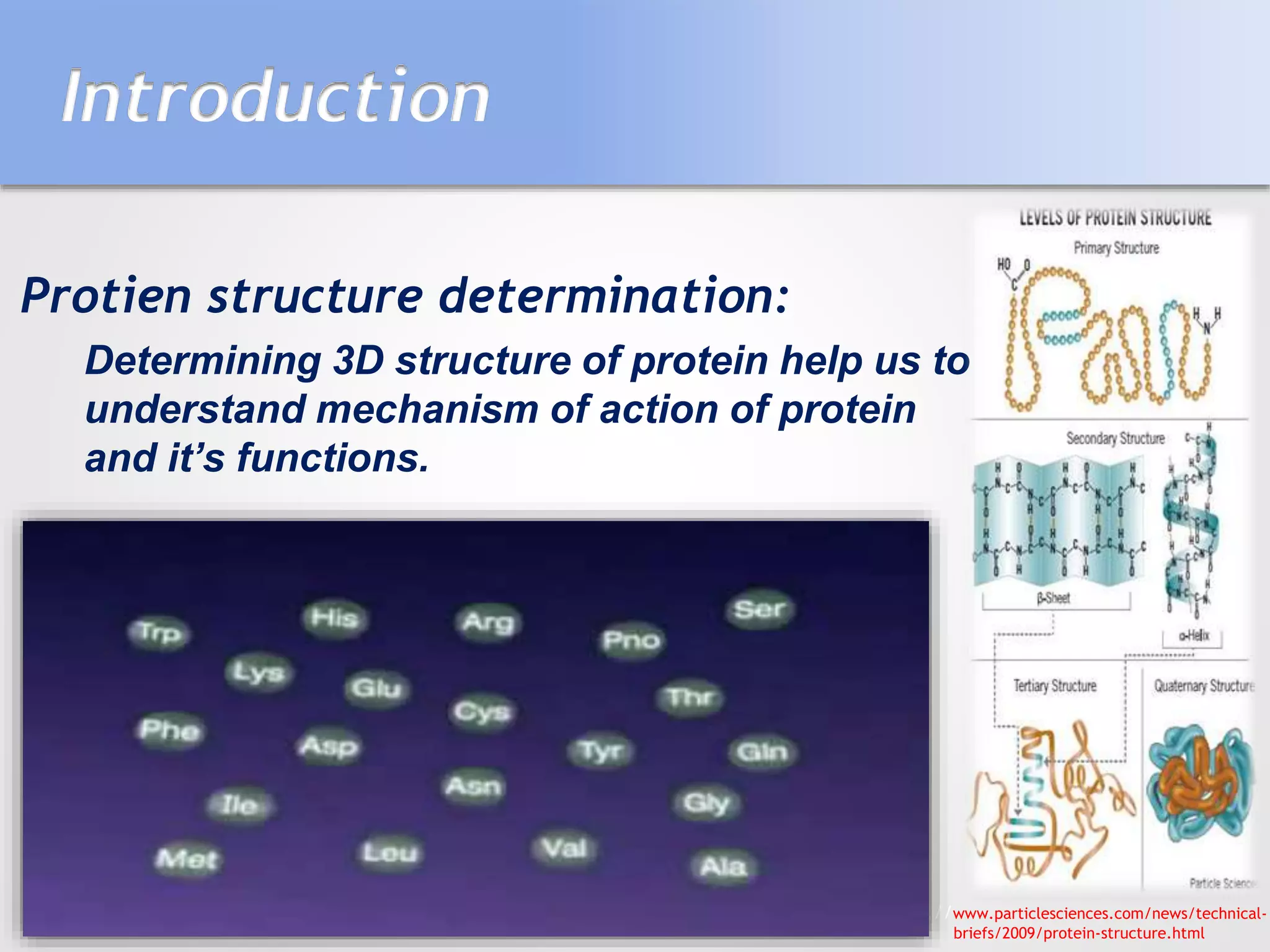
