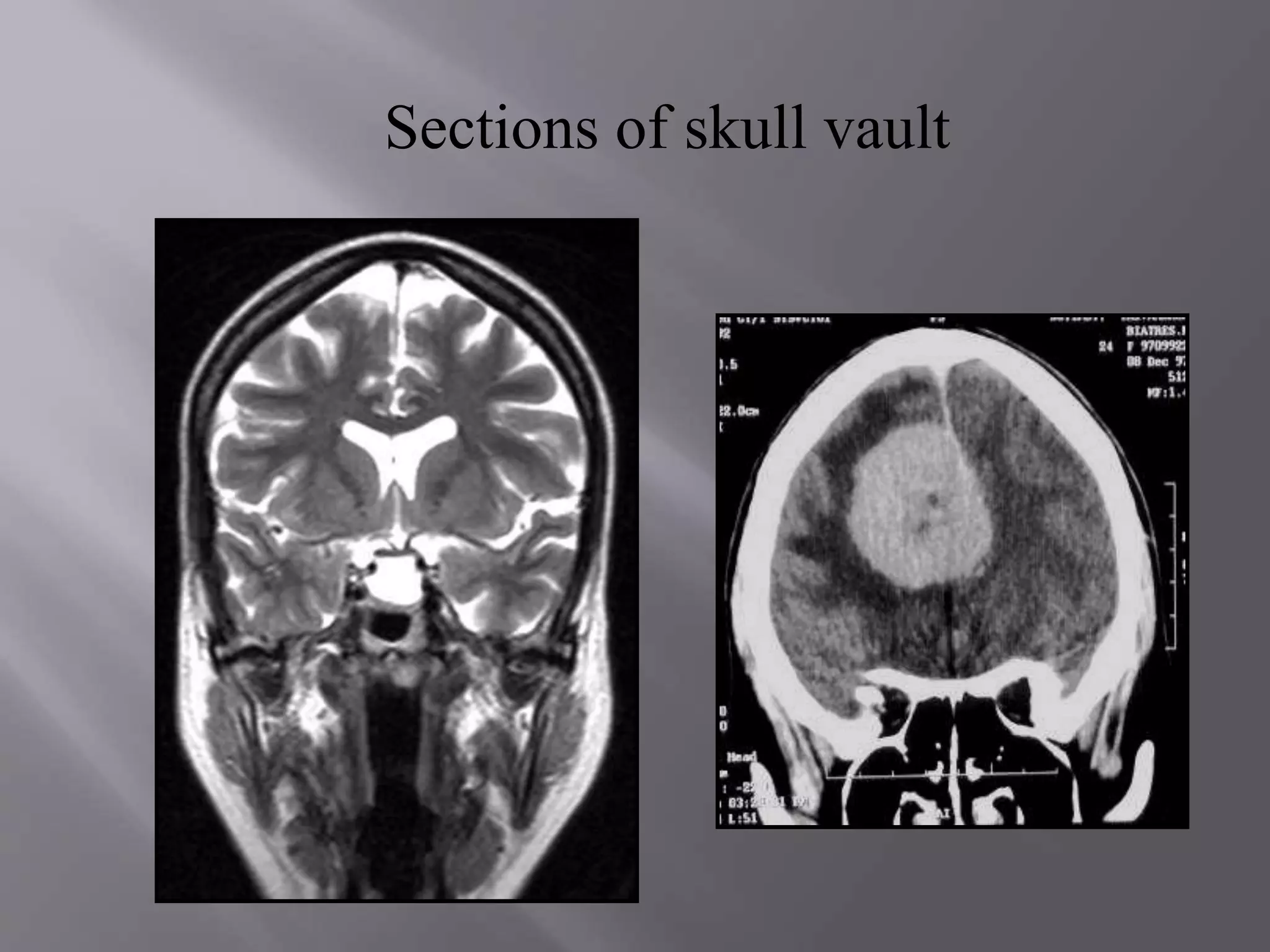
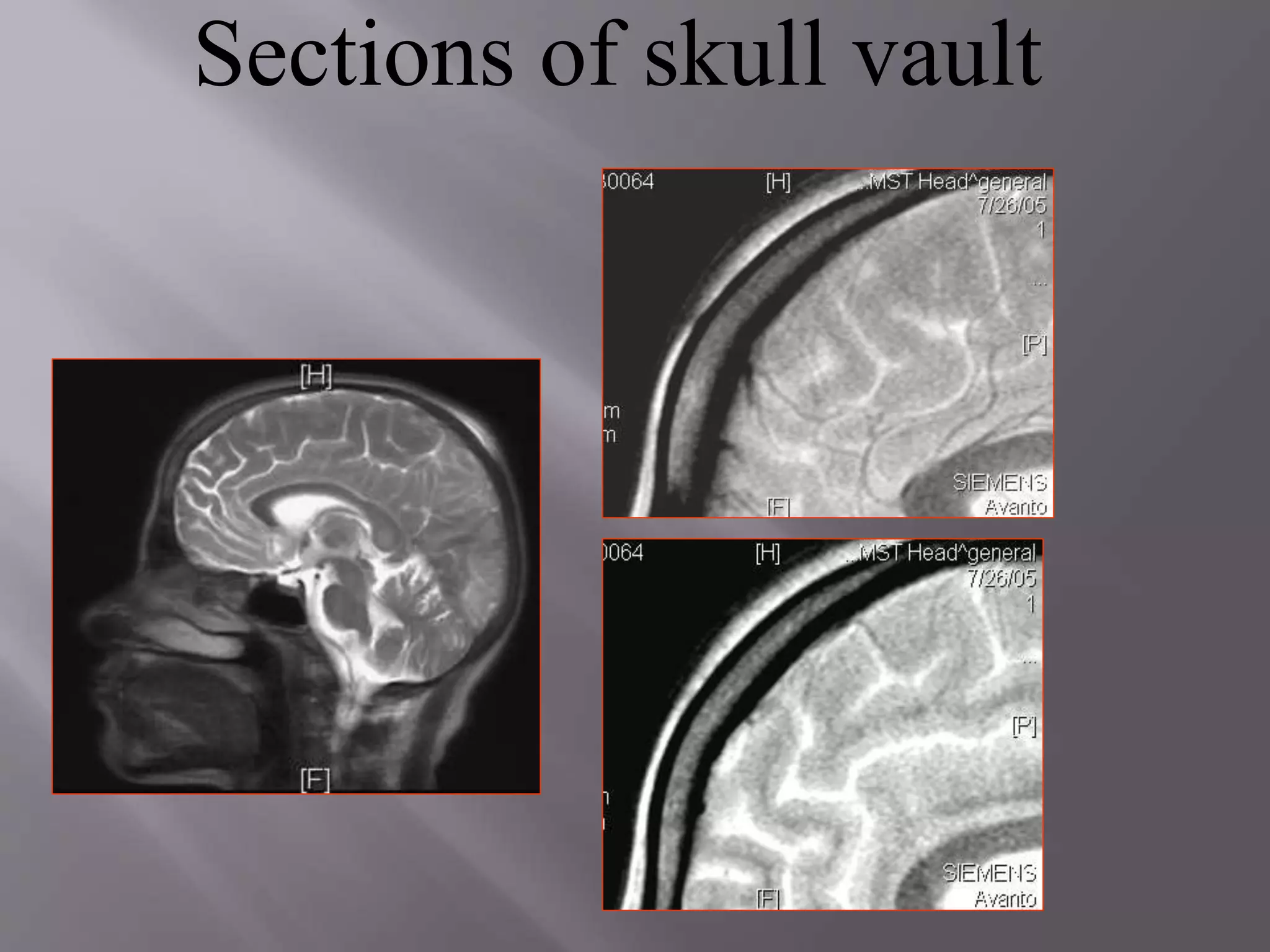
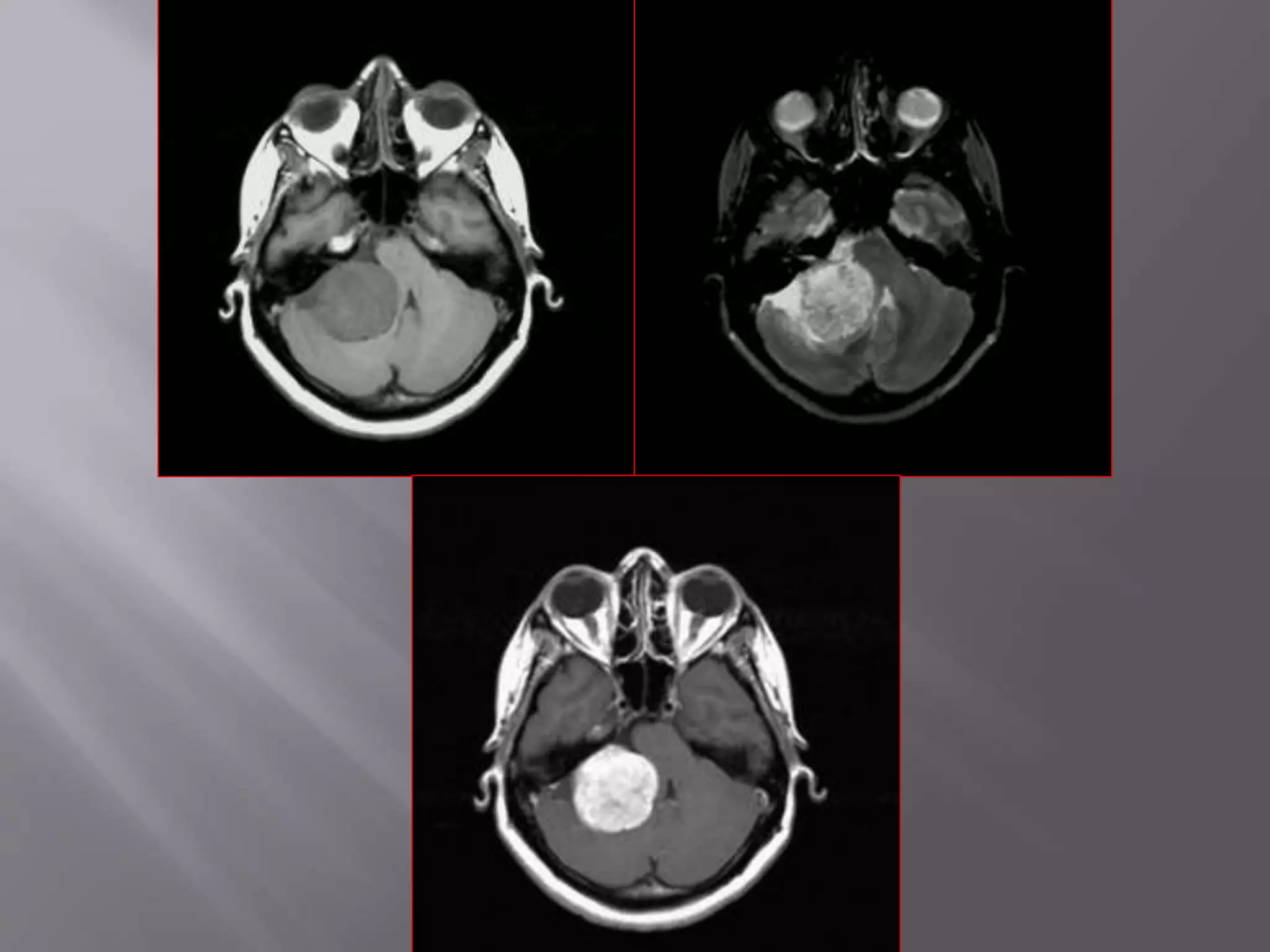
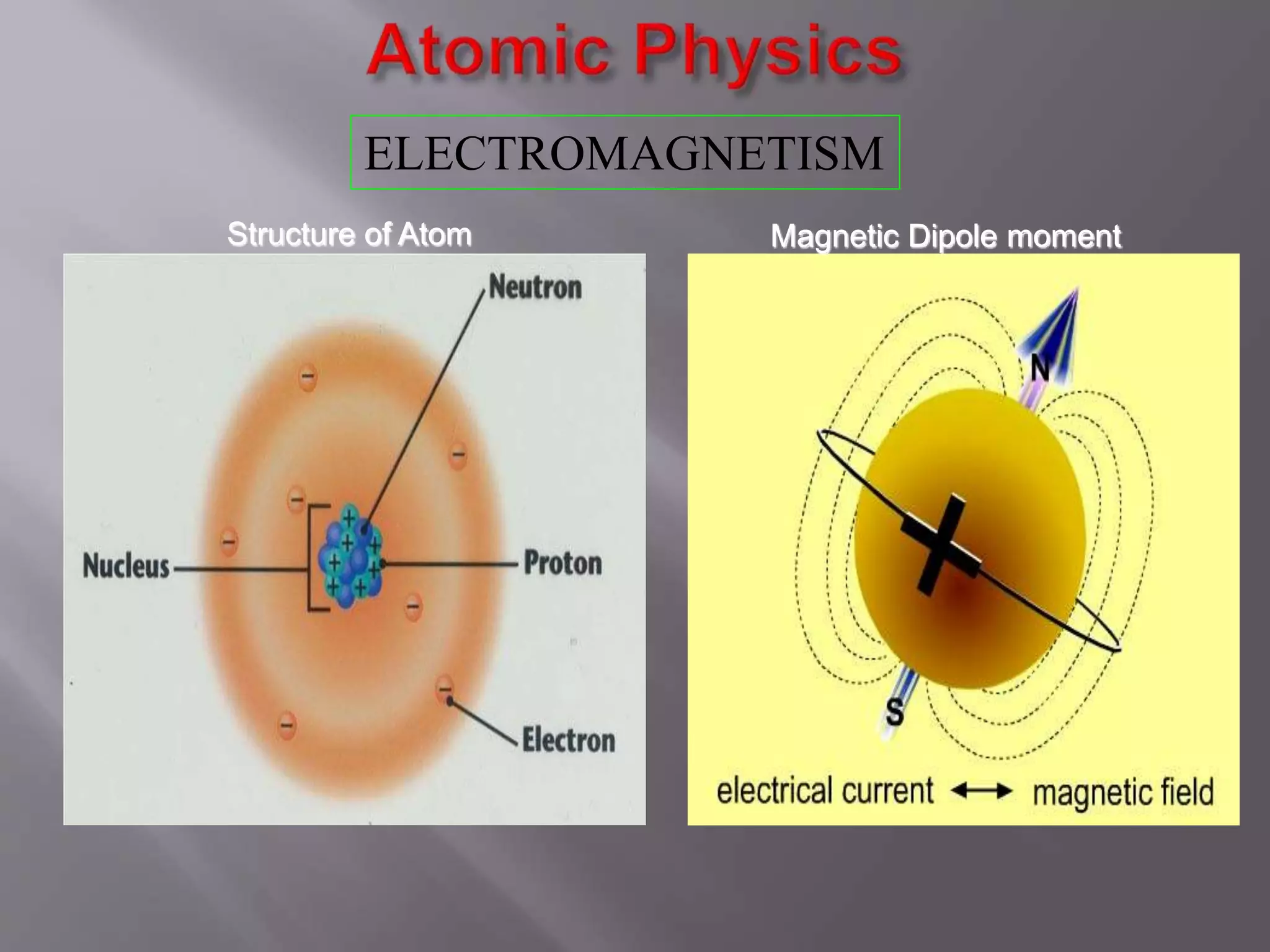
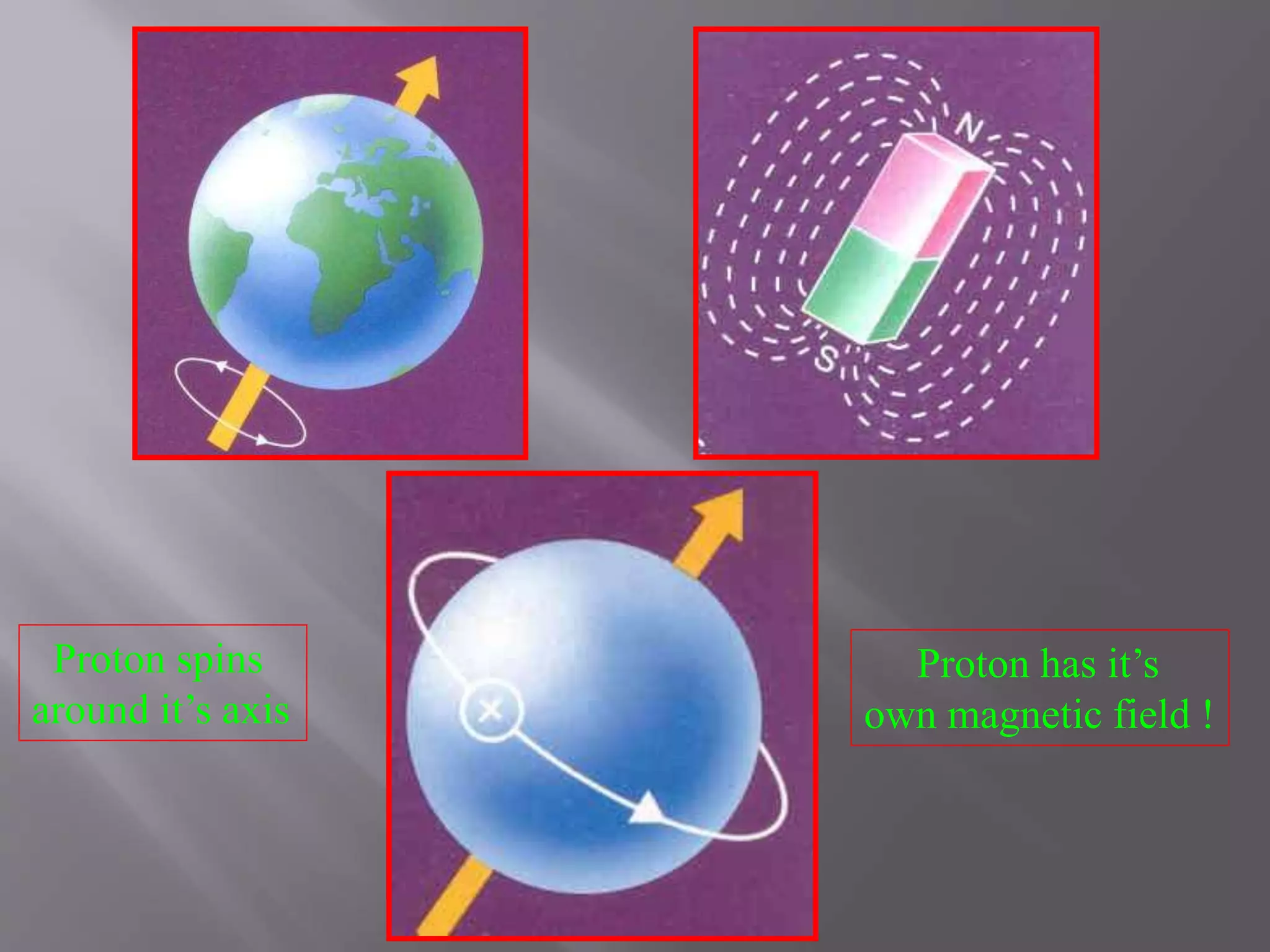
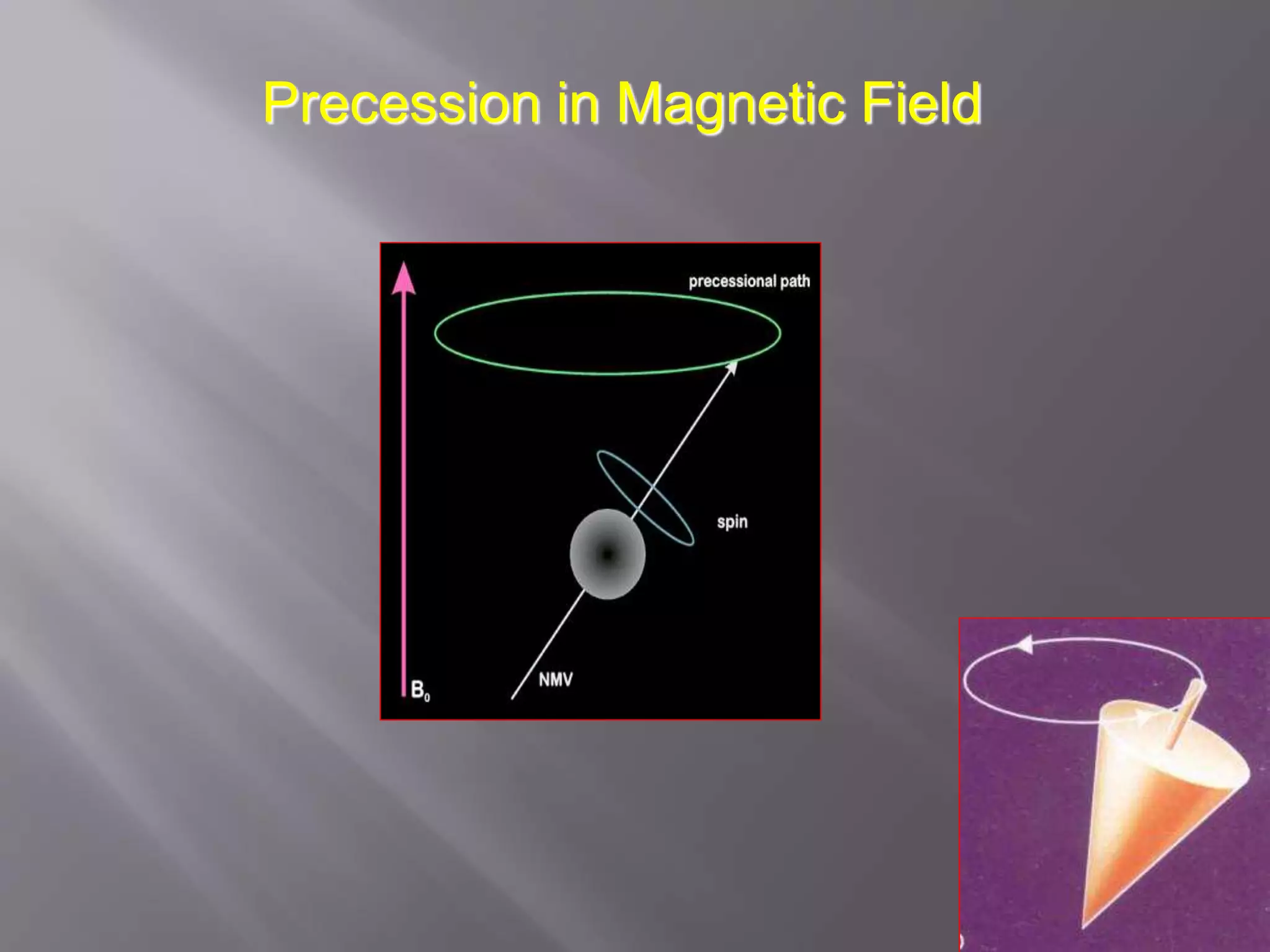
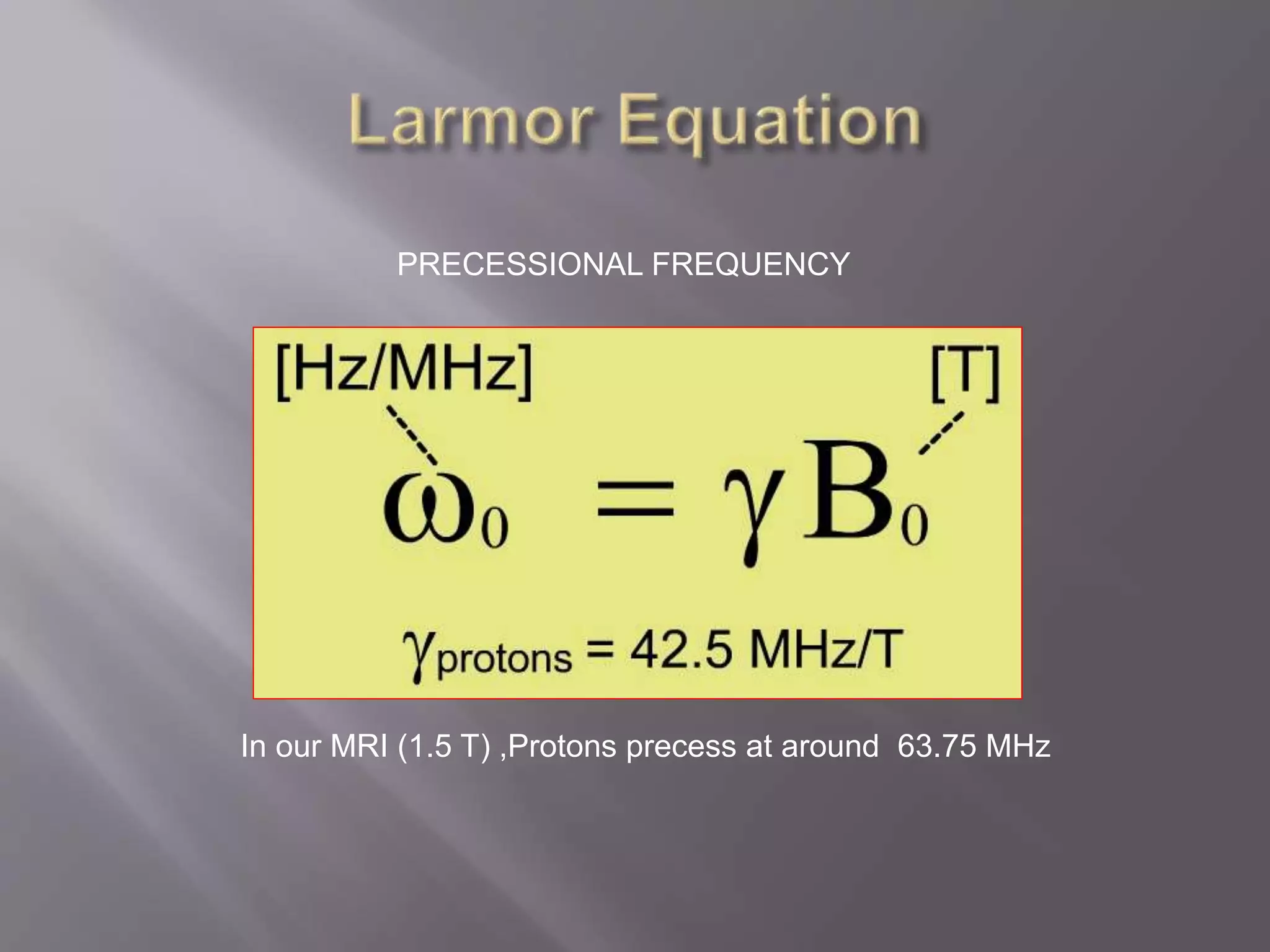
