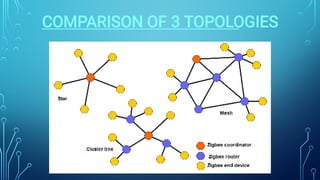
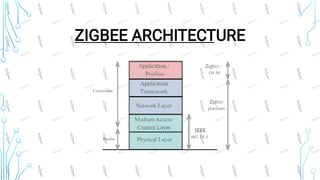
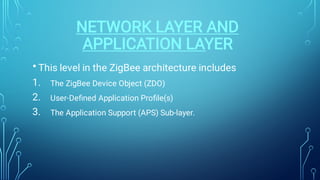
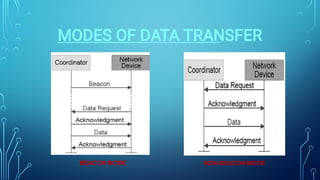
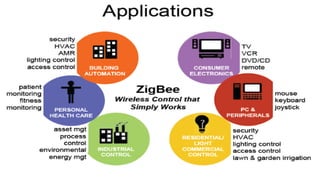
Zigbee is a wireless networking technology built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It was created to satisfy the need for a low-cost, low-power wireless solution for monitoring and control applications. Zigbee devices can operate for years on inexpensive batteries and support a variety of network topologies. While it has a lower data rate than Bluetooth, Zigbee consumes less power and is better suited for remote control and sensor applications requiring long battery life.