The document defines key concepts in vector spaces including vector space, subspace, span of a set of vectors, and basis. It provides examples to illustrate these concepts. Specifically:
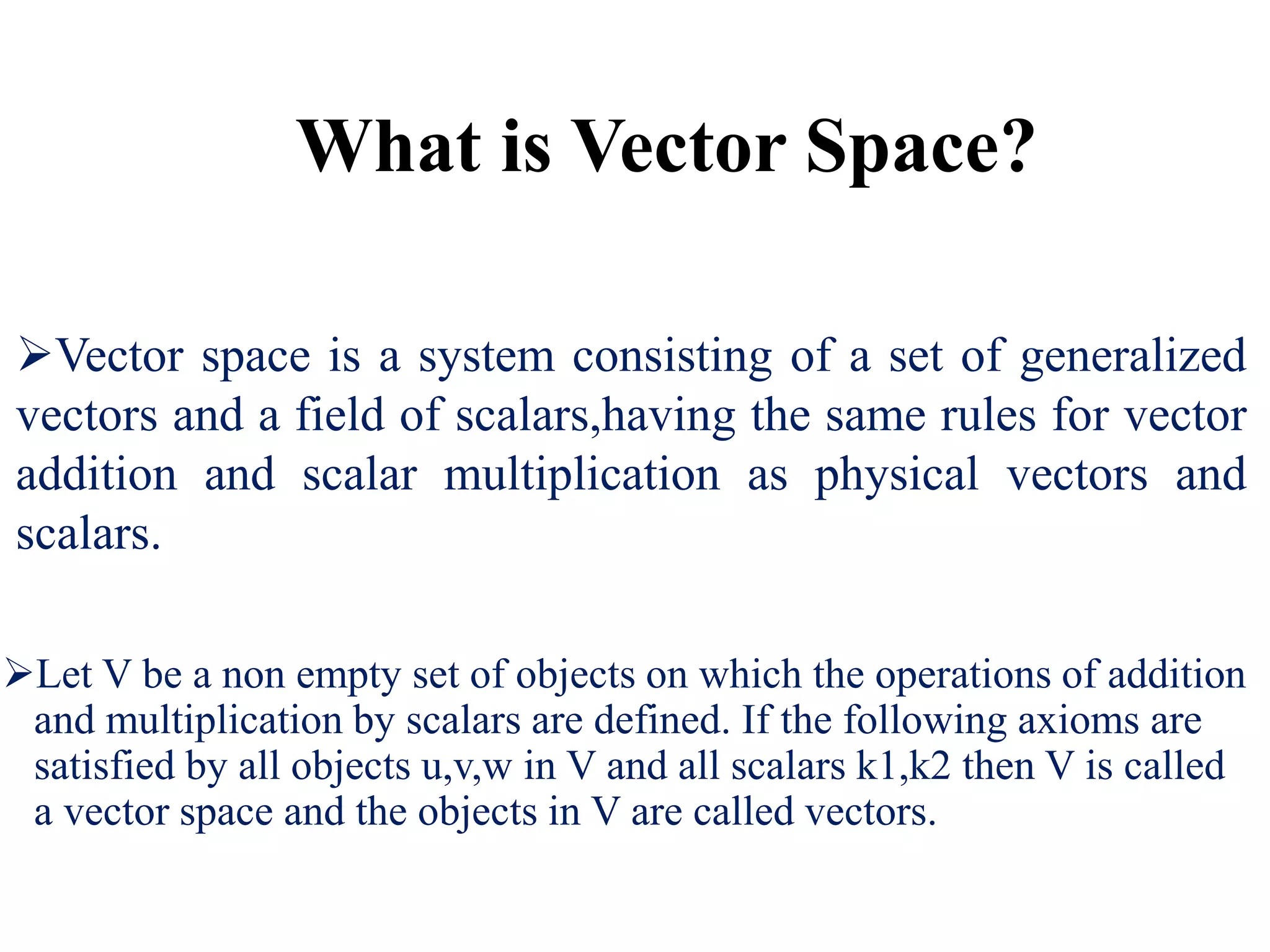
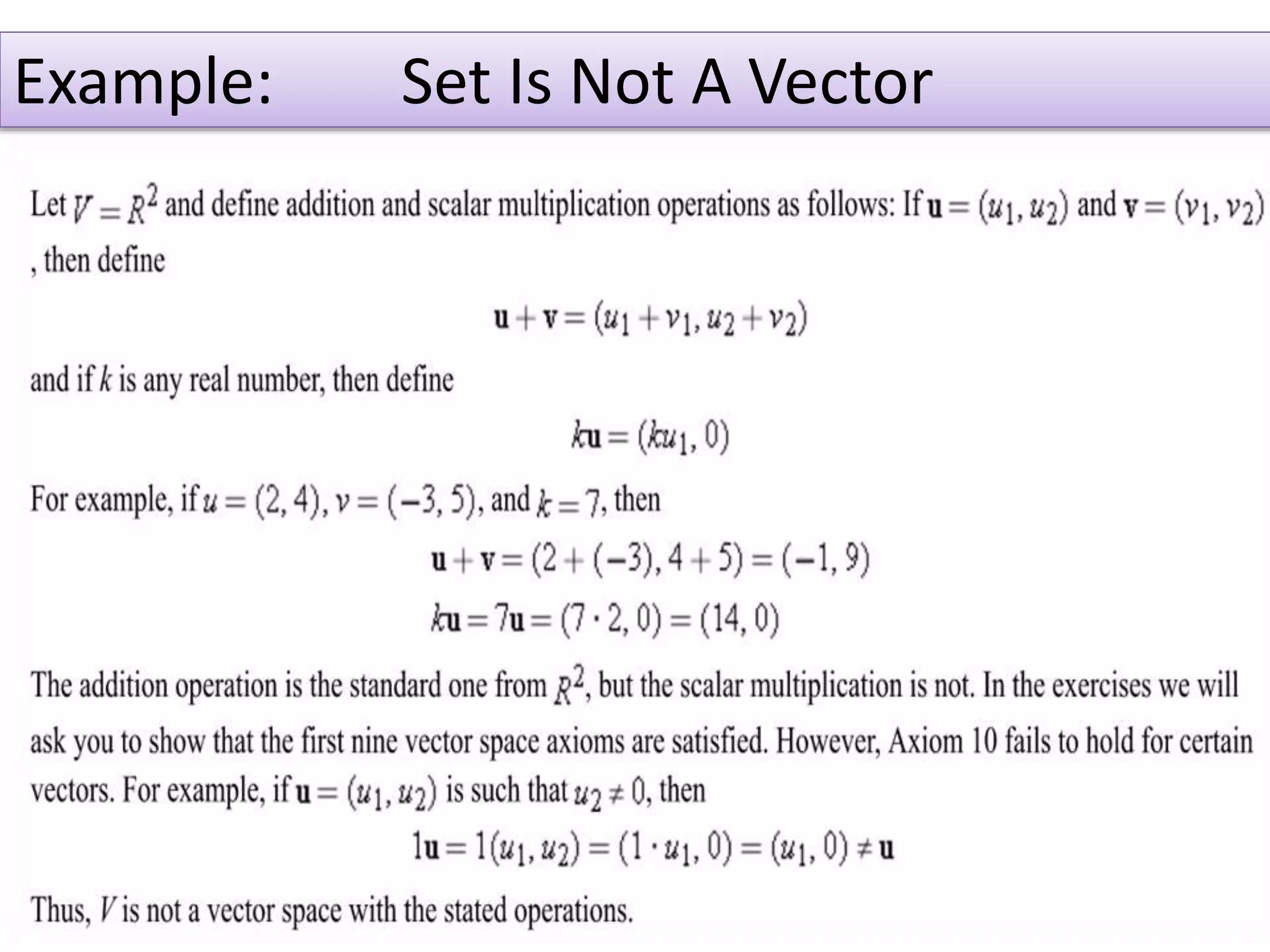
- A vector space is a set of objects called vectors that can be added together and multiplied by scalars, satisfying certain properties.
