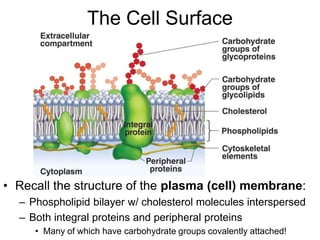
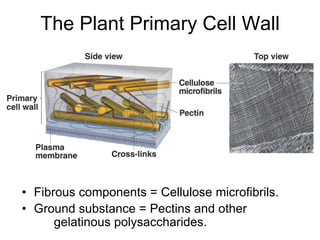
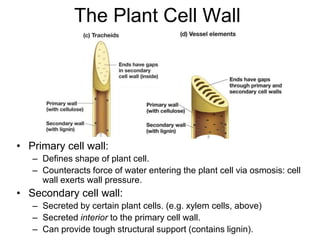
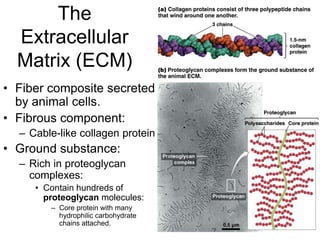
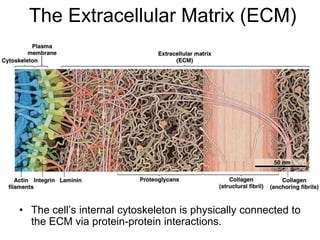
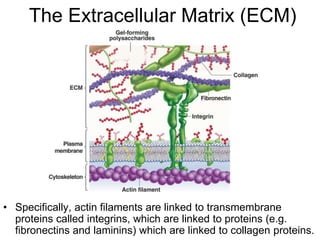
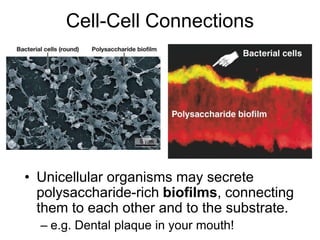
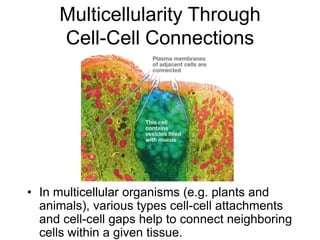
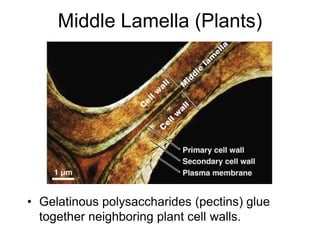
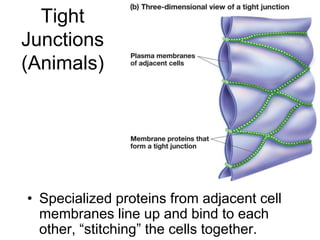
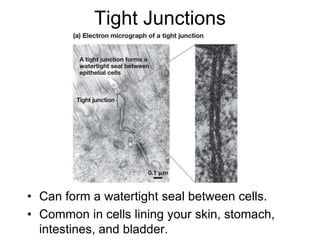
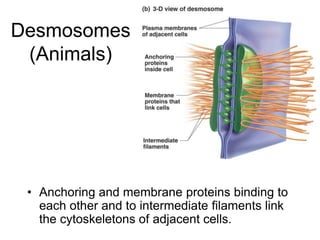
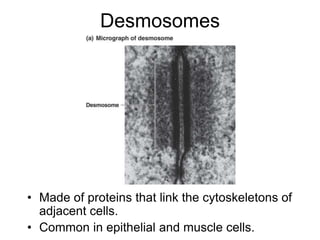
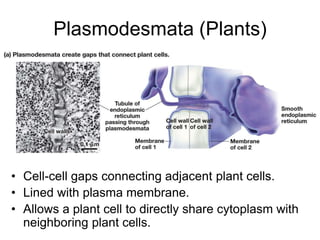
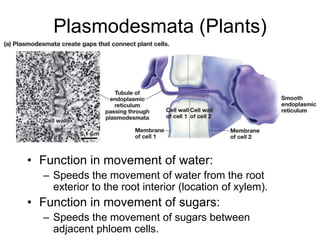
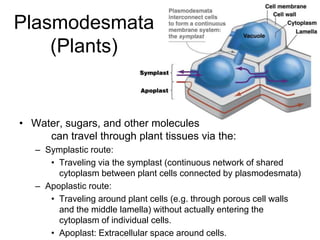
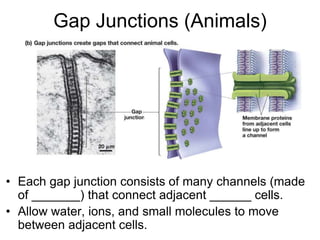
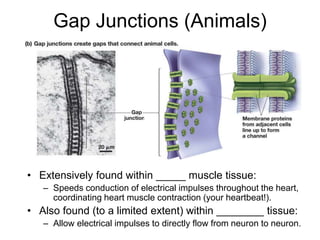
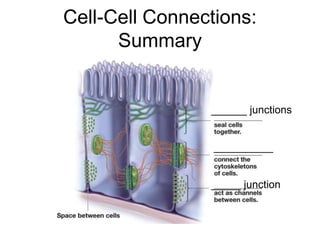
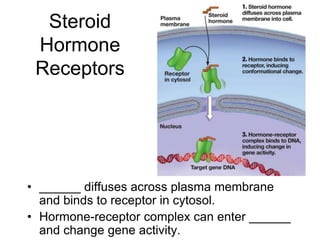
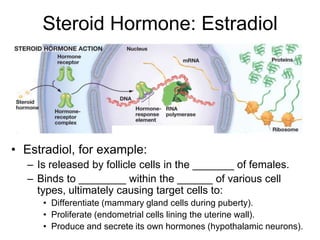
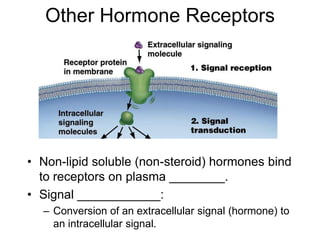
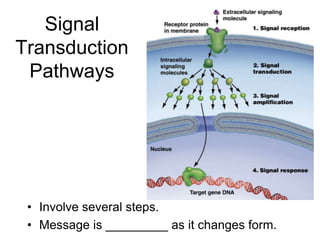
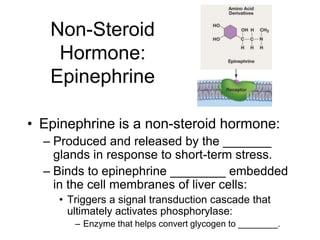
