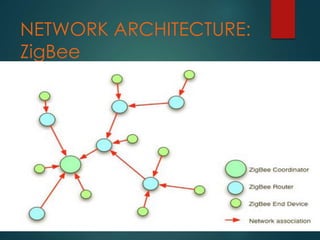
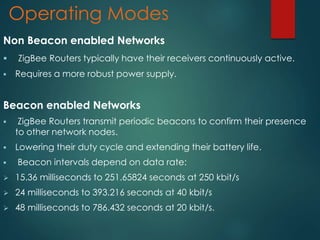
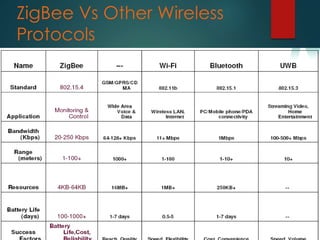
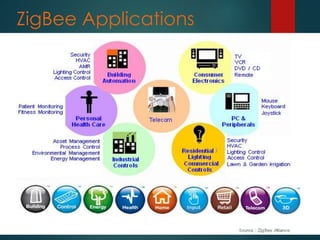
Zigbee is a specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks from small, low-power digital radios. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and provides data rates of 250 kbps, 40 kbps, and 20 kbps in different frequency bands. Zigbee devices can transmit data over long distances by passing through a mesh network and has a range of 10-100 meters. The technology targets applications requiring low data transfer rates and long battery life and is often used in industrial automation and home automation through devices like door locks and security sensors.