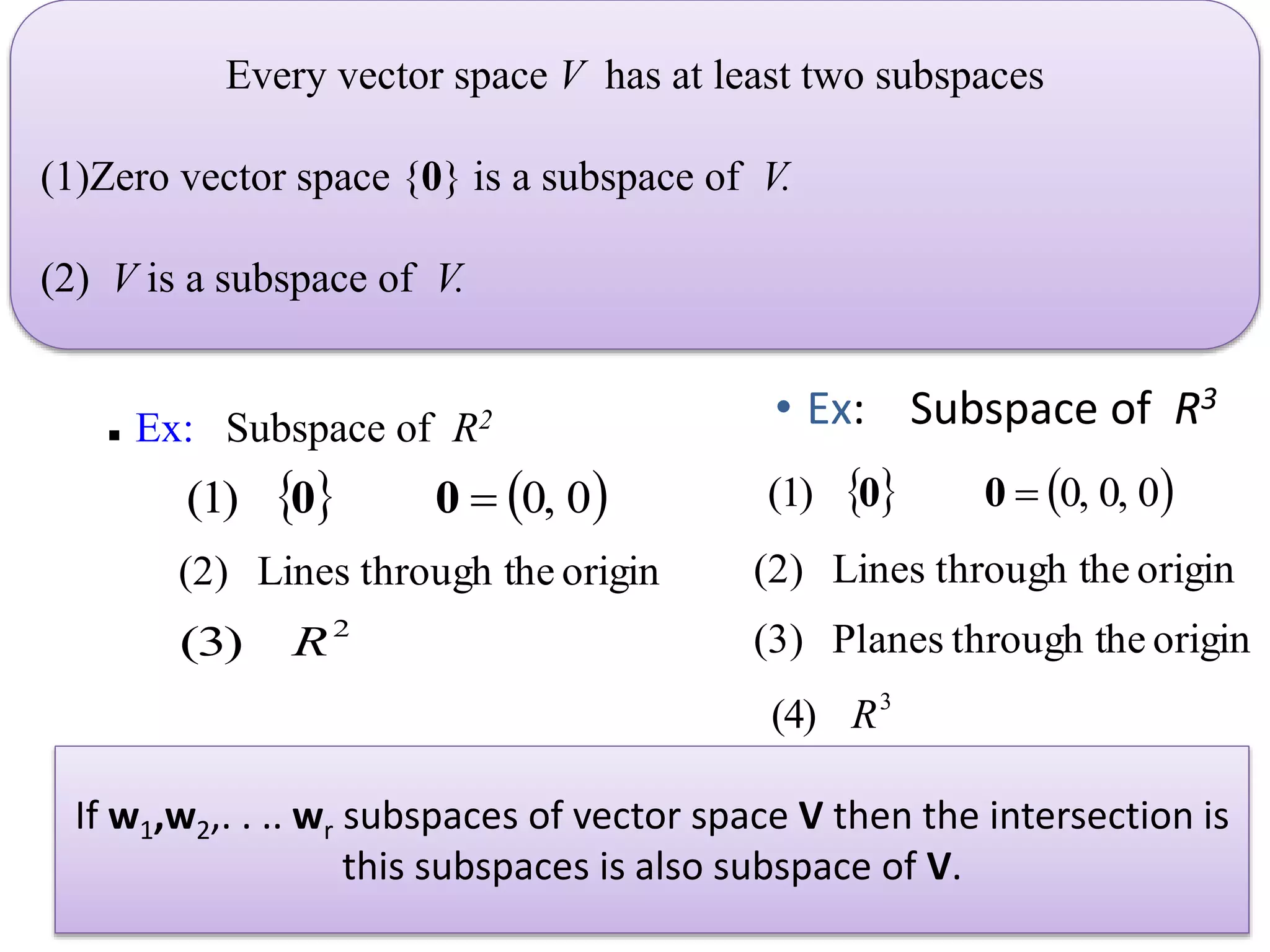
- A subspace is a subset of a vector space that is itself a vector space under the operations of the original space.
