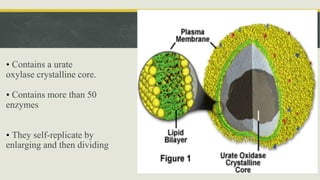
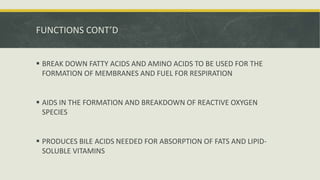
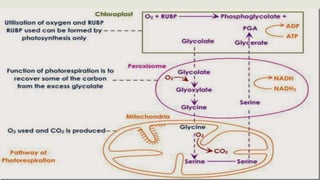
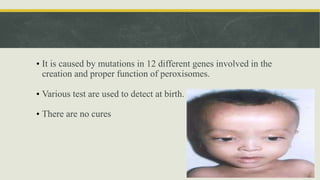
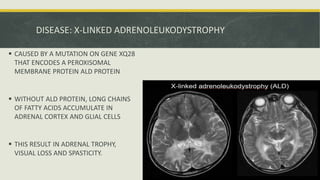
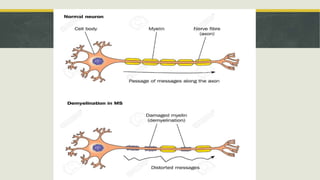
Peroxisomes are small organelles found in the cytoplasm of cells. They contain enzymes that break down fatty acids and reactive oxygen species. Specifically, peroxisomes contain catalase which breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. They also play roles in photosynthesis, beta-oxidation of fatty acids, and producing bile acids. Certain genetic diseases can result from defects in peroxisome function, such as Zellweger syndrome.