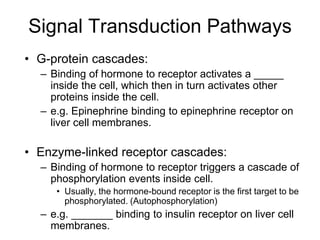
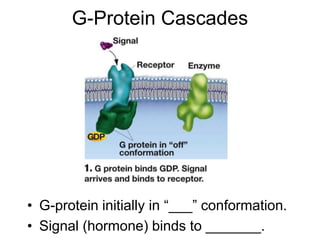
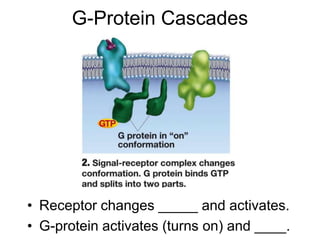
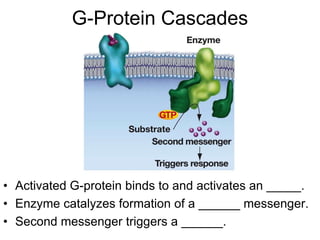
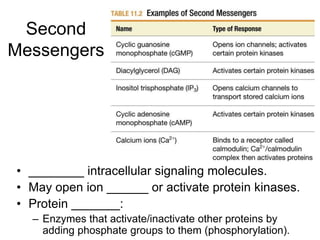
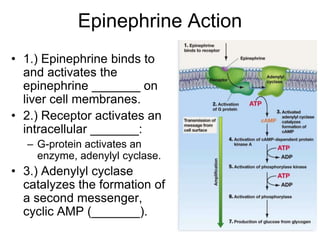
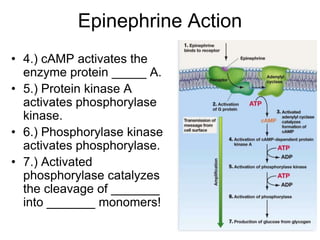
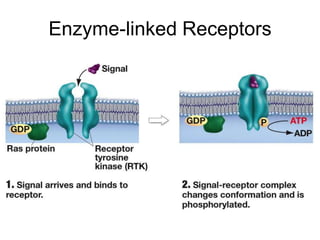
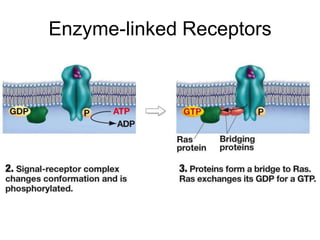
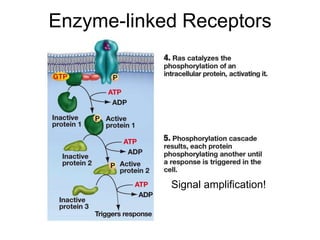
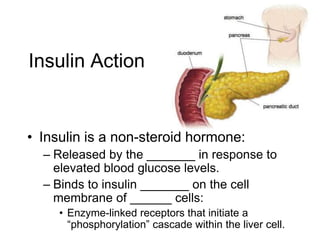
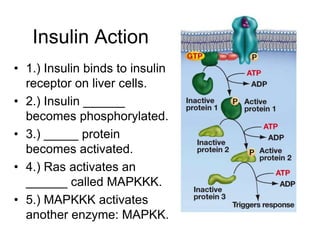
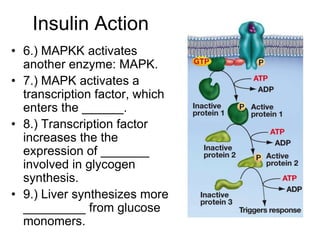
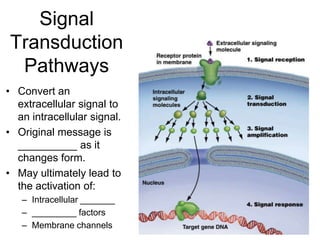
Cell-cell interactions involve the cell surface, extracellular matrix or cell wall, and connections between cells. Neighboring plant cells are joined by plasmodesmata, which allow sharing of cytoplasm, while animal cells use tight junctions and desmosomes. Gap junctions and plasmodesmata form direct connections, and hormones facilitate long-distance communication between distant cells.