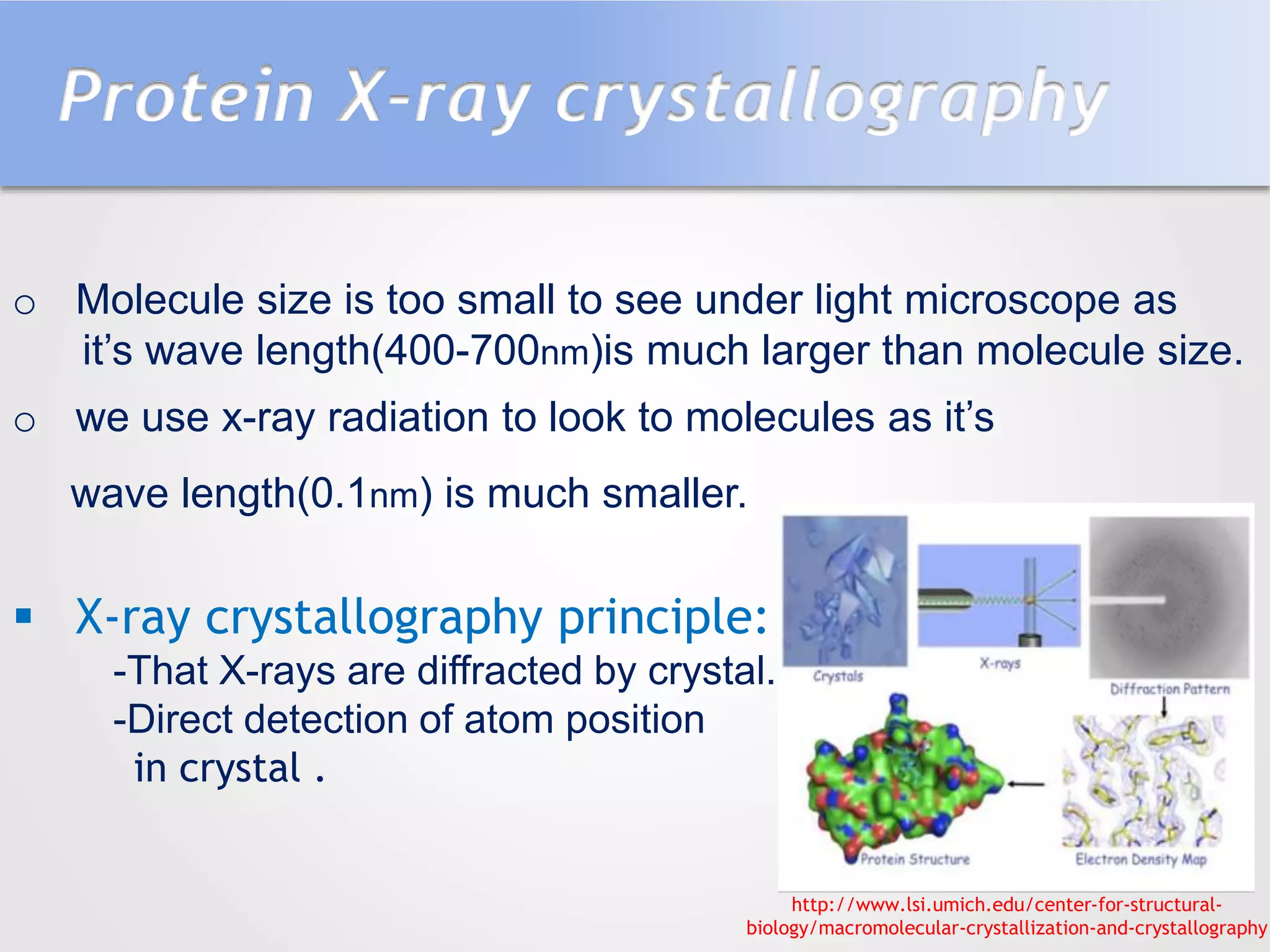