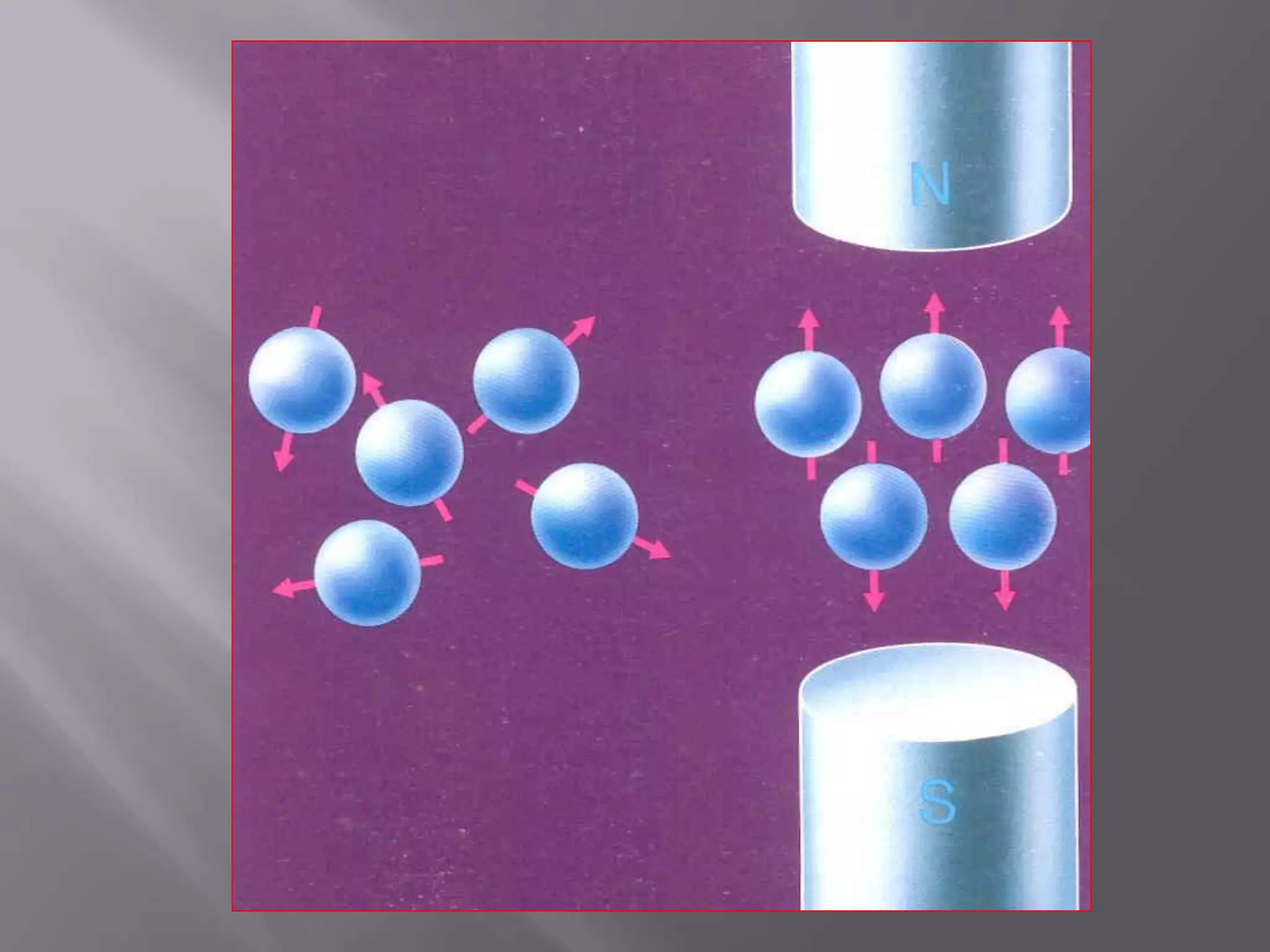
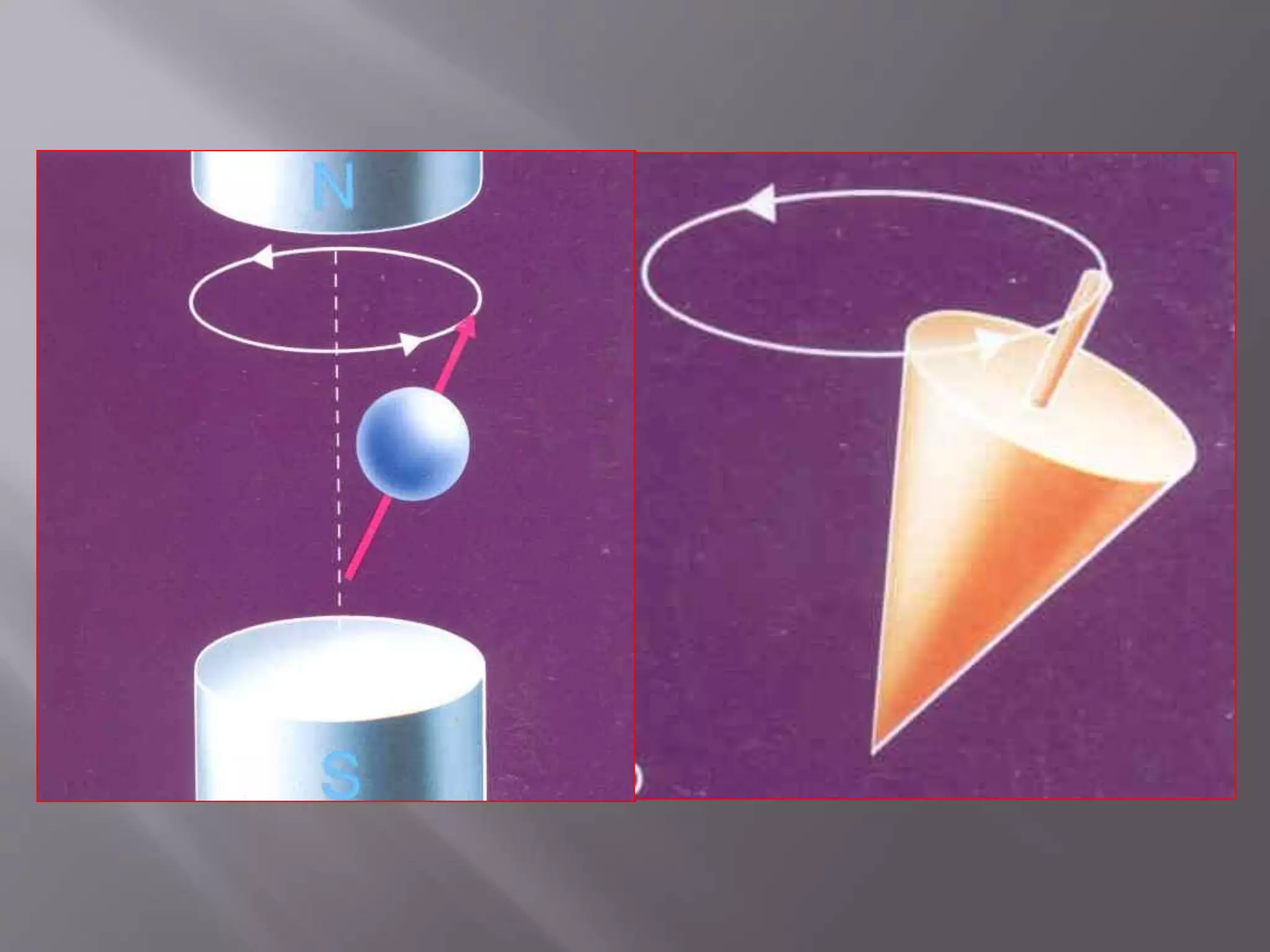
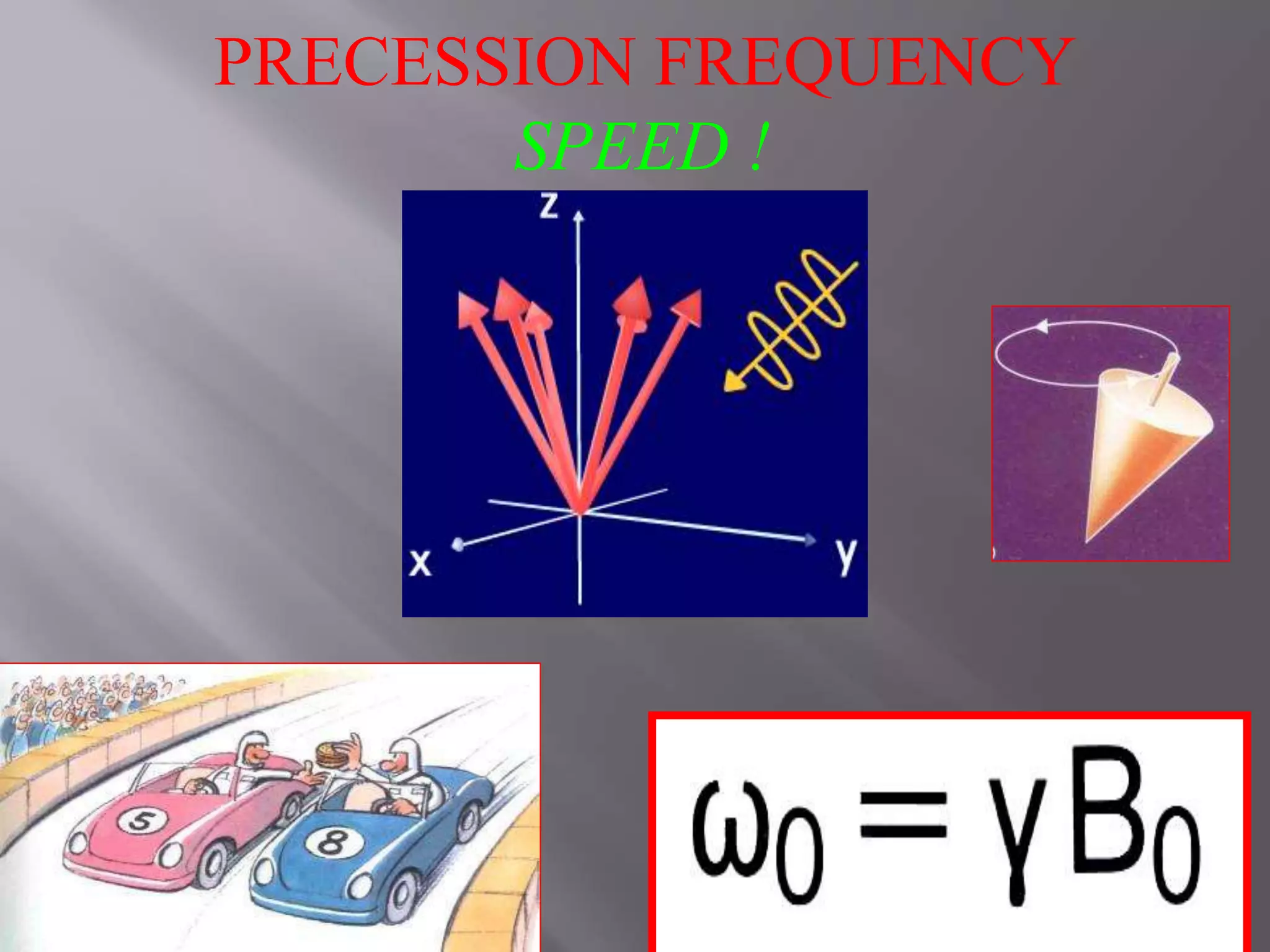
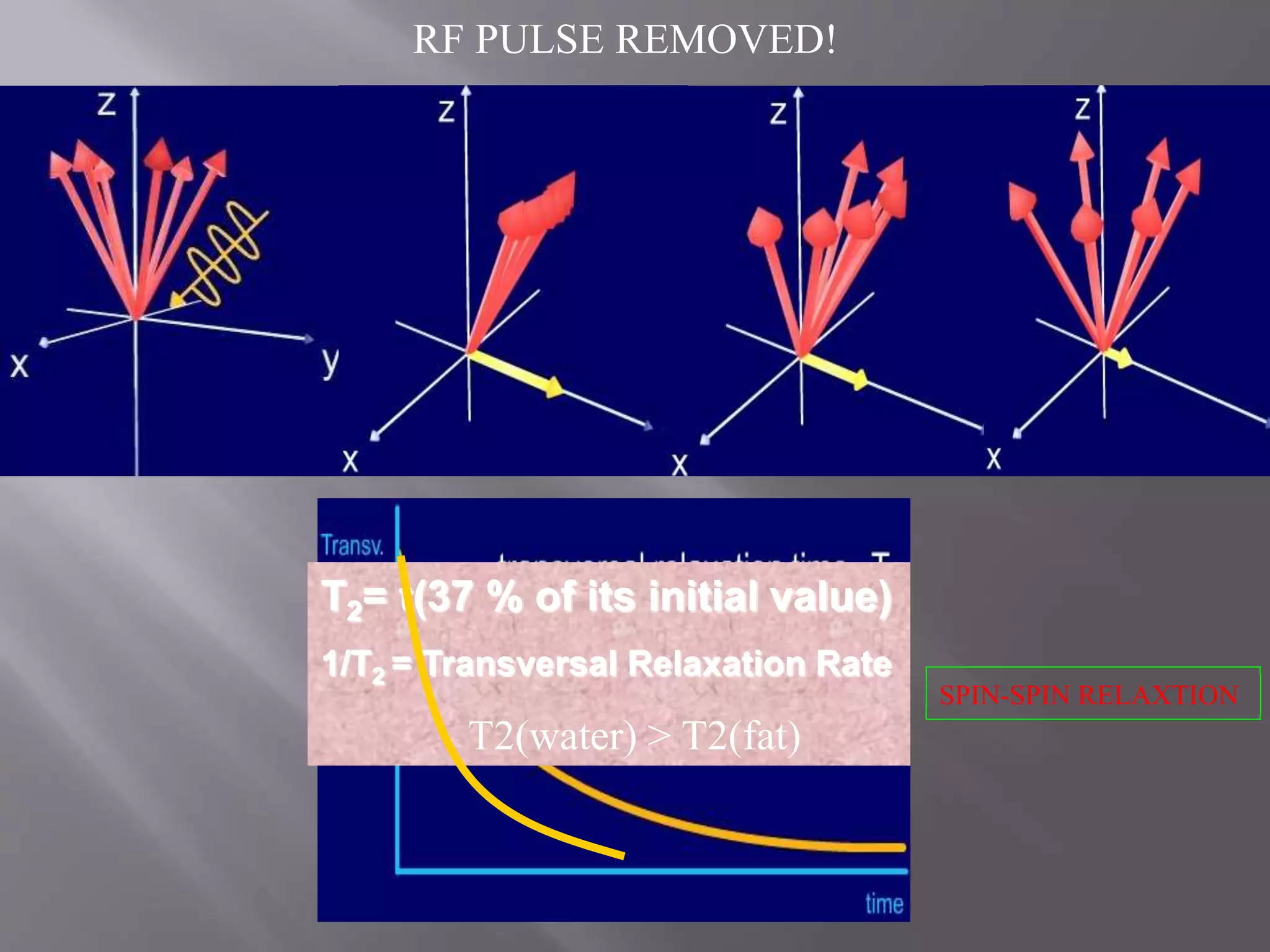
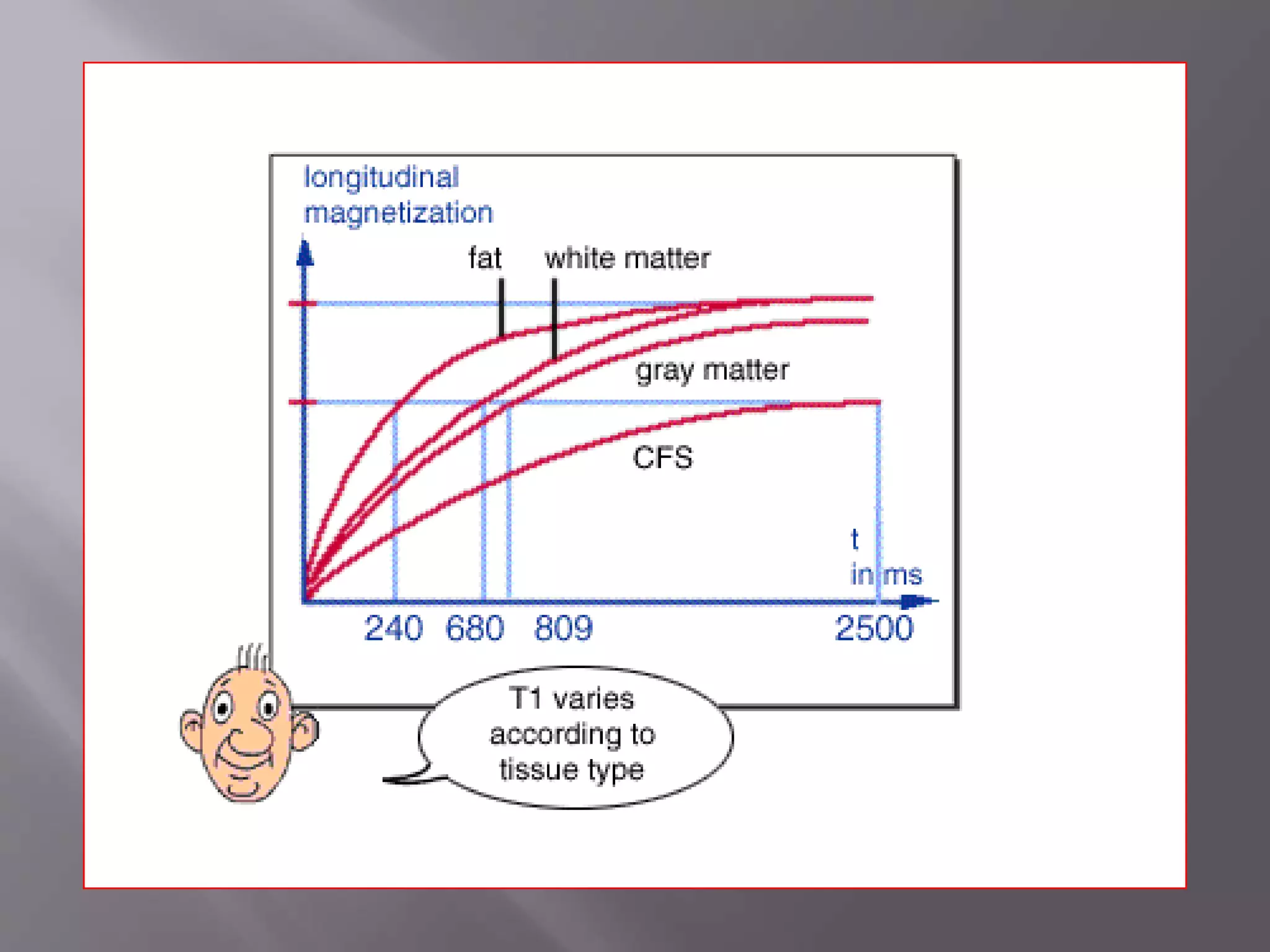
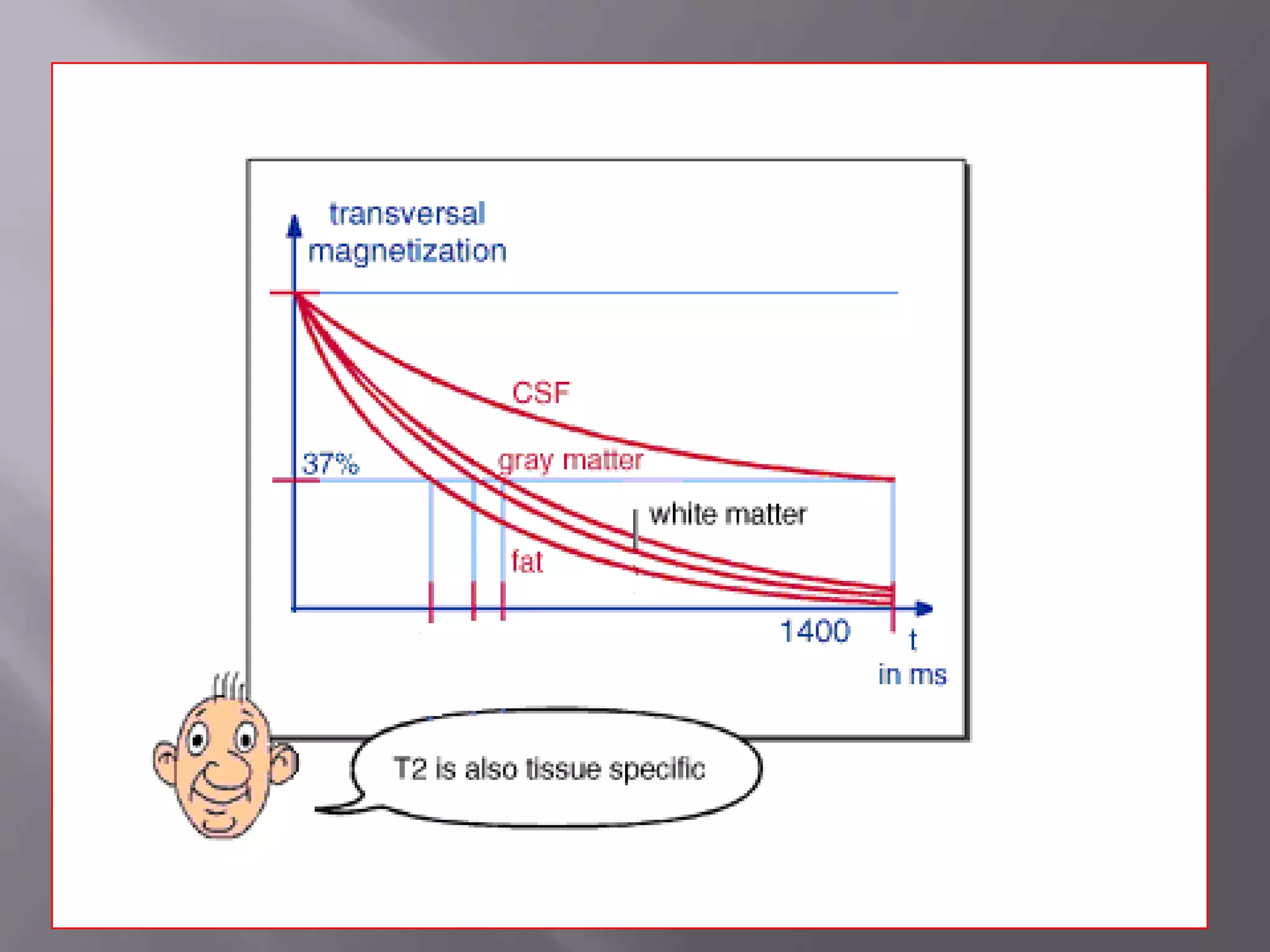