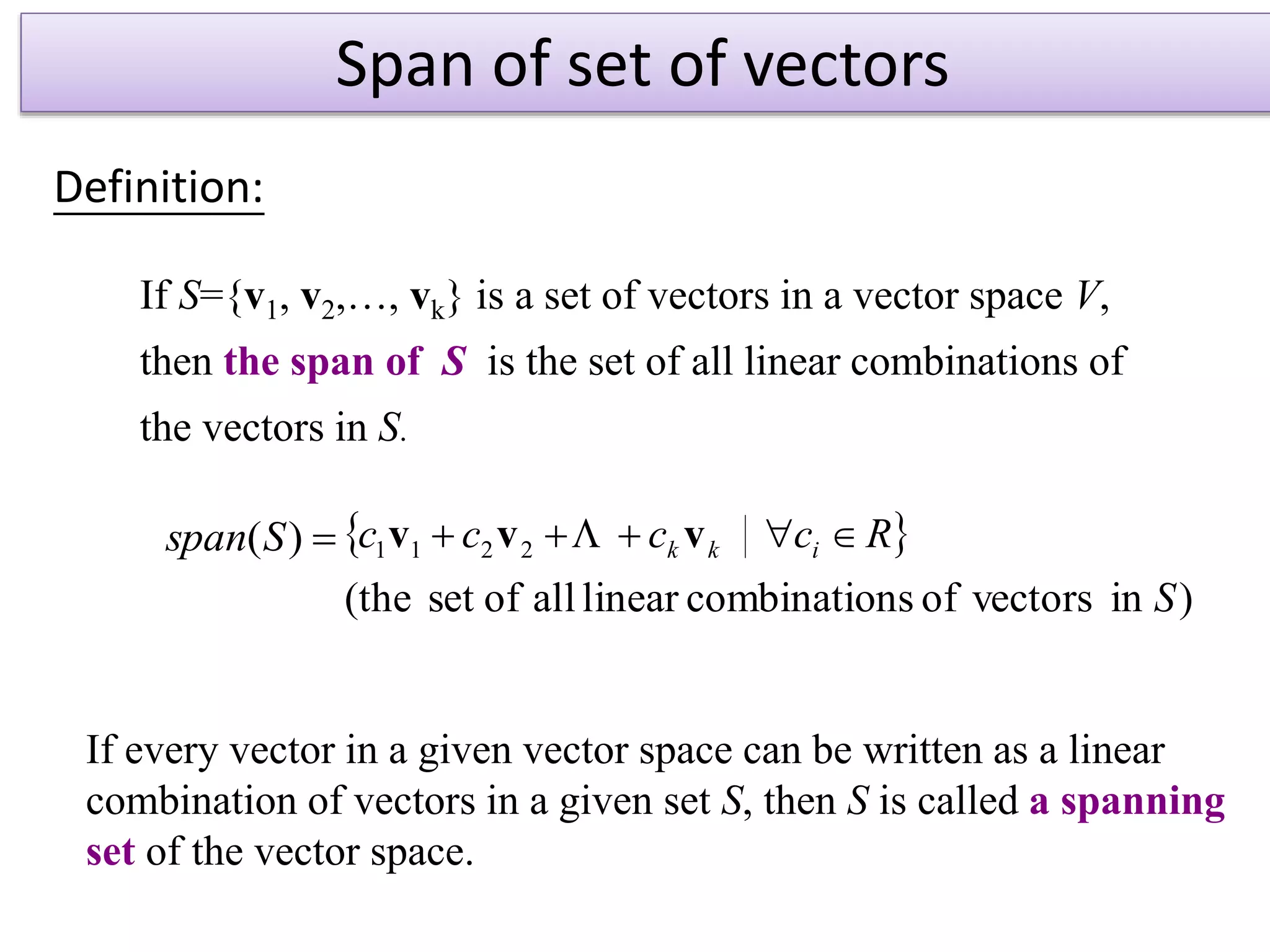
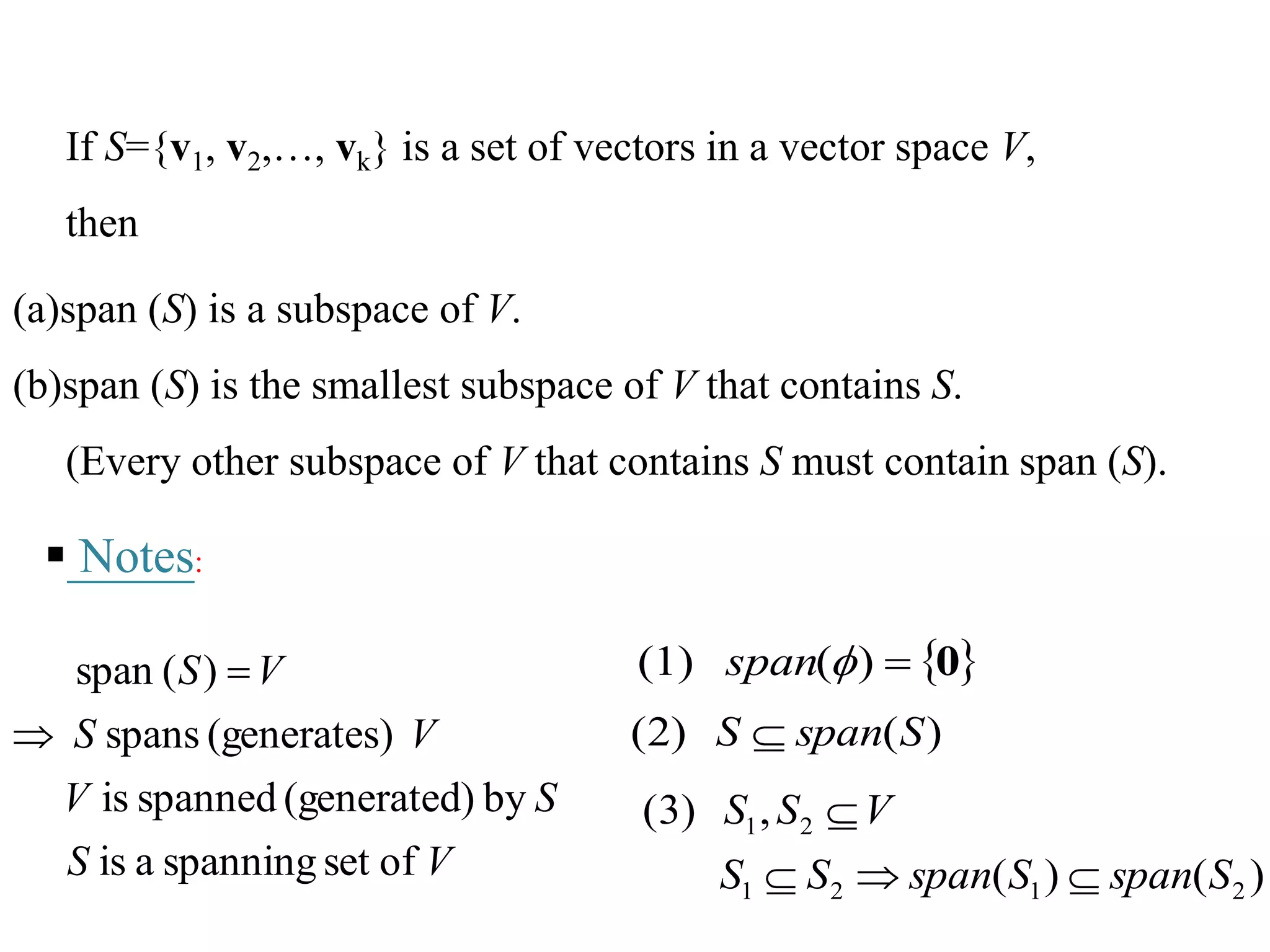
- The span of a set of vectors S is the set of all possible linear combinations of the vectors in S.
