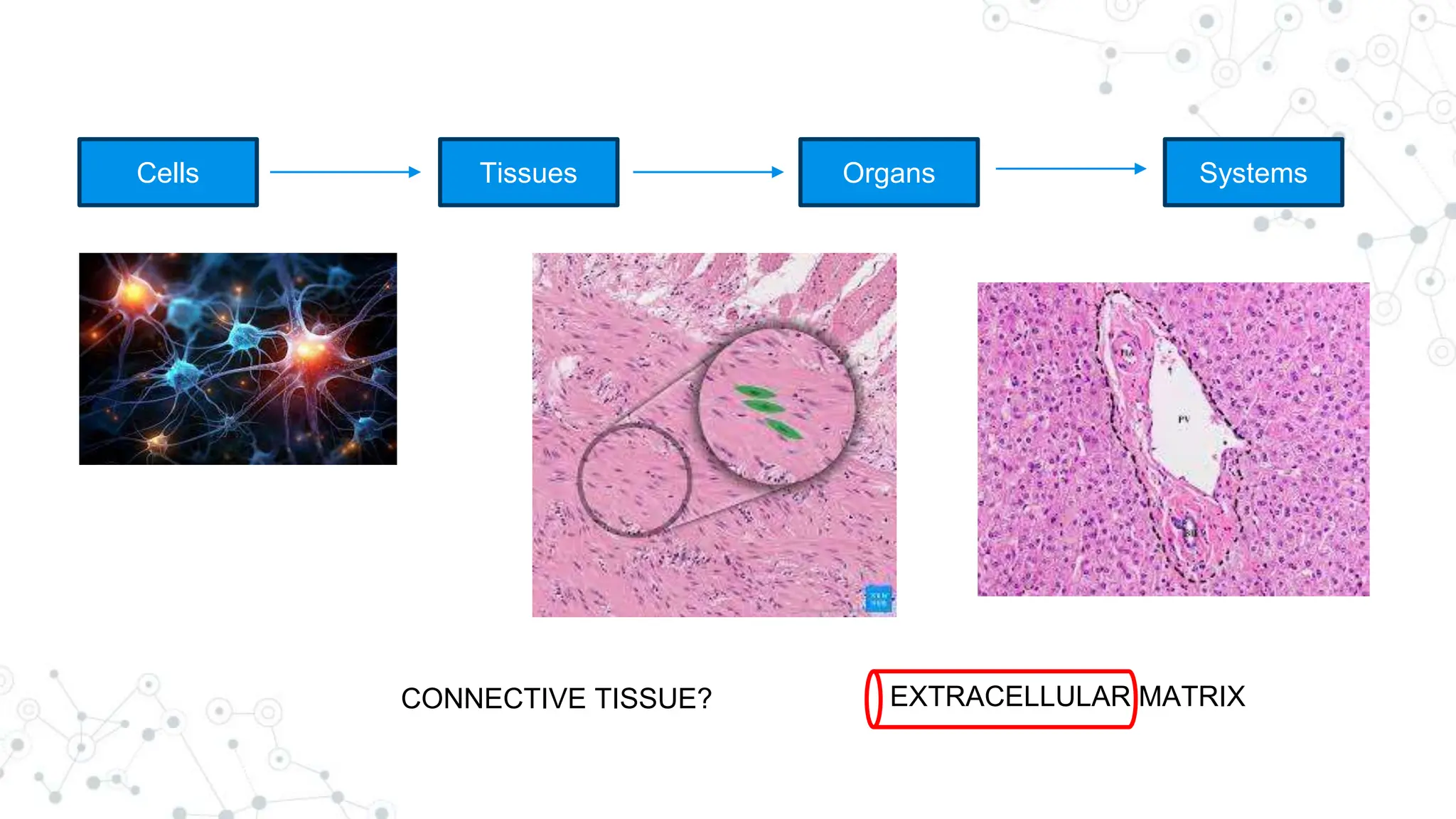
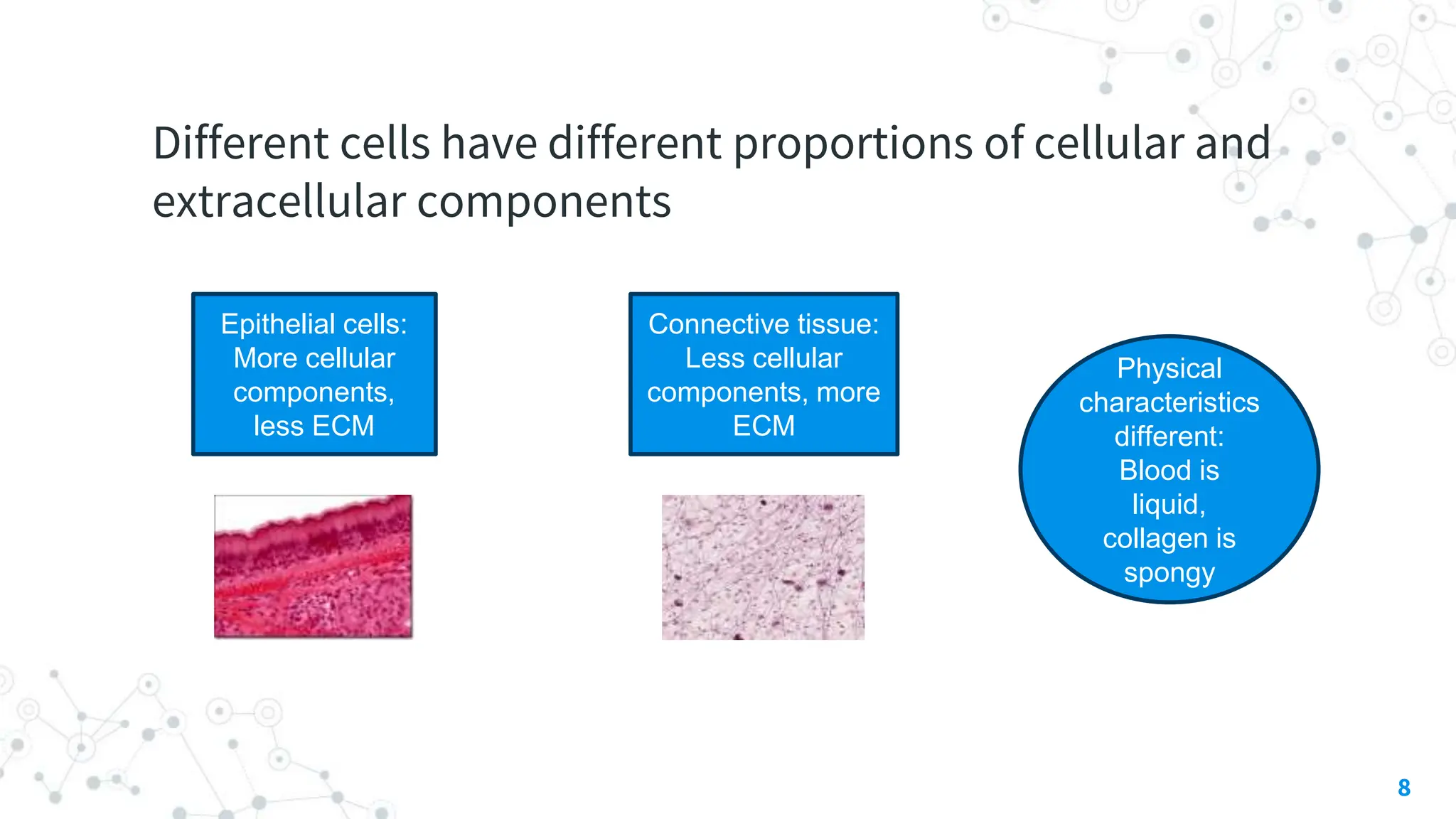
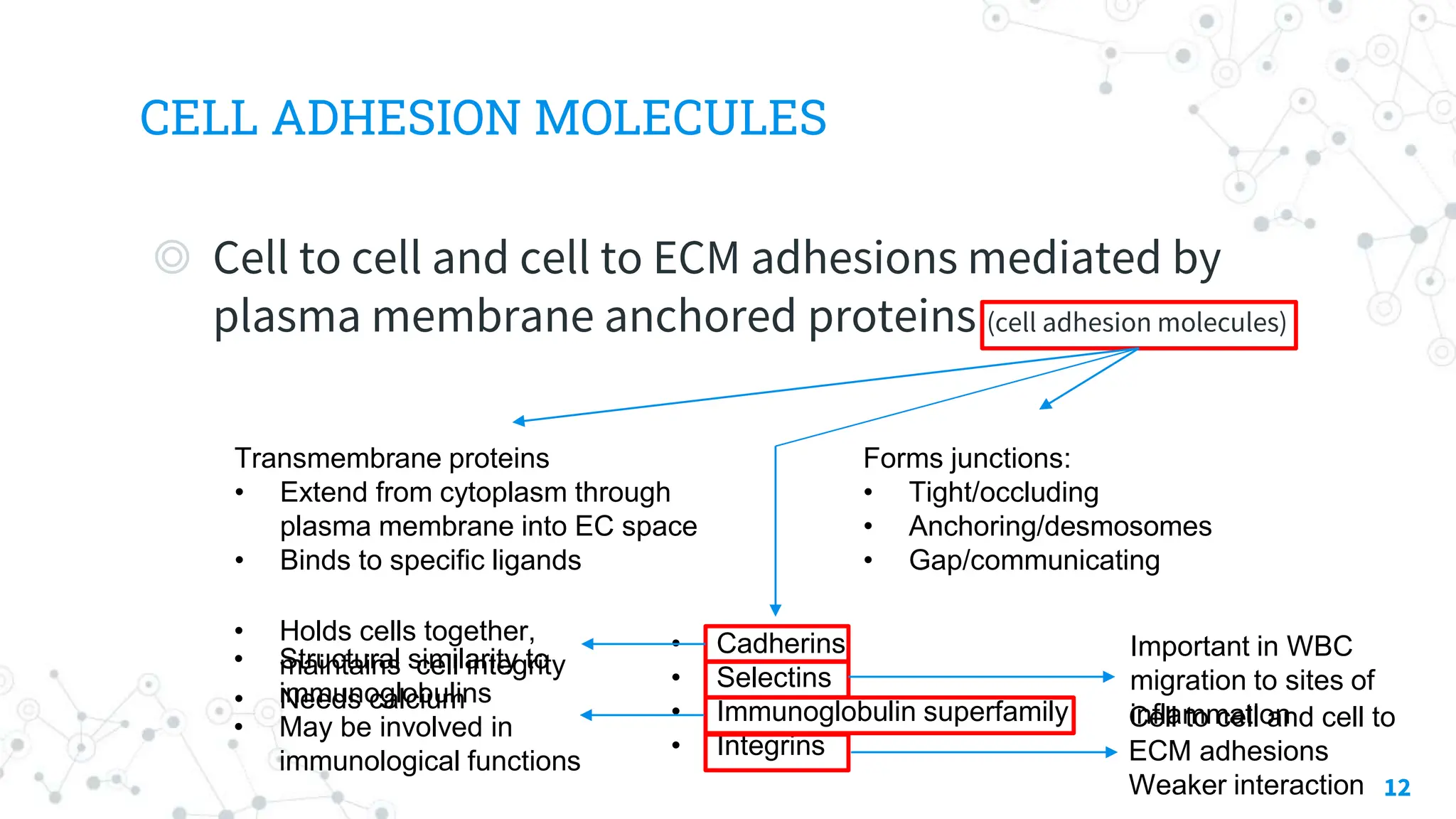
This document discusses the extracellular matrix (ECM), including its composition, functions, and role in health and disease. The ECM is made up of three main components - glycans, proteoglycans, and fibrous proteins. It provides structural support and helps with cell adhesion. Diseases associated with abnormalities in ECM components include scurvy resulting from vitamin C deficiency impairing collagen formation, osteogenesis imperfecta causing brittle bones from collagen gene mutations, and Marfan syndrome stemming from mutations in the gene coding for fibrillin in the ECM protein elastin. The ECM plays an important role in both health and a variety of diseases.