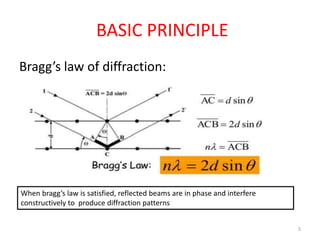
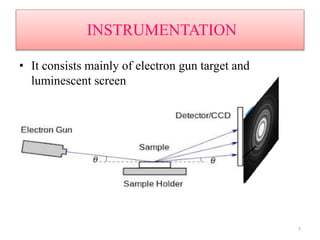
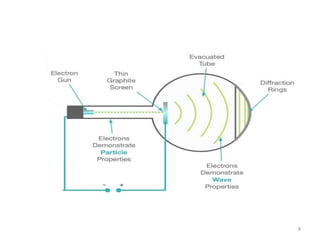
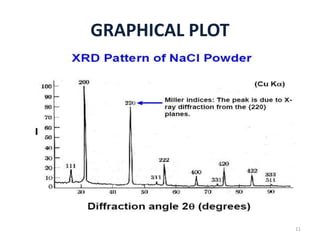
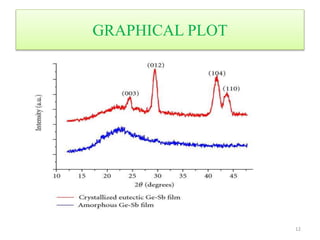
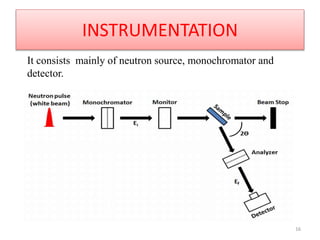
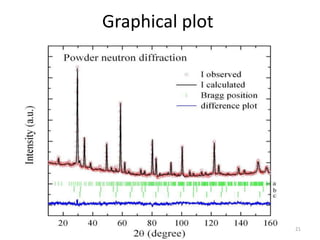
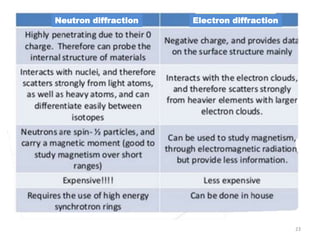
This document discusses electron diffraction and neutron diffraction techniques. Electron diffraction works by firing electrons at a crystal sample and observing the interference pattern of diffracted electrons. This allows determining atomic structure. Neutron diffraction also determines atomic structure by firing neutrons at samples and observing diffraction patterns. Key advantages of neutron diffraction are its ability to locate light atoms and detect isotopes via nuclear scattering, and reveal magnetic structure via magnetic scattering. Both techniques provide structural information at the atomic scale but neutron diffraction can analyze bulk properties and magnetic structures.