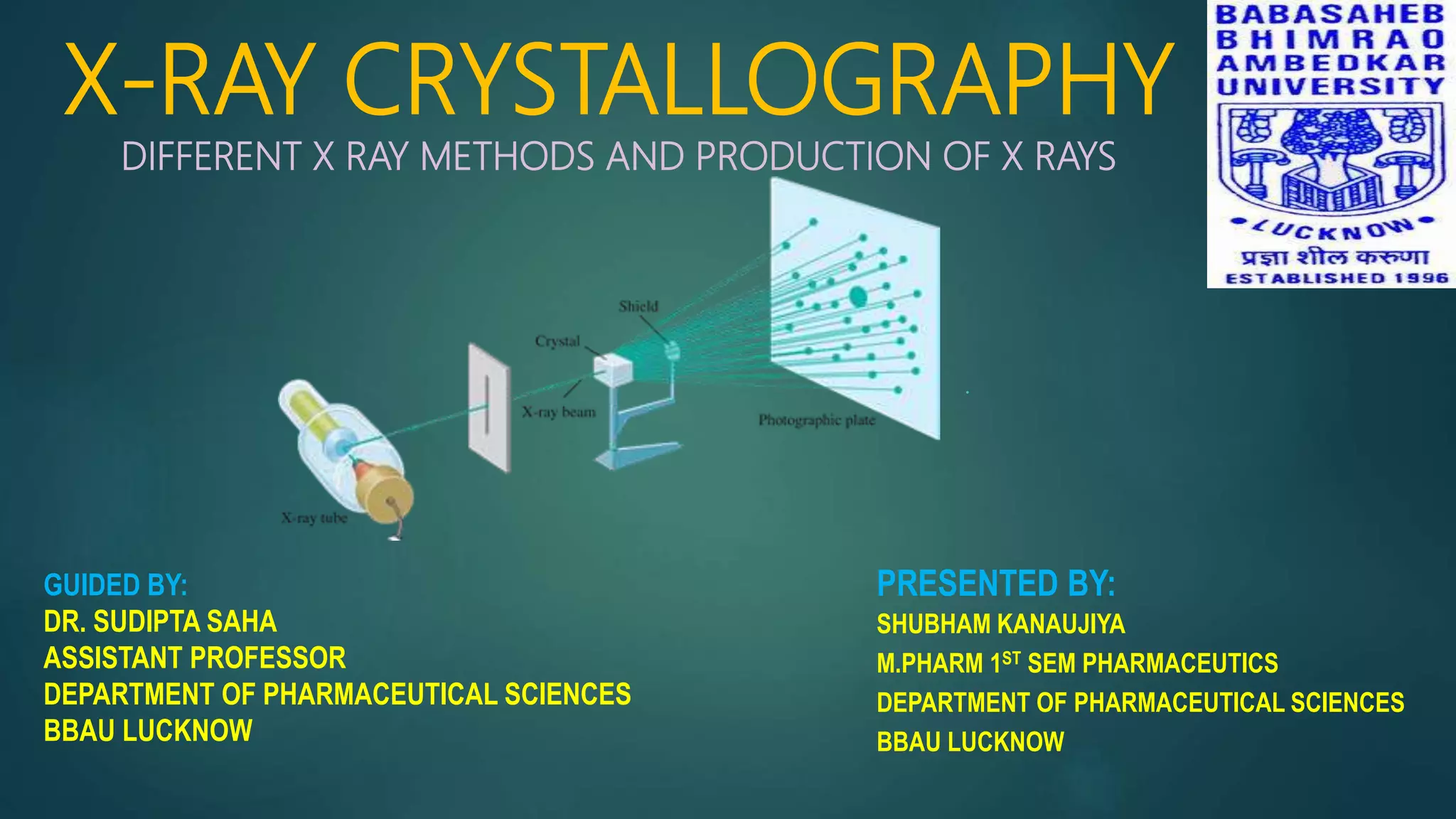
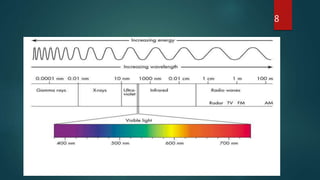
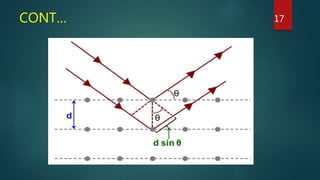
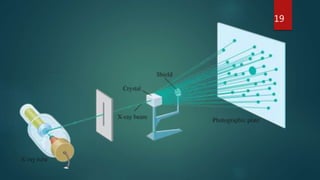
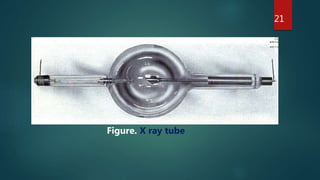
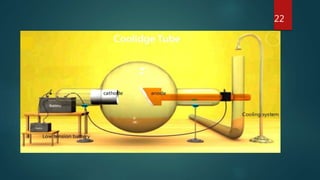
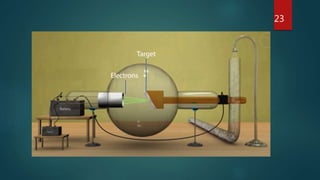
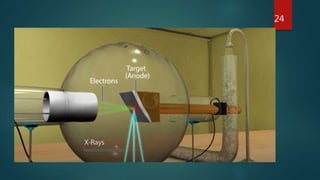
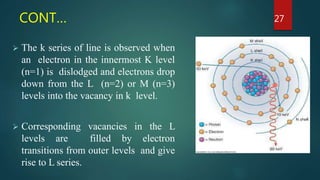
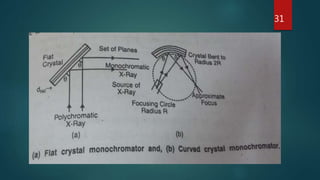
X-ray crystallography is a technique that uses X-ray diffraction from a crystalline sample to determine its atomic structure. Crystals cause an incident X-ray beam to diffract into specific directions, and by measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, the electron density and positions of atoms in the crystal can be deduced. Key aspects of X-ray crystallography covered include the production of X-rays, the use of crystals to fix molecular conformations, different X-ray methods like diffraction, and applications like determining the structures of proteins and DNA.