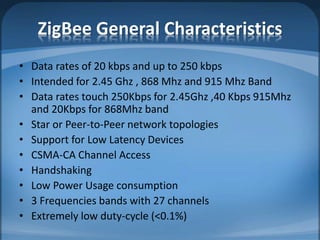
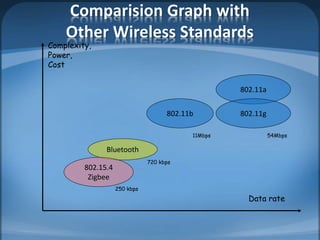
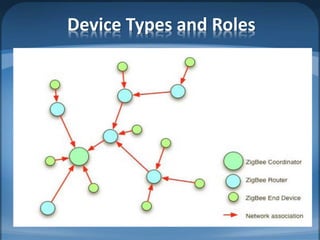
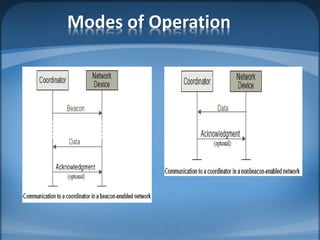
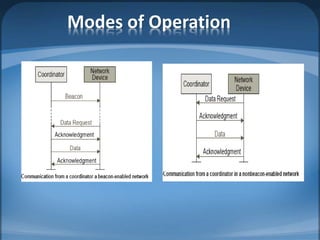
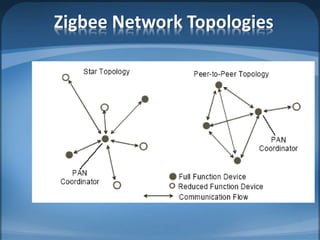
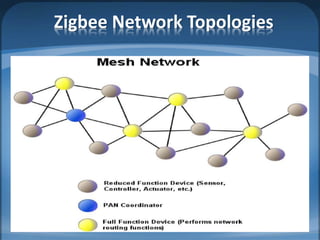
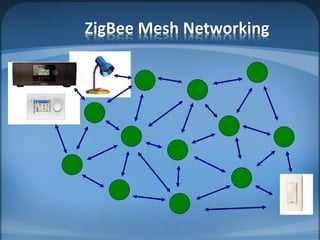
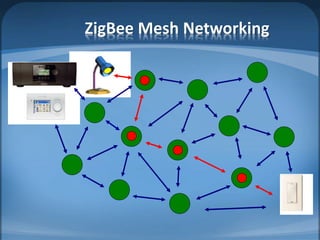
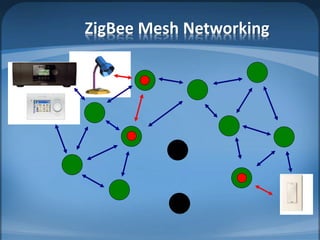
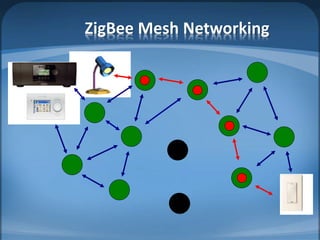
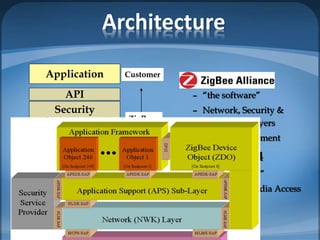
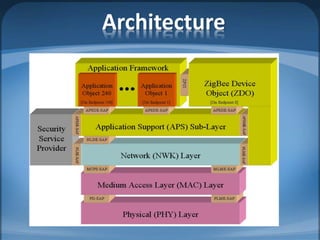
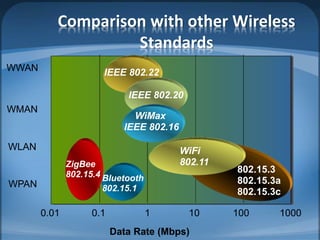
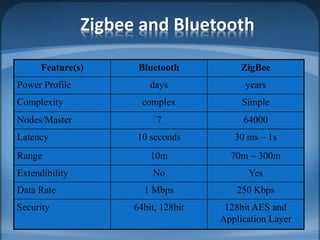
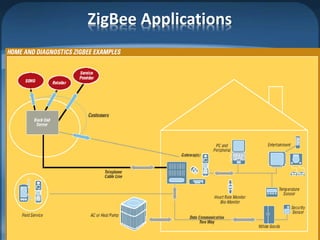
The document discusses ZigBee/IEEE 802.15.4, which is a wireless communication standard designed for low-power wireless networks. It was created to address the needs of wireless sensor networks that required low cost, low power consumption, and reliability. ZigBee networks operate within the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and have low data rates, low power consumption, and support star, tree, and mesh network topologies. ZigBee is targeted towards wireless control and sensor applications such as wireless lighting, thermostats, and other home and industrial automation devices.