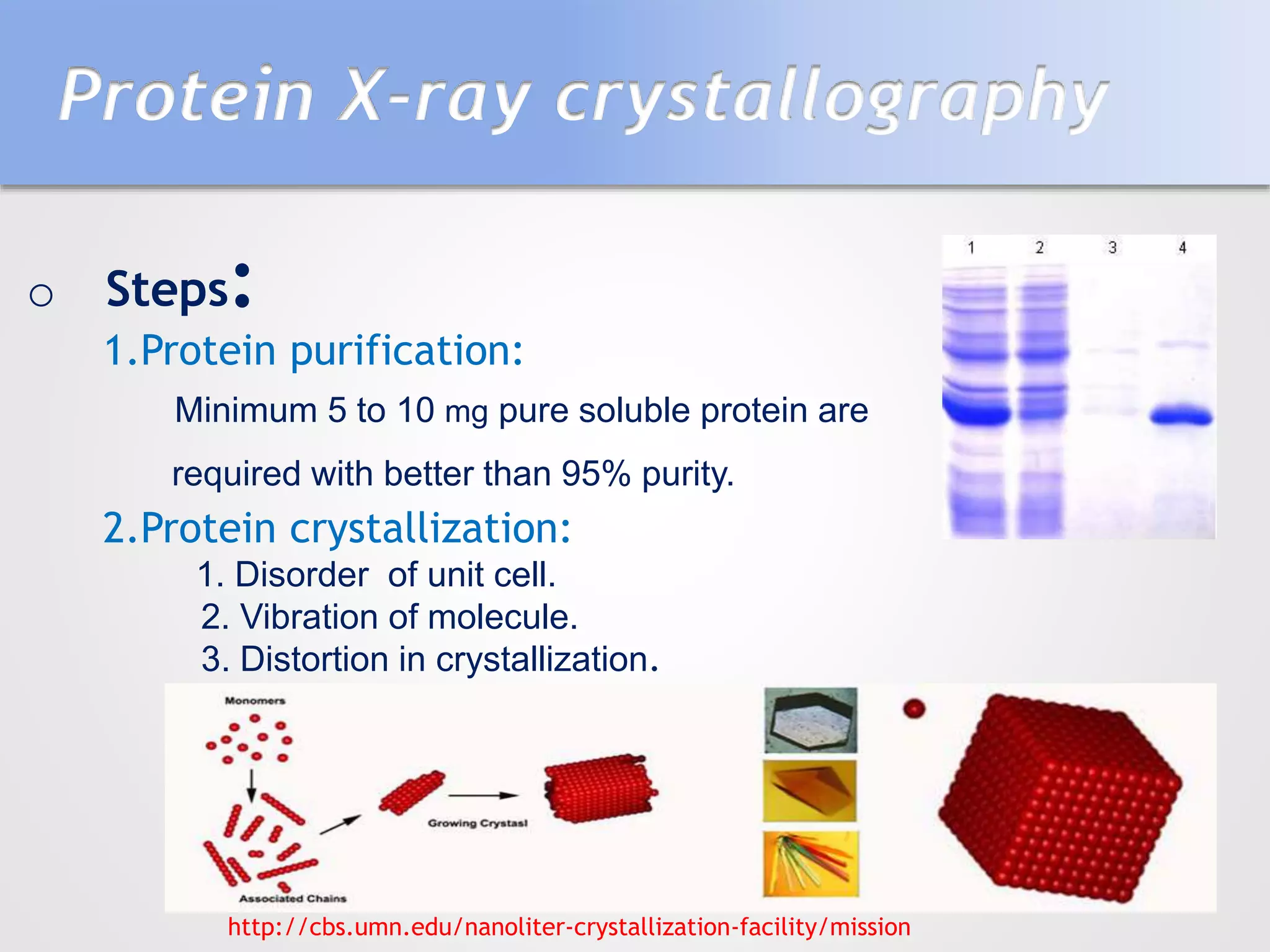
