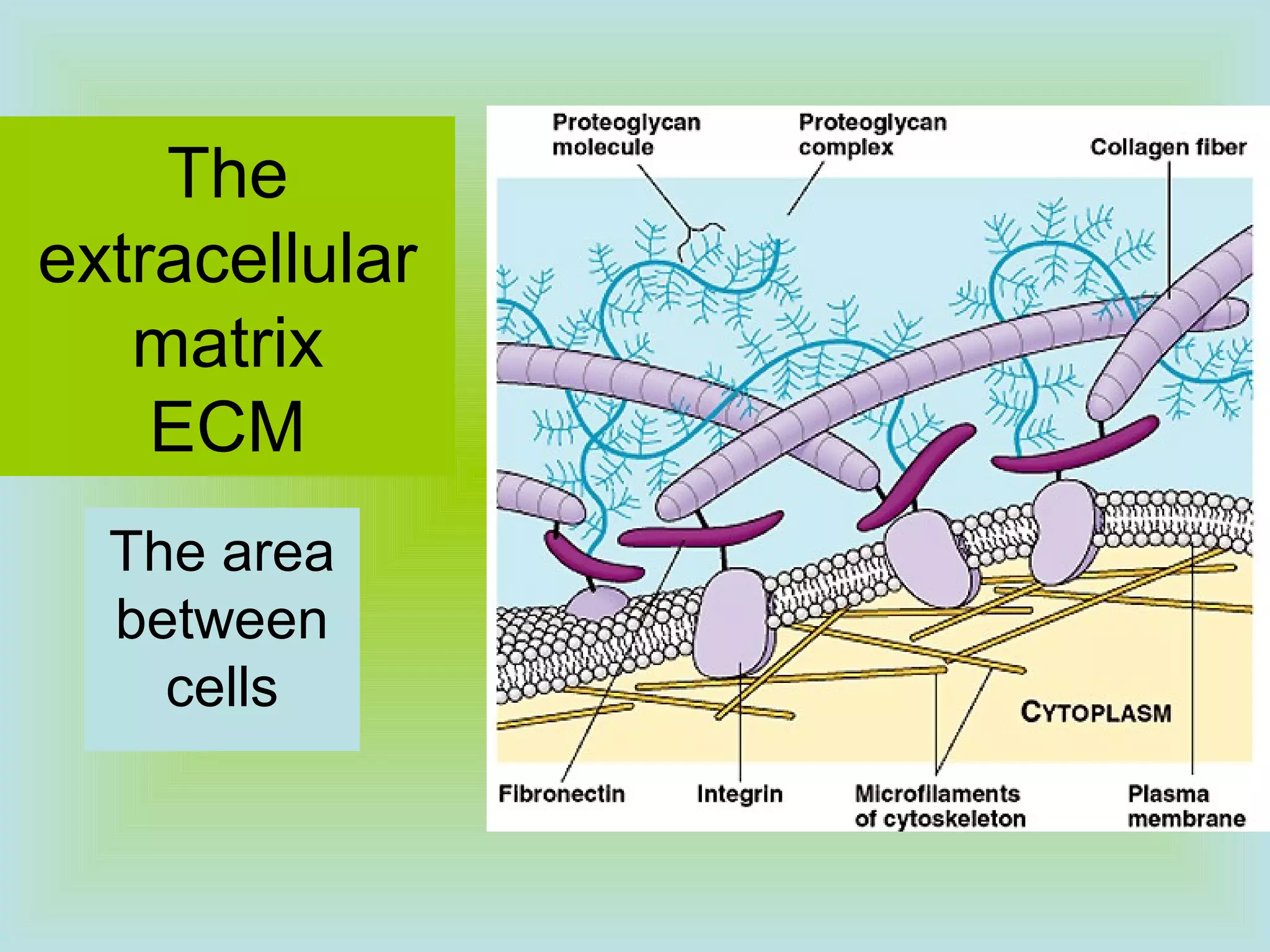
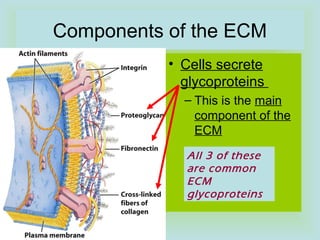
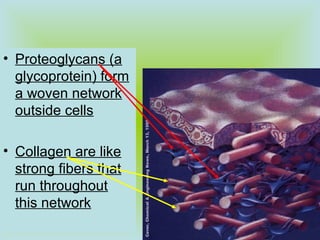
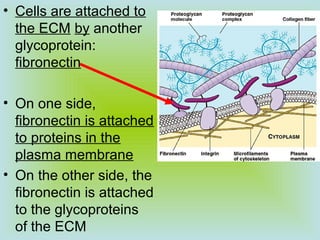
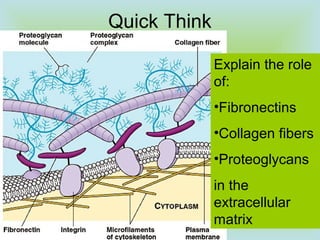
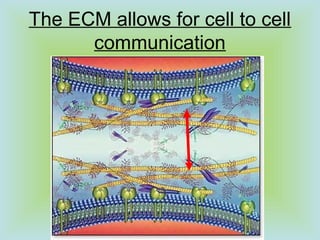
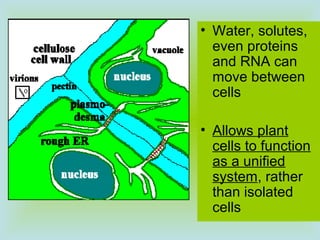
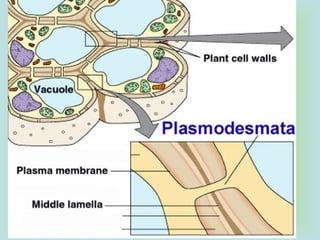
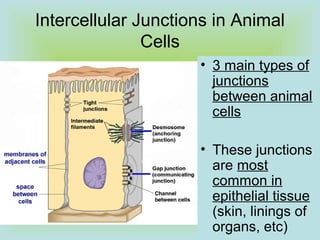
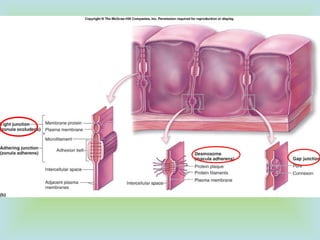
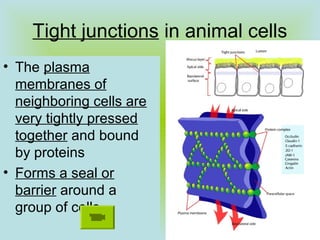
Tight junctions form a seal between plasma membranes of adjacent cells and create a barrier around groups of cells. Desmosomes anchor cells together strongly through keratin filaments. Gap junctions contain channels that allow cytosol and small molecules to pass between neighboring cells, enabling cell-to-cell communication important in tissues like the heart and embryos.