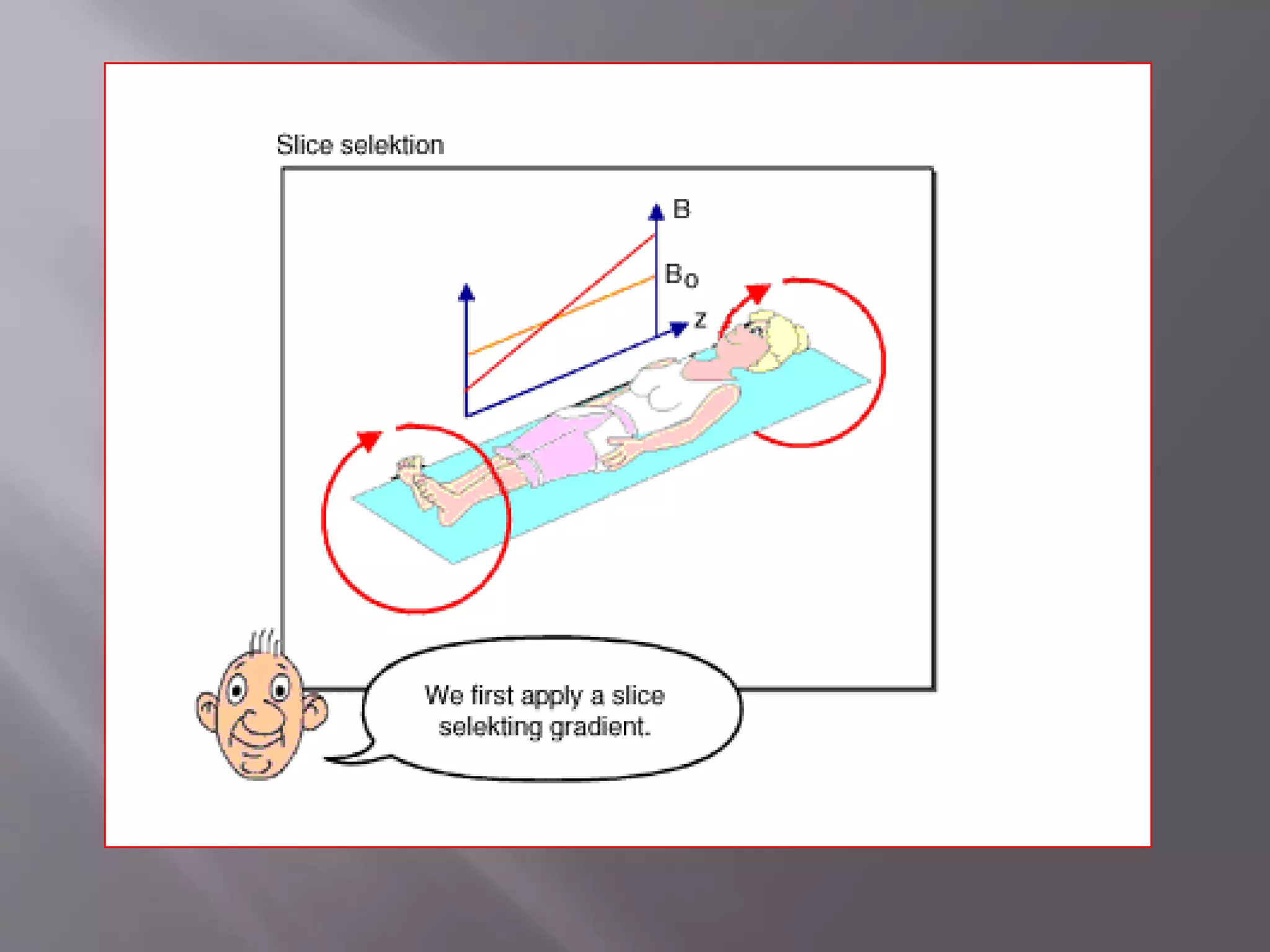
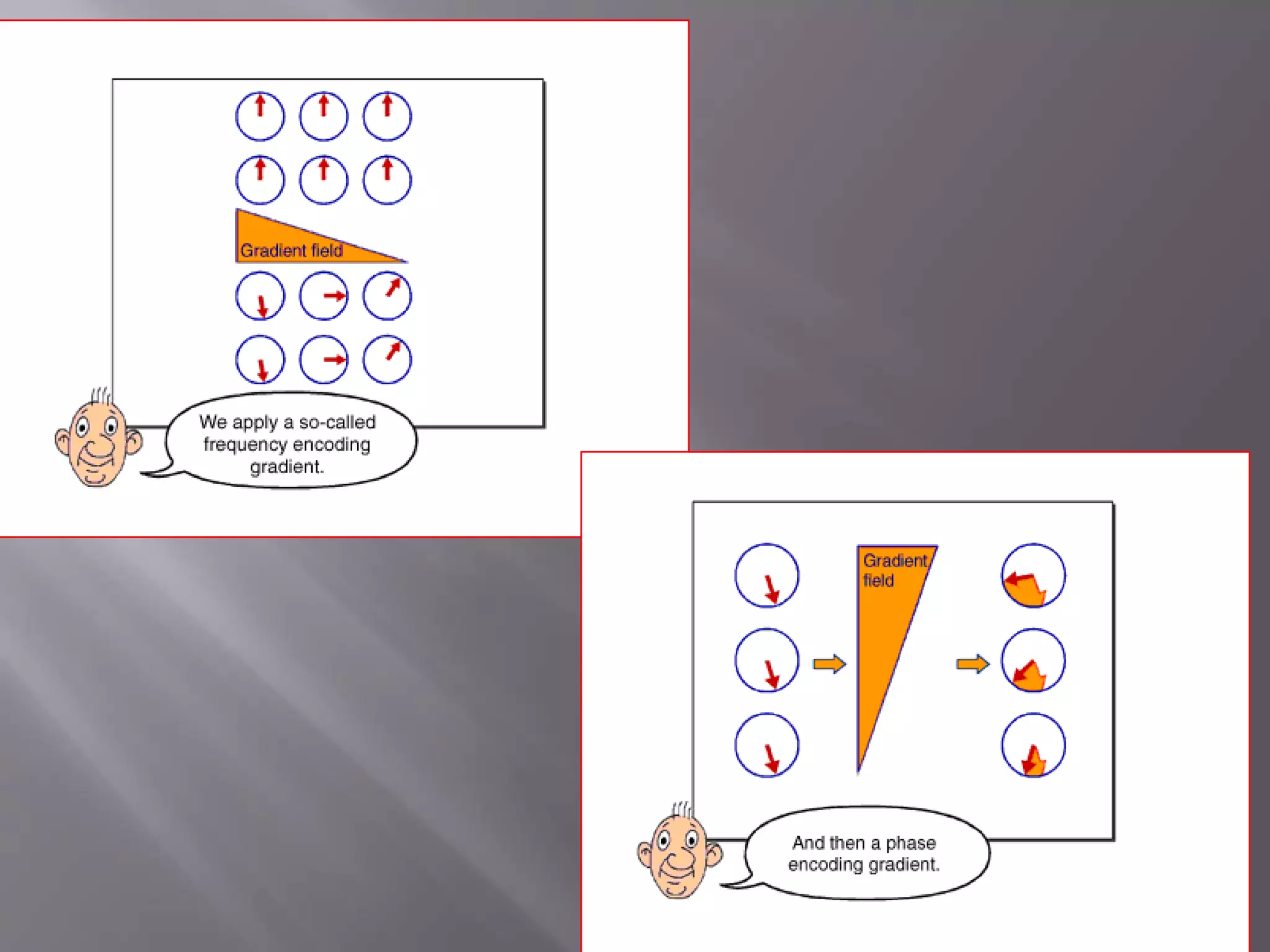
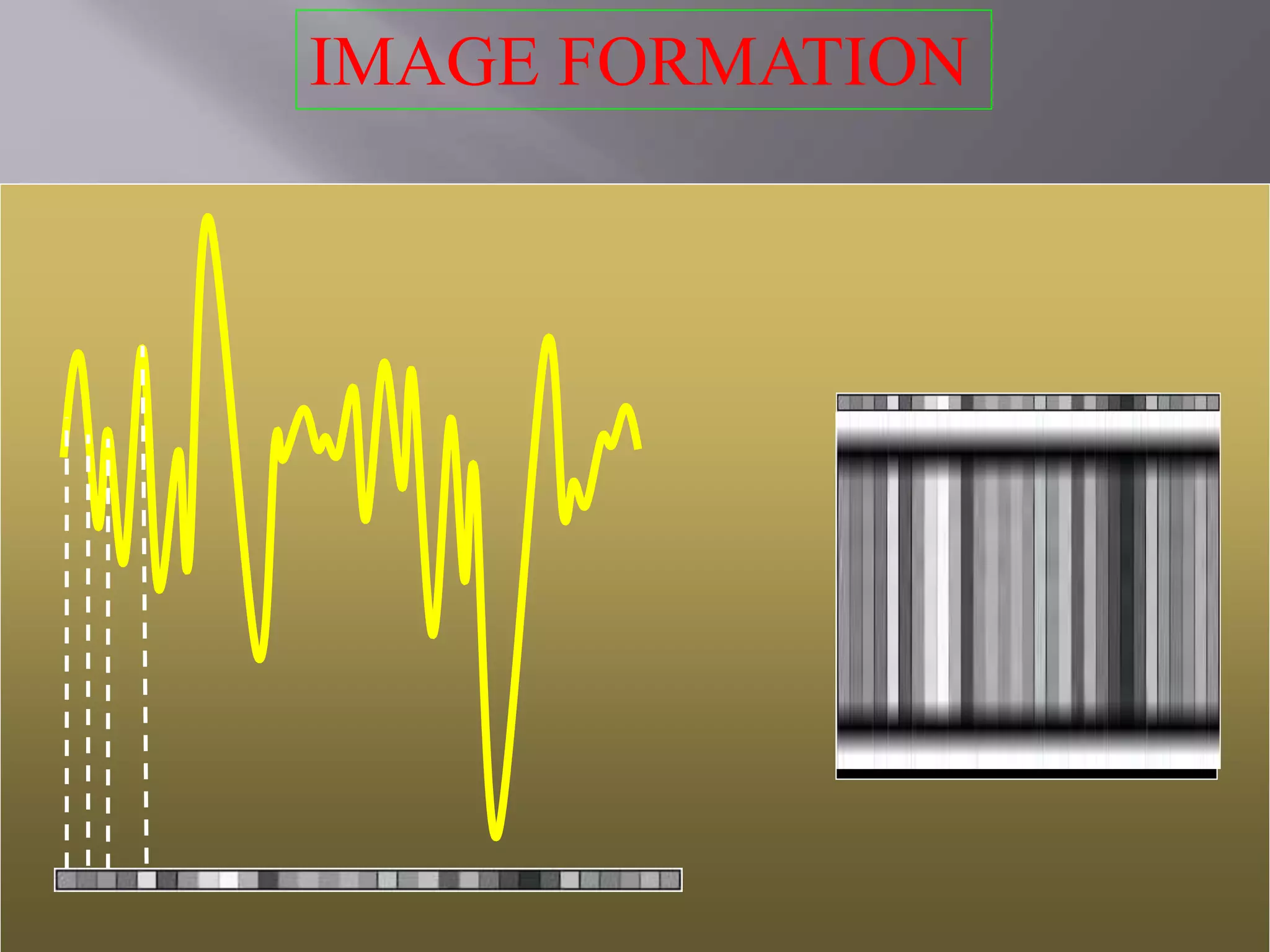
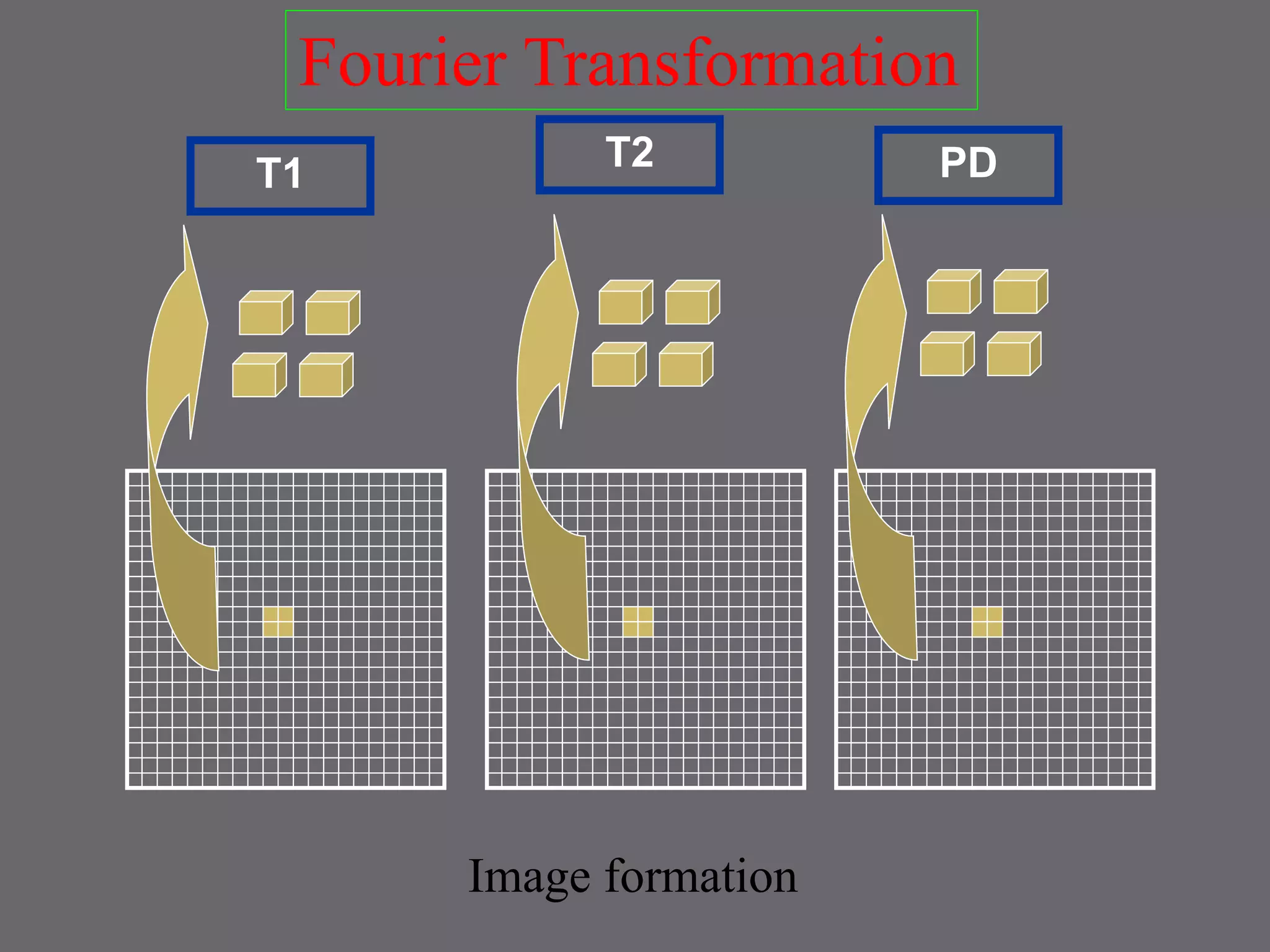
The document provides an overview of the history and development of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology. It