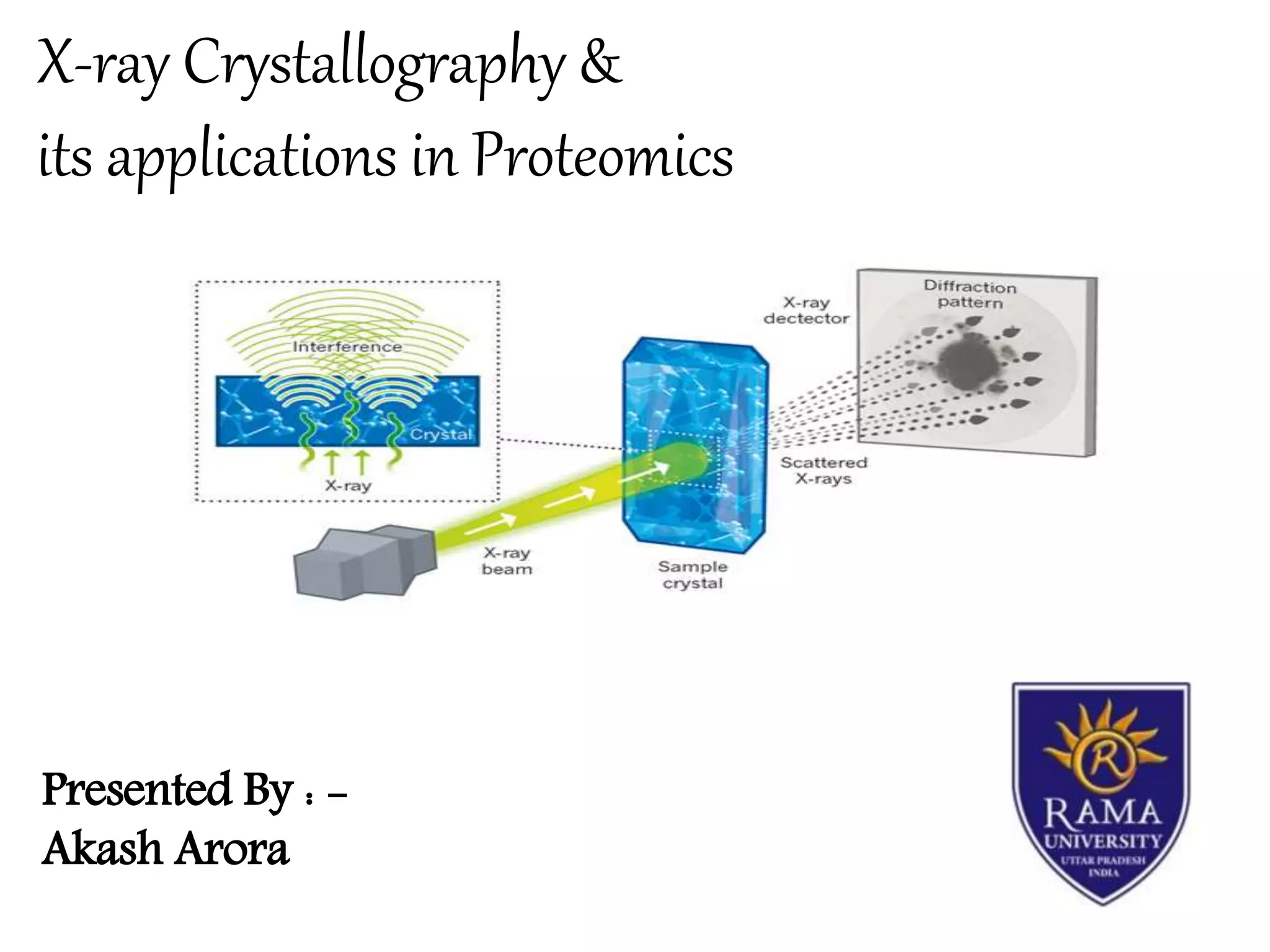
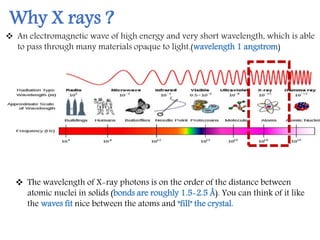
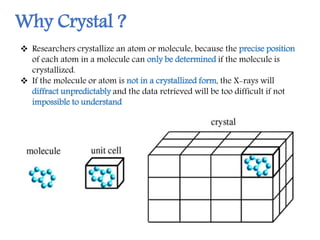
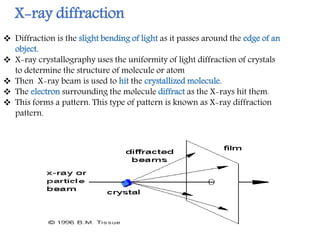
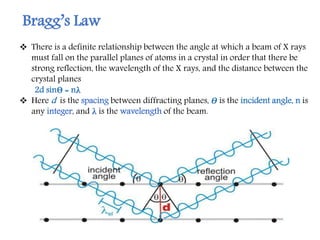
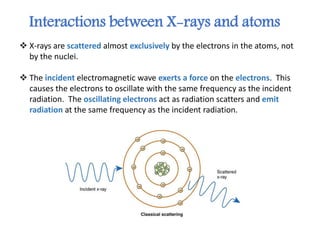
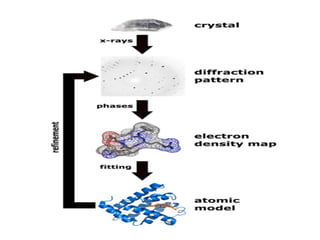
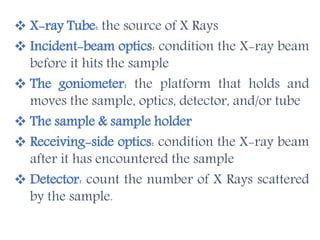
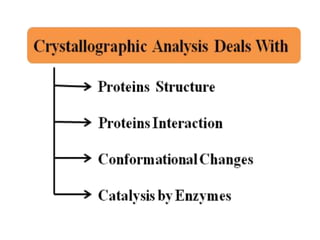
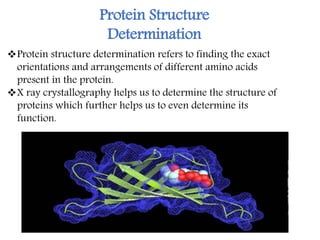
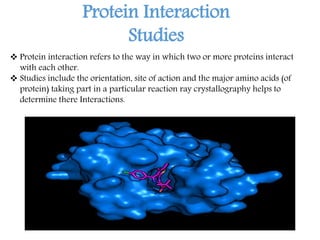
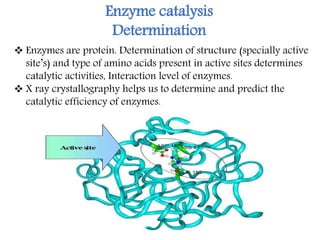
X-ray crystallography is a technique that uses X-rays to determine the atomic structure of crystals. It involves crystallizing molecules and bombarding them with X-rays, which produce a diffraction pattern. This pattern is used to deduce the molecular structure. X-ray crystallography has many applications in proteomics, including determining protein structures, studying protein interactions, and elucidating enzyme catalysis mechanisms. It provides atomic-level insights that advance understanding of protein function.