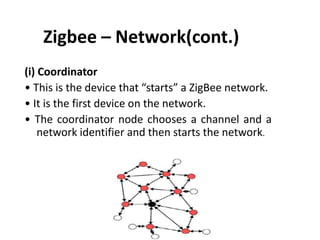
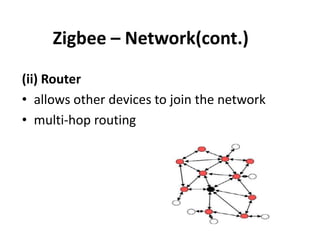
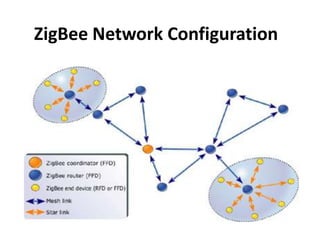
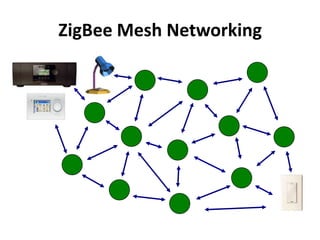
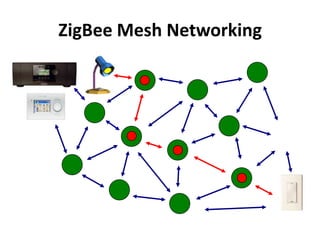
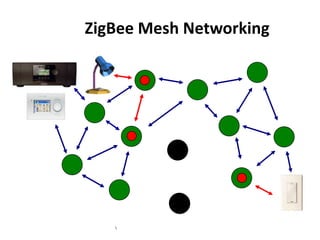
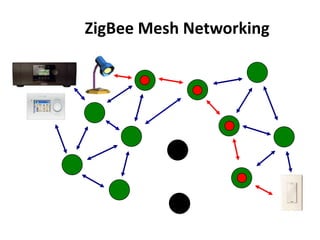
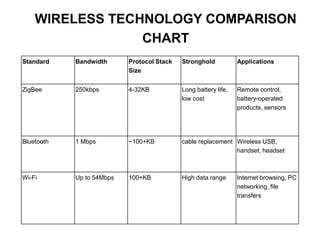
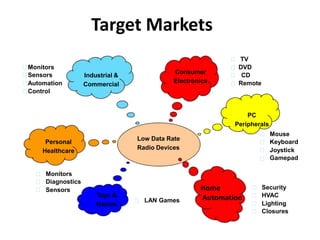
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard using mesh networking topologies to transmit data over long distances with low power consumption. Zigbee networks consist of coordinator, router, and end devices and are used in applications that require long battery life, security, low data rates and cost such as lighting, HVAC and sensors. Research continues to expand Zigbee's capabilities for use in more devices and markets going forward.