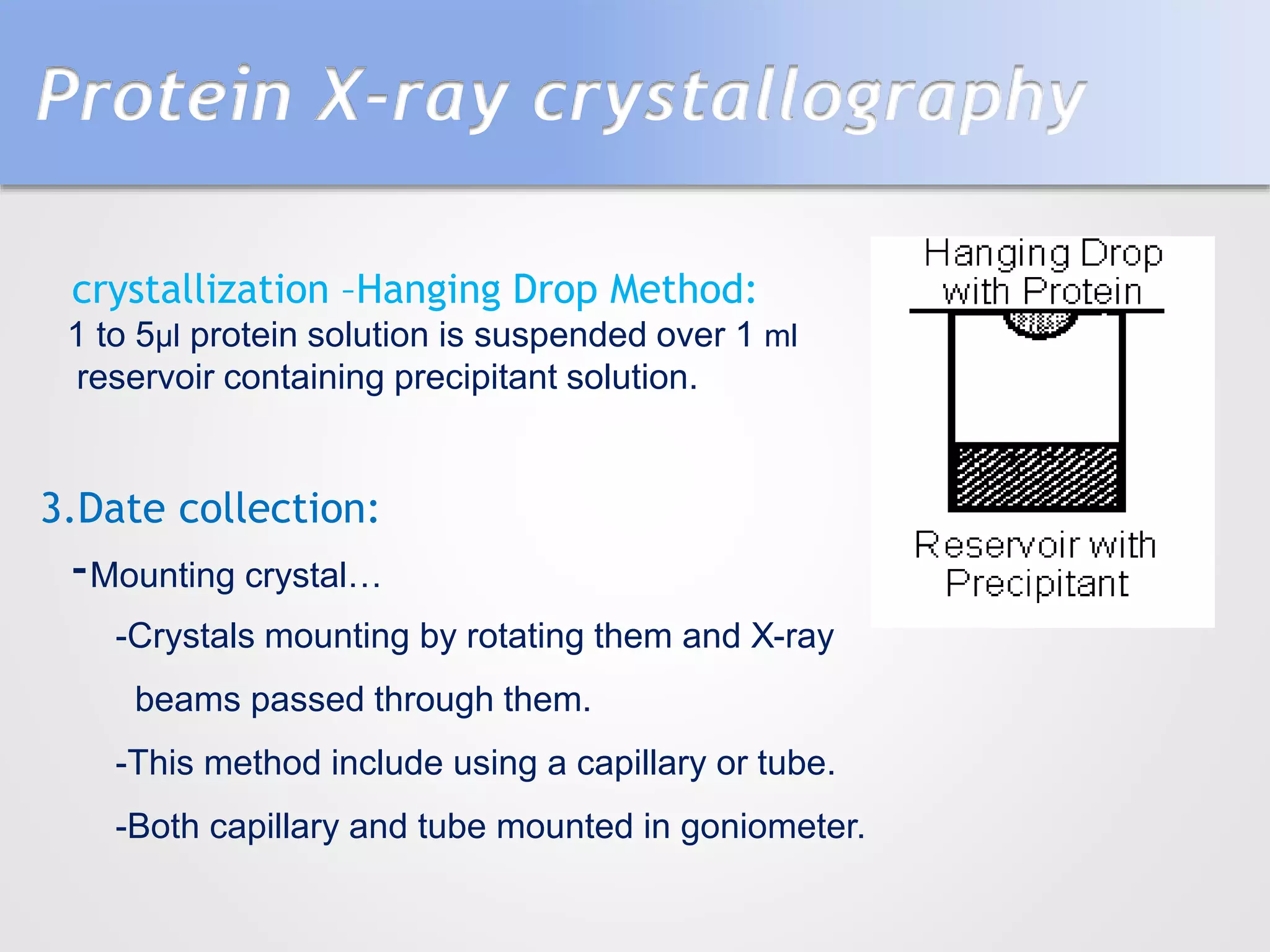