discusses several key figures who contributed discoveries that advanced MRI, such as Felix Bloch and Edward Purcell conducting the first NMR experiment in 1946, Raymond Damadian constructing the first MRI scanner in 1977, and Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield who developed techniques for spatial encoding and fast imaging in the 1970s. The document also outlines some of the basic physics principles behind MRI such as precession frequency, T1 and T2 relaxation times, and the use of gradient coils and RF pulses to encode spatial information and form images.




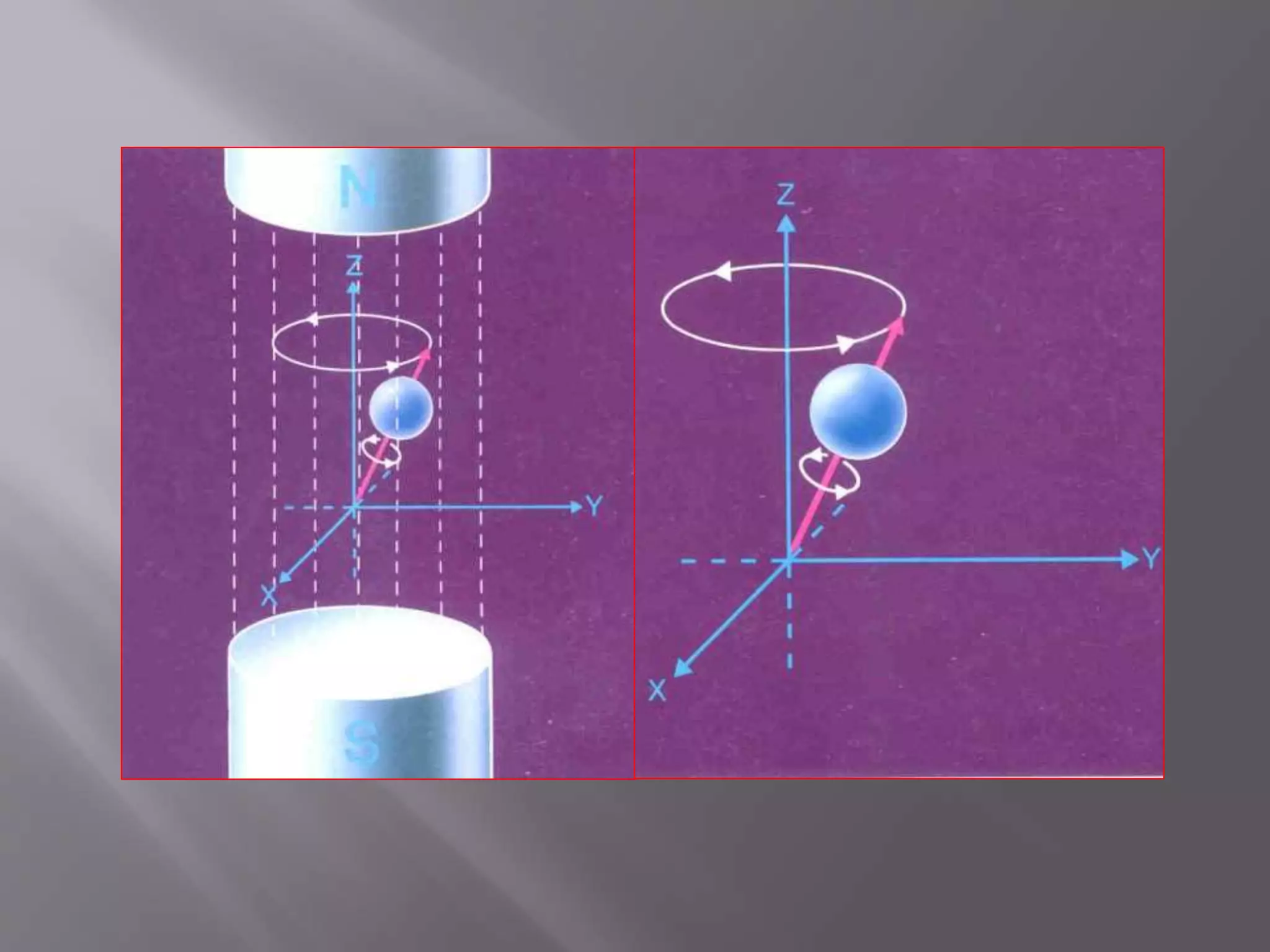
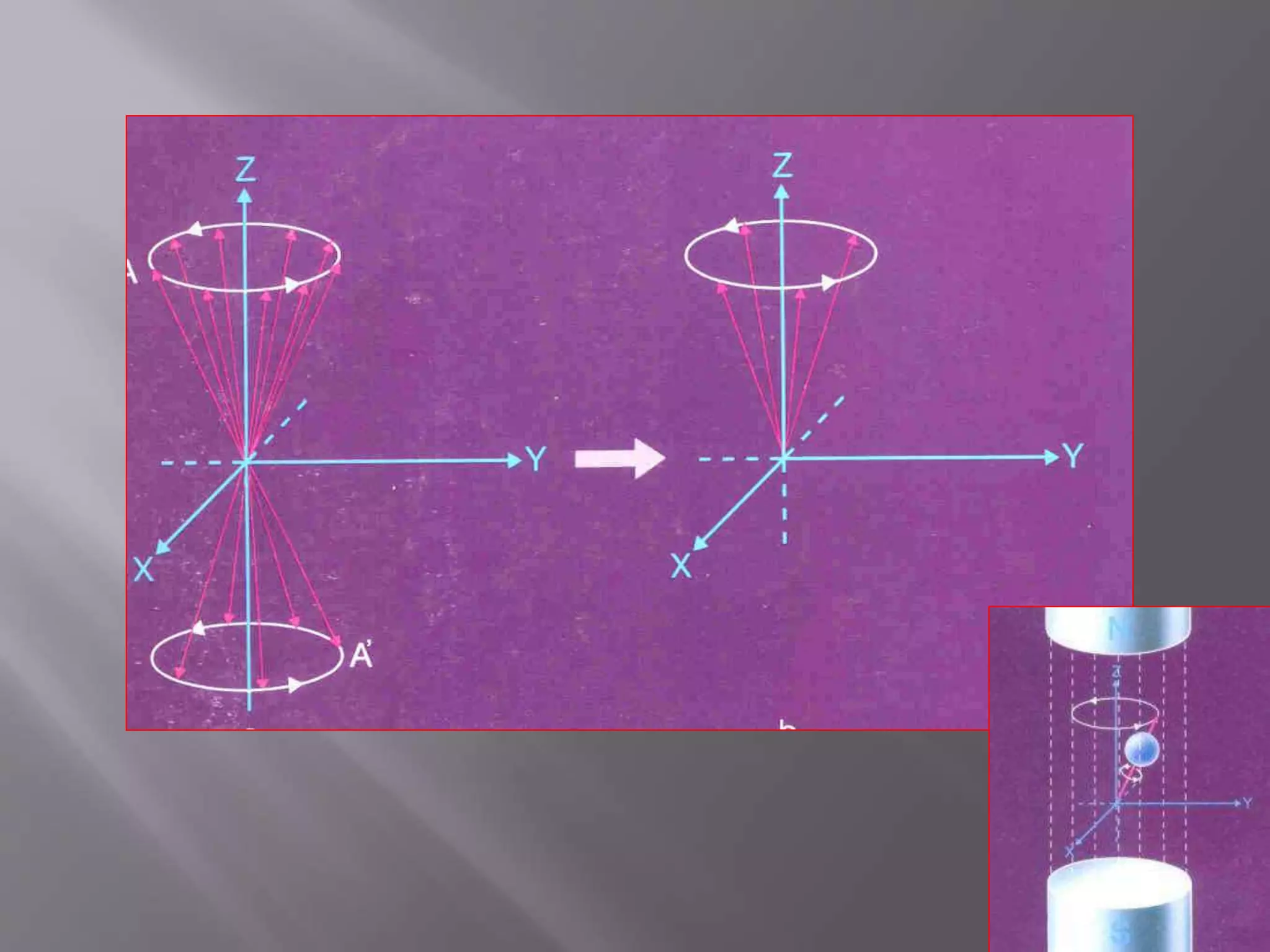
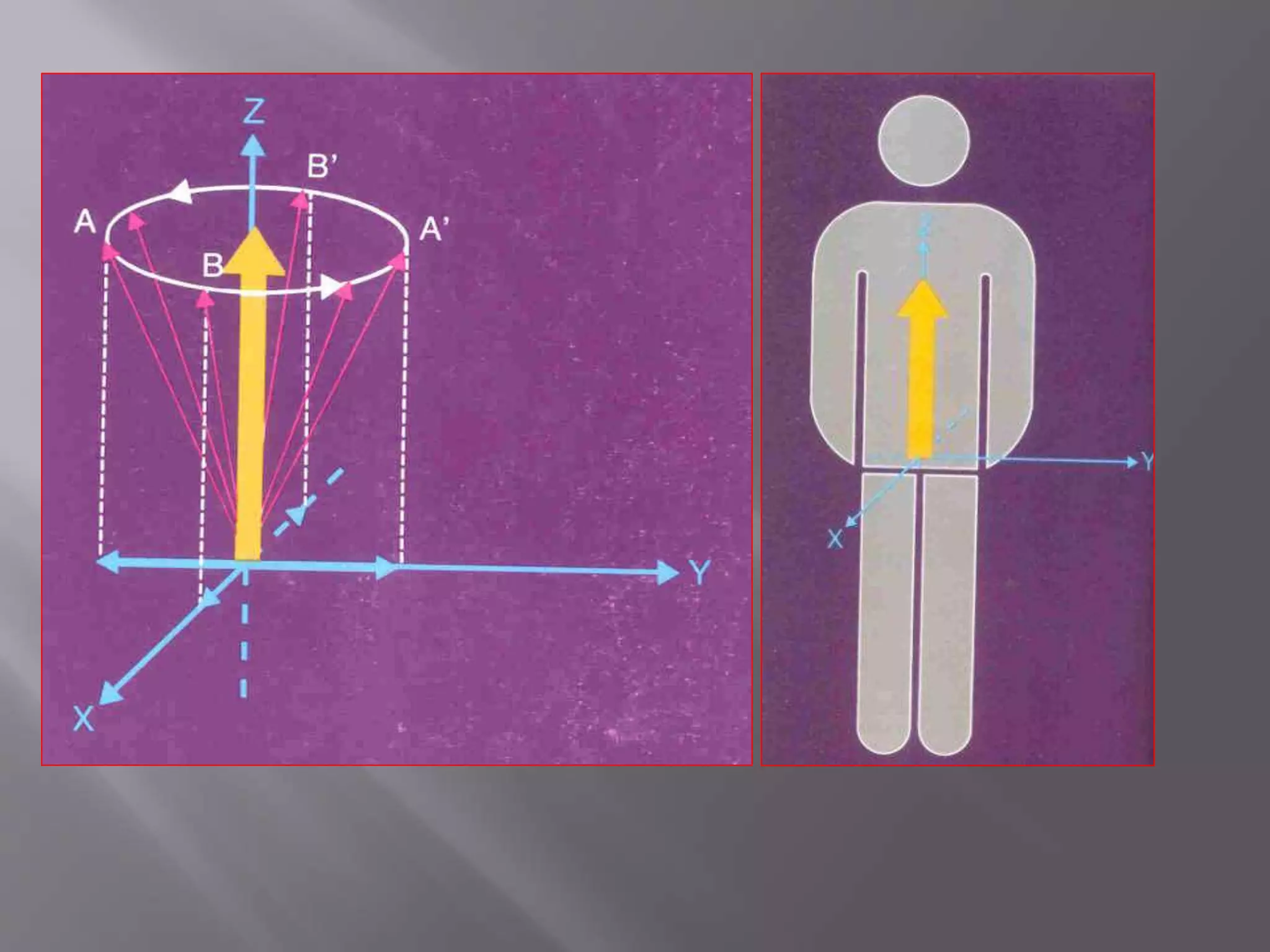



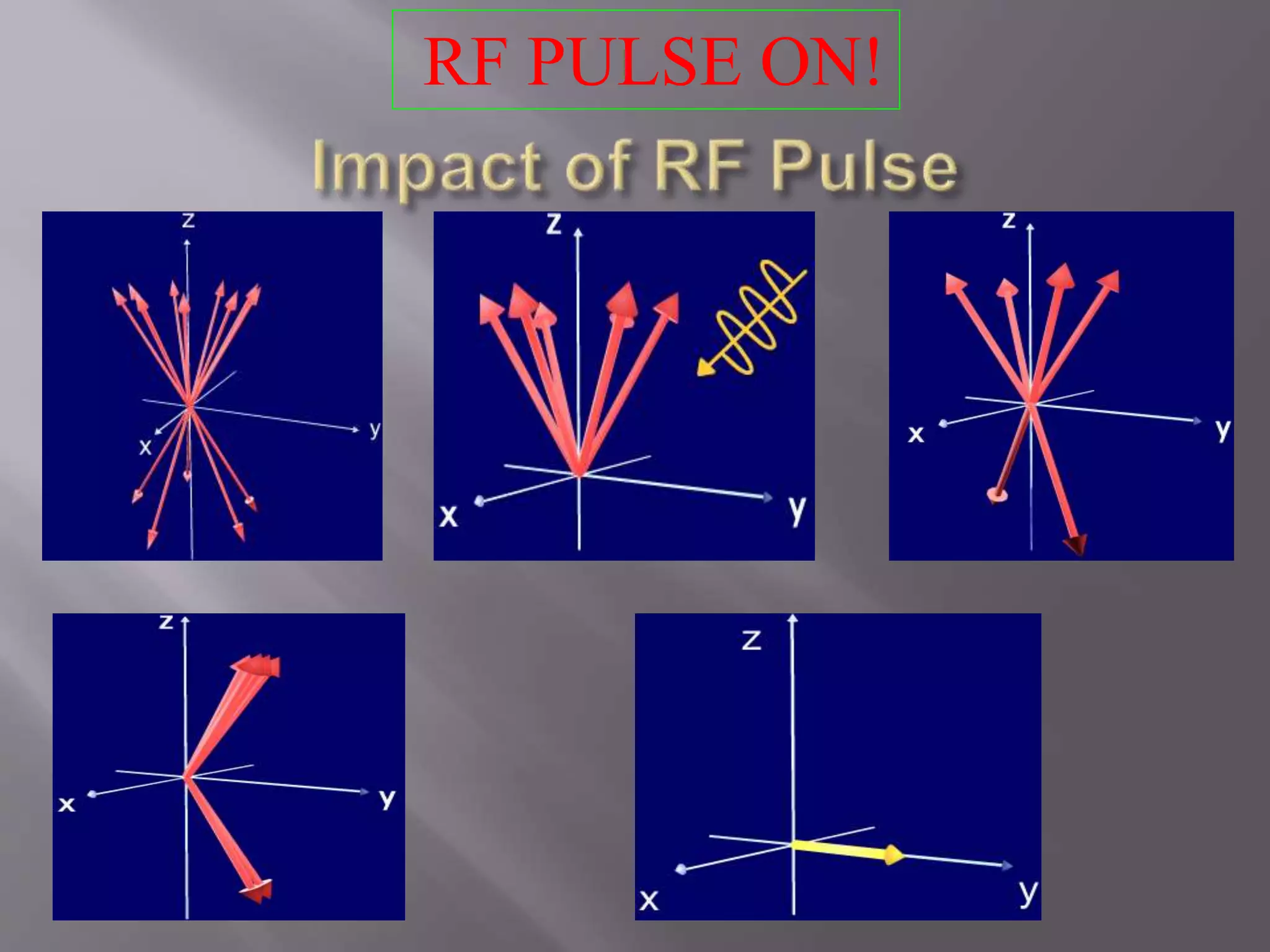





![1) Put subject in big magnetic field
