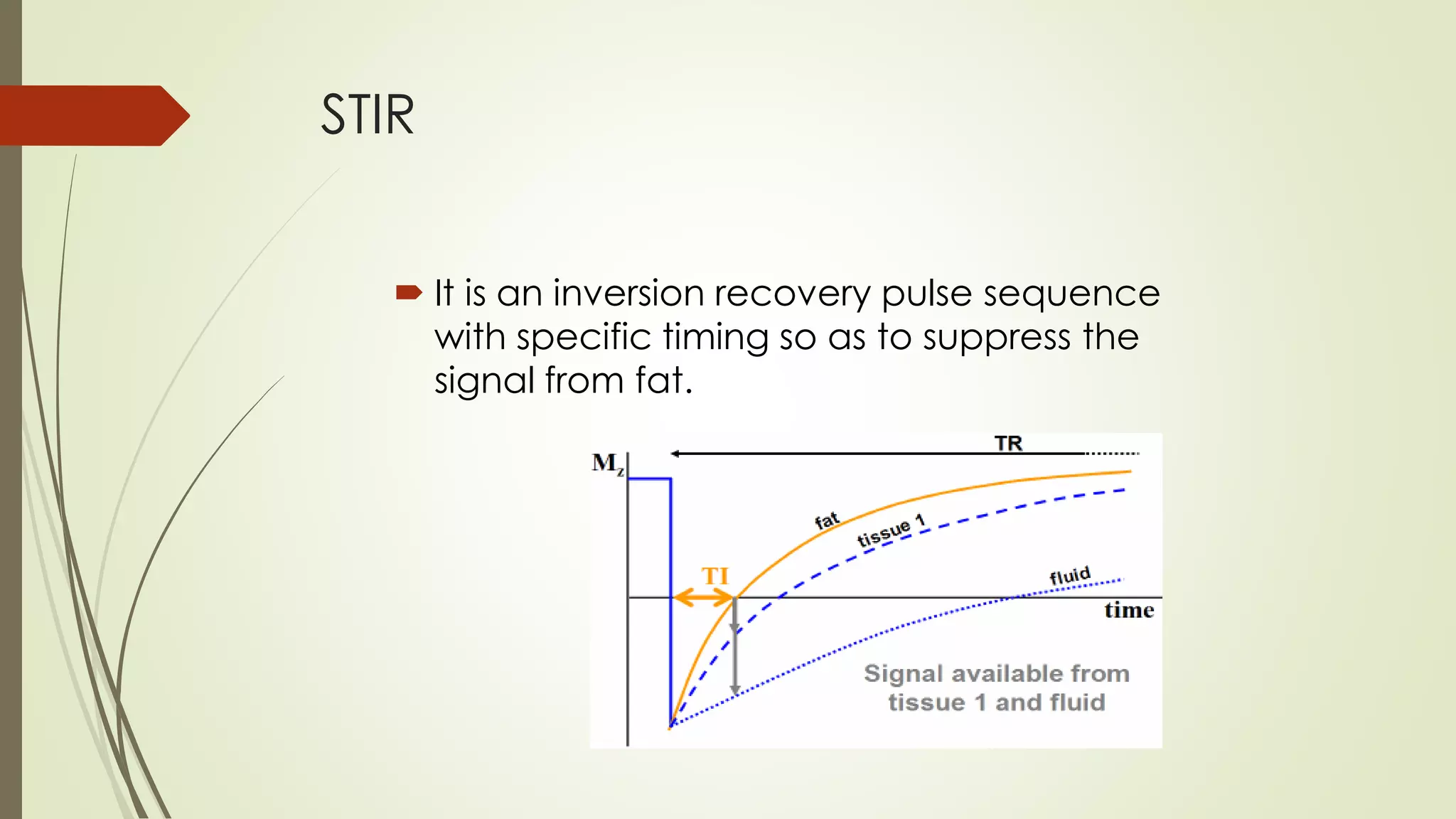
Fat suppression MRI techniques suppress the signal from fat tissues to improve visualization of other tissues. The main techniques are STIR, CHESS, SPIR, and SPAIR which use inversion recovery pulses or chemical saturation of fat protons at different resonance frequencies than water. Newer Dixon-based methods extract water-only and fat-only images from multiple echoes acquired at different echo times to achieve fat suppression without sensitivity to magnetic field inhomogeneities. These techniques are used for tissue characterization, detecting contrast enhancement, and reducing chemical shift artifacts.