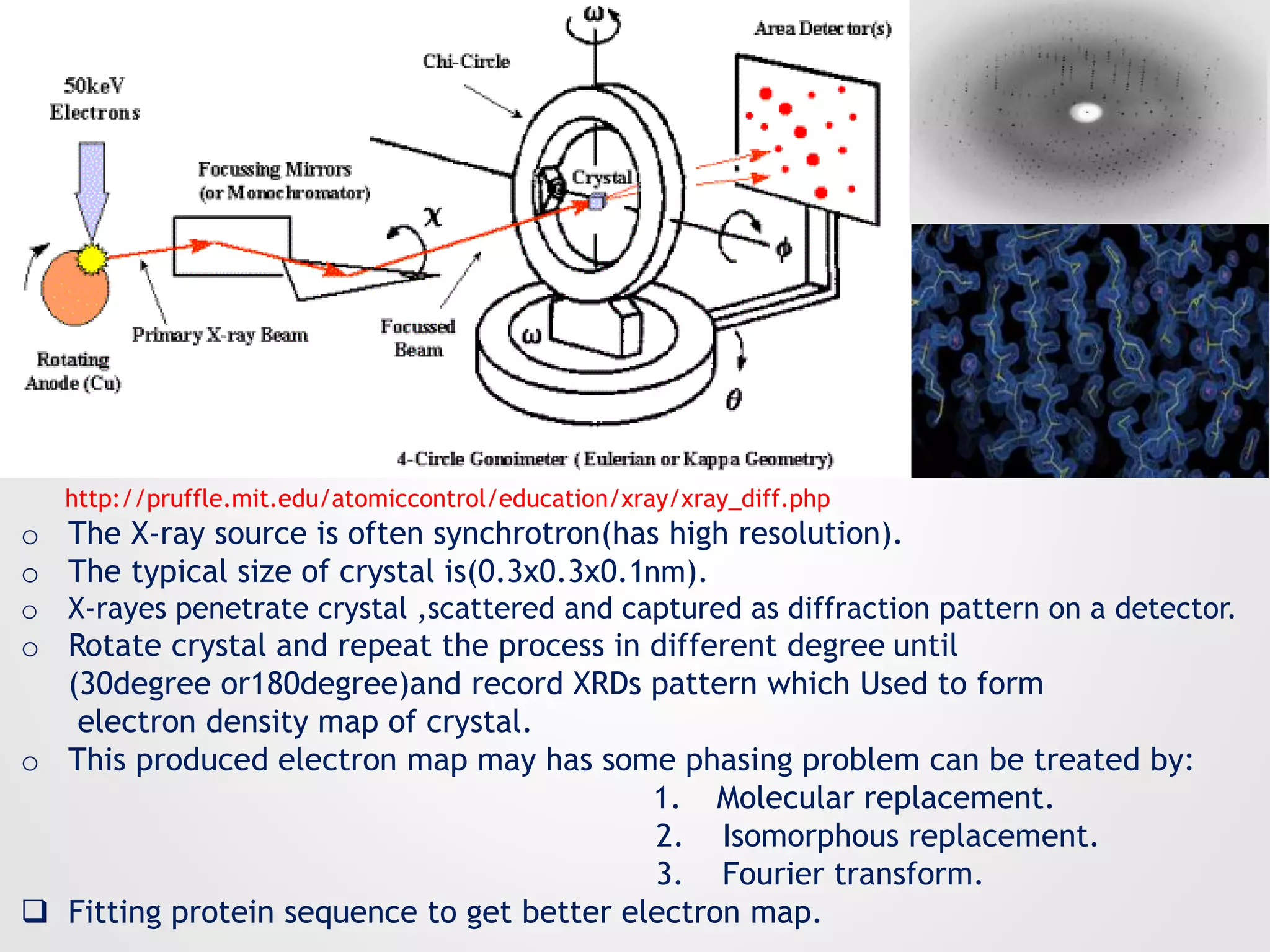