2) Transmit radio waves into subject [about 3 ms]
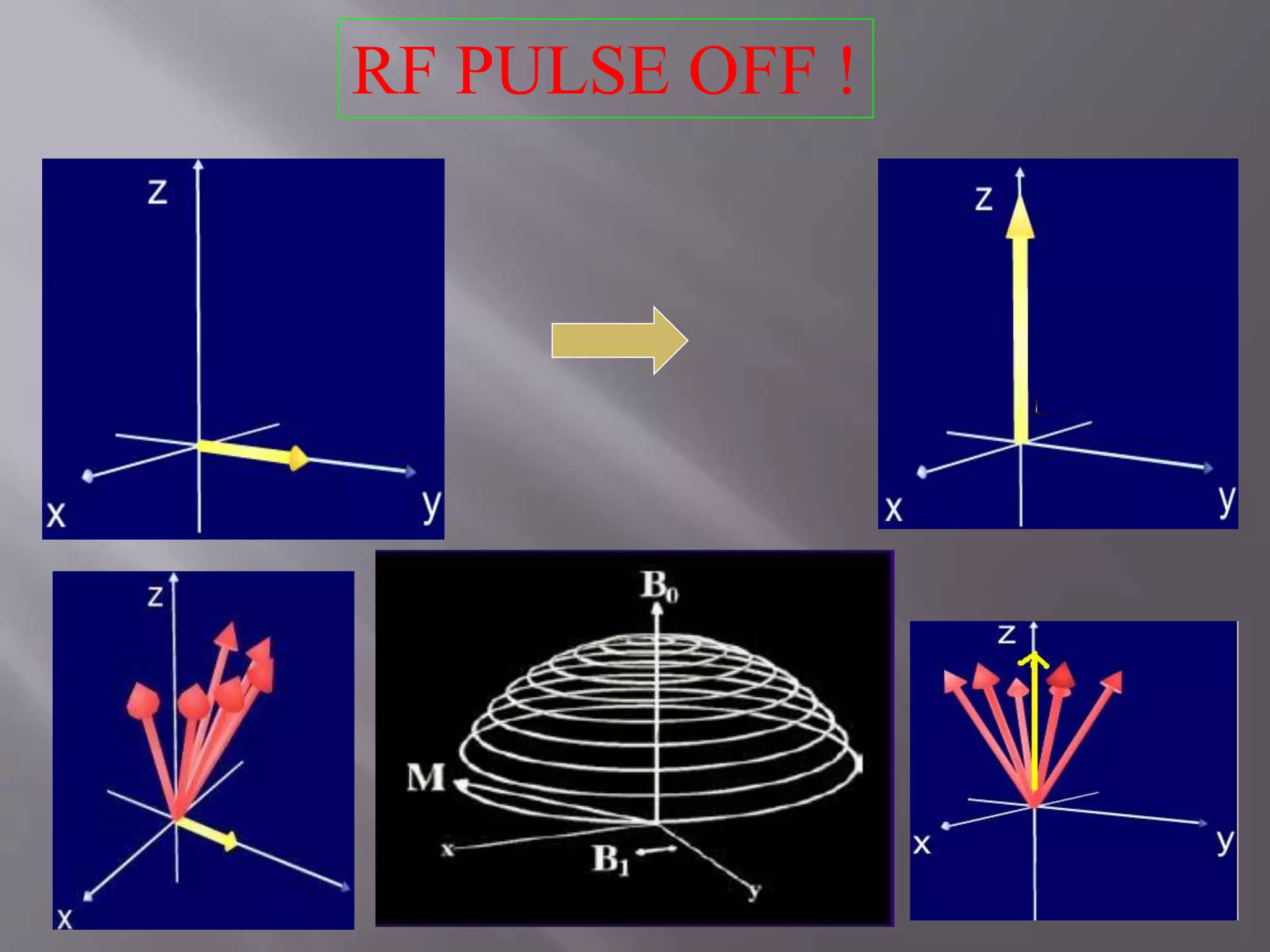
3) Turn off radio wave transmitter
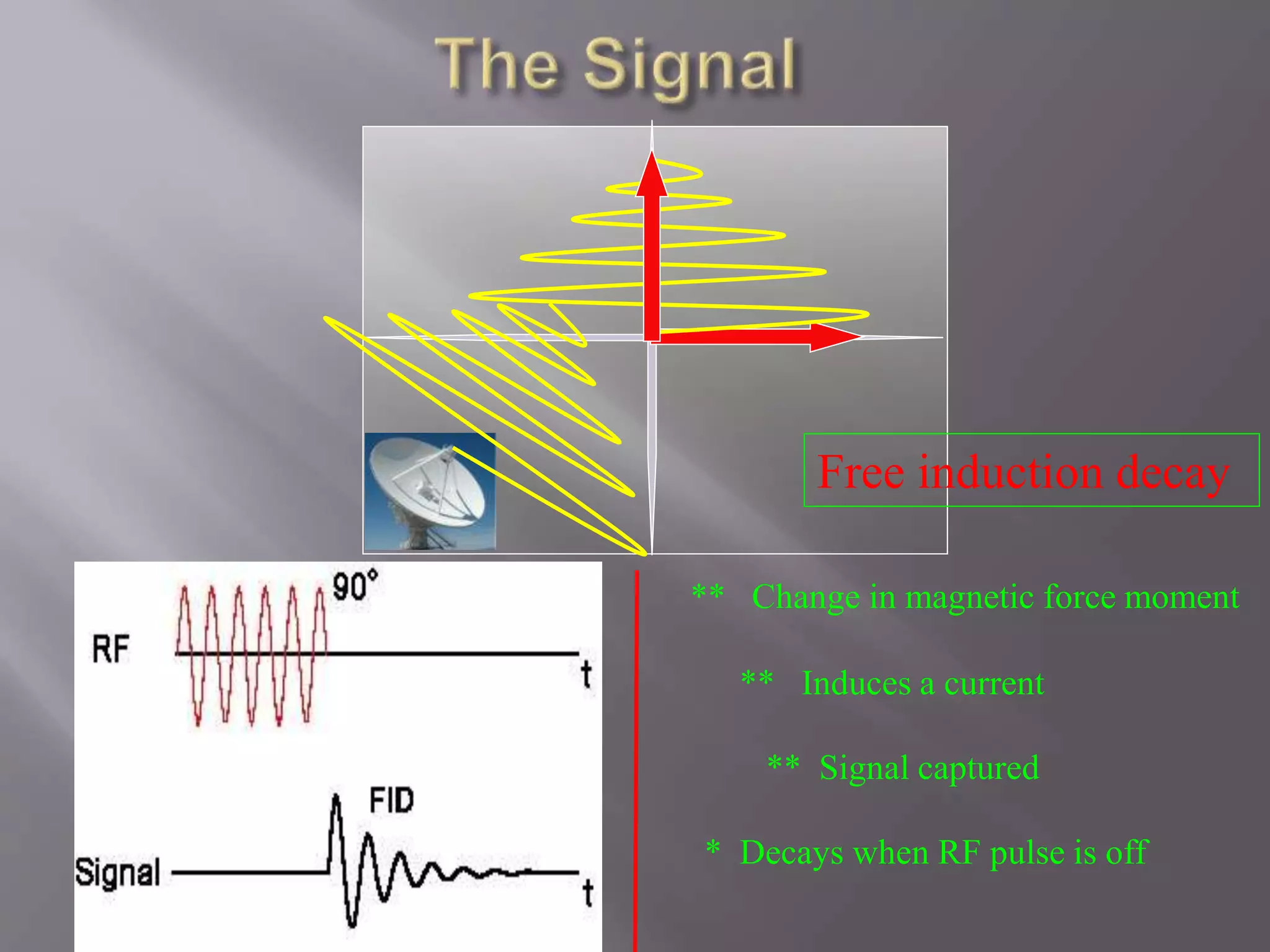
4) Receive radio waves re-transmitted by subject
5) Store measured radio wave data vs. time
