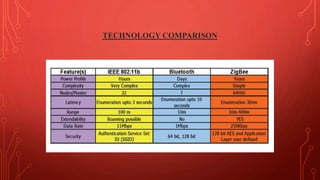
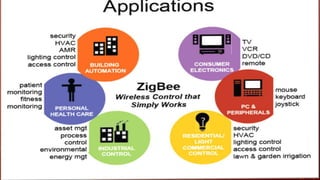
ZigBee is a wireless networking technology built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard designed for low-power wireless networks. It was created to satisfy the need for an inexpensive, low-power, reliable, and secure wireless standard for monitoring and control applications. The ZigBee Alliance develops the ZigBee standard and its applications. ZigBee operates on three frequency bands and uses CSMA-CA to reduce interference. There are three device types - coordinator, router, and end device. ZigBee supports star, mesh, and peer-to-peer topologies and is well-suited for wireless sensor networks due to its low power consumption.