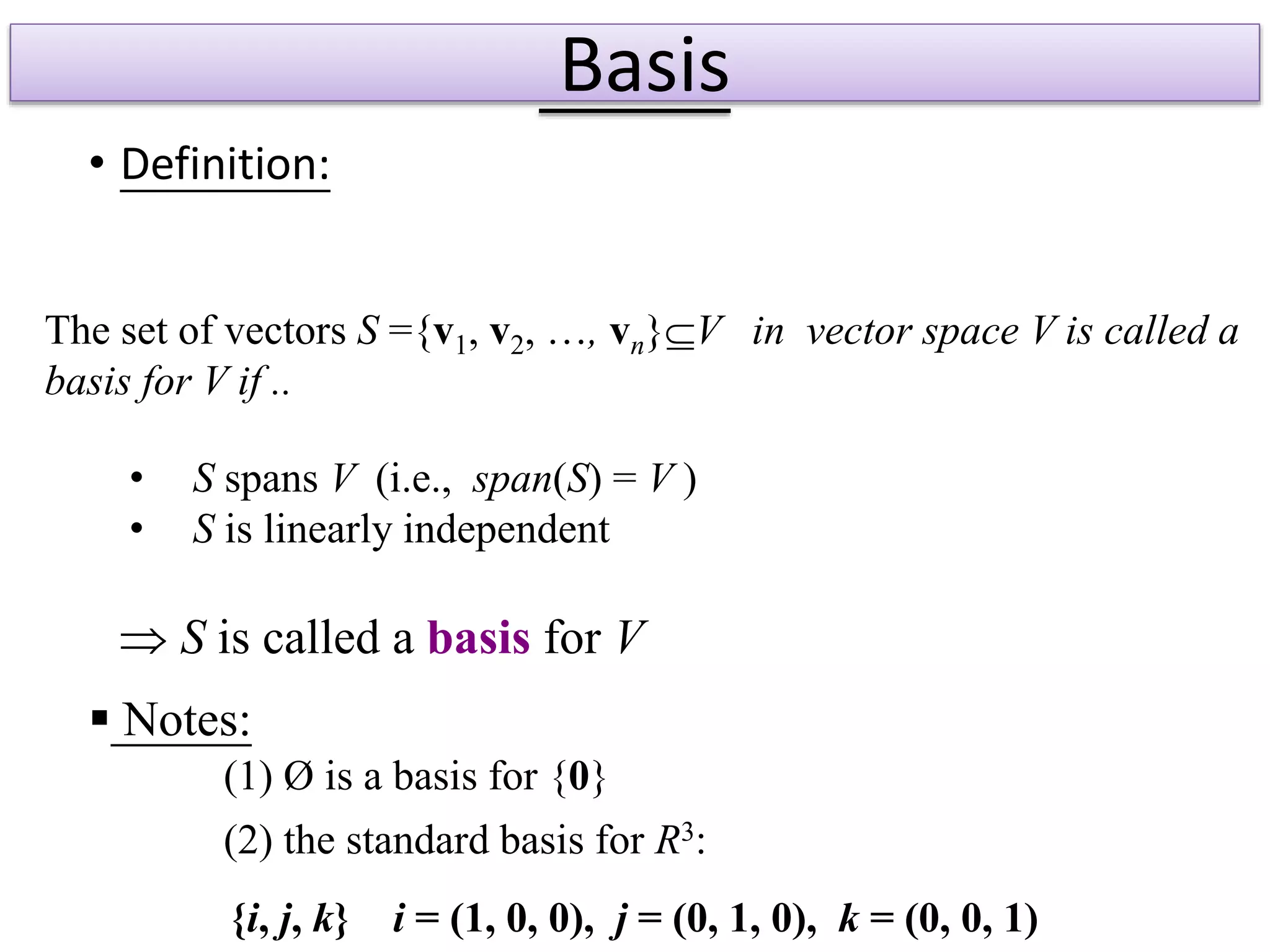
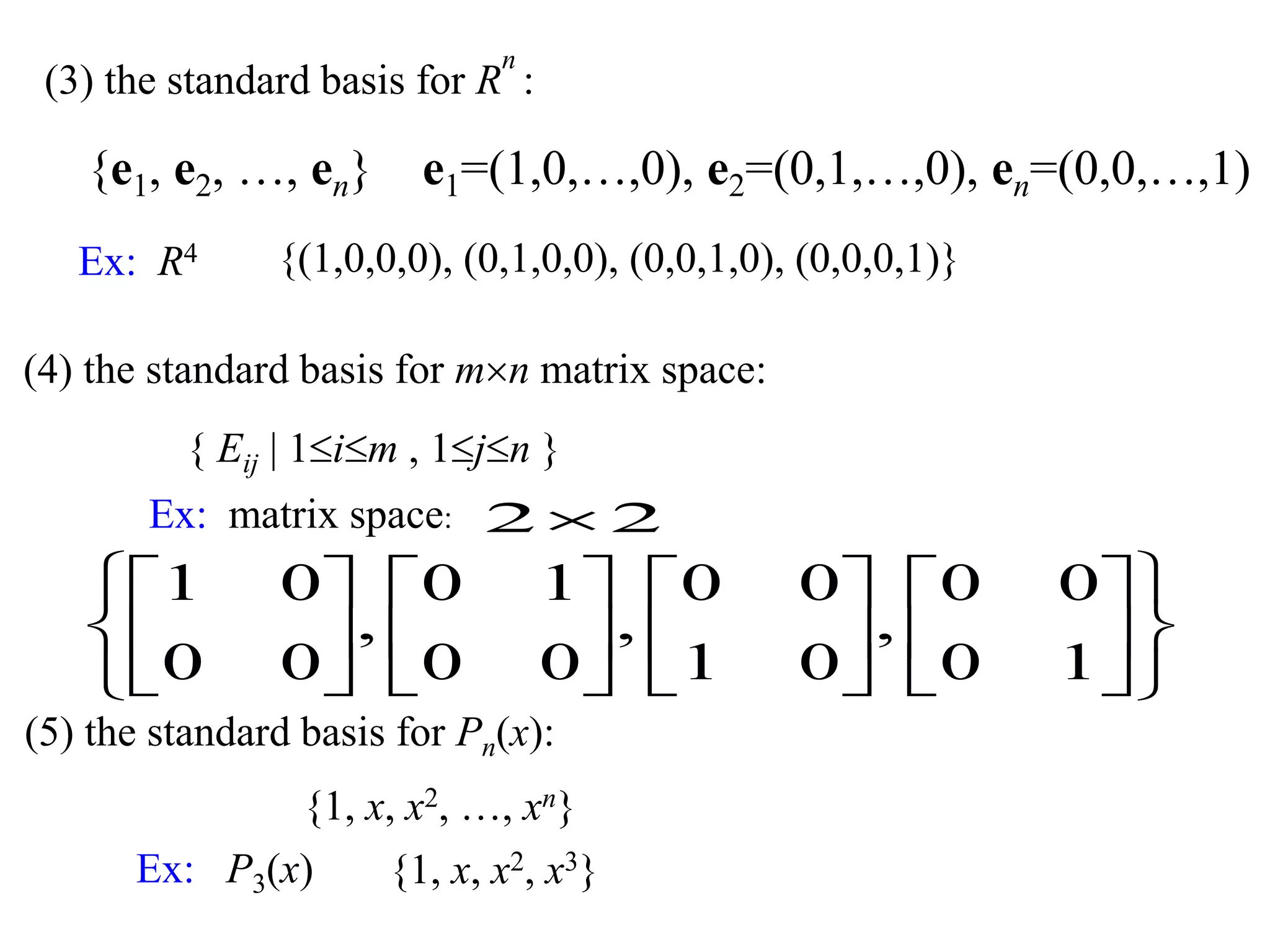
- A basis is a set of vectors that spans a vector space and is linearly independent. It provides a standard representation for vectors in the space.