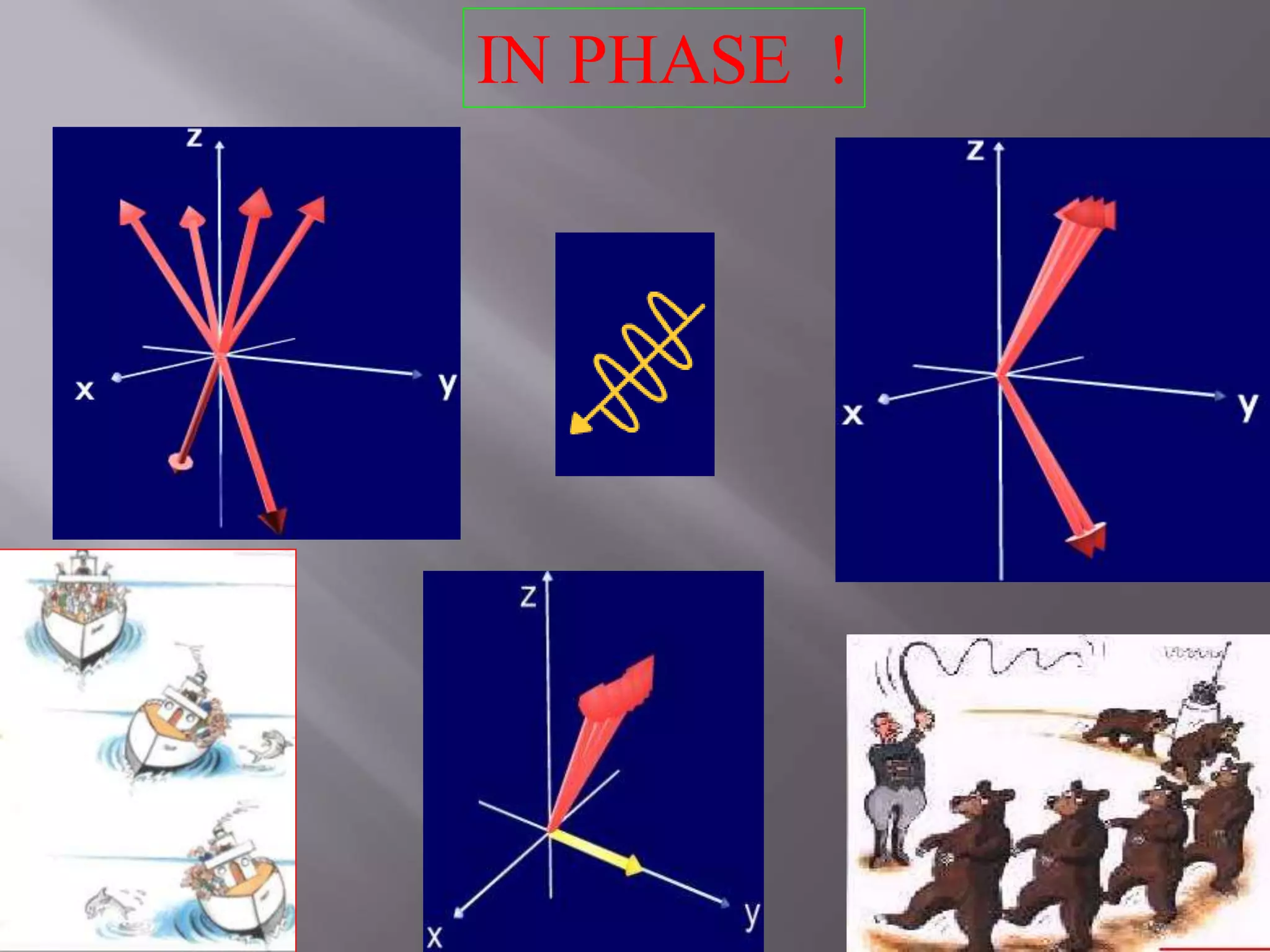
– Now go back to step(2) to get some more data
6) Process raw data to reconstruct images
NUT SHELL!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mribasics-150118121019-conversion-gate01/75/Mri-basics-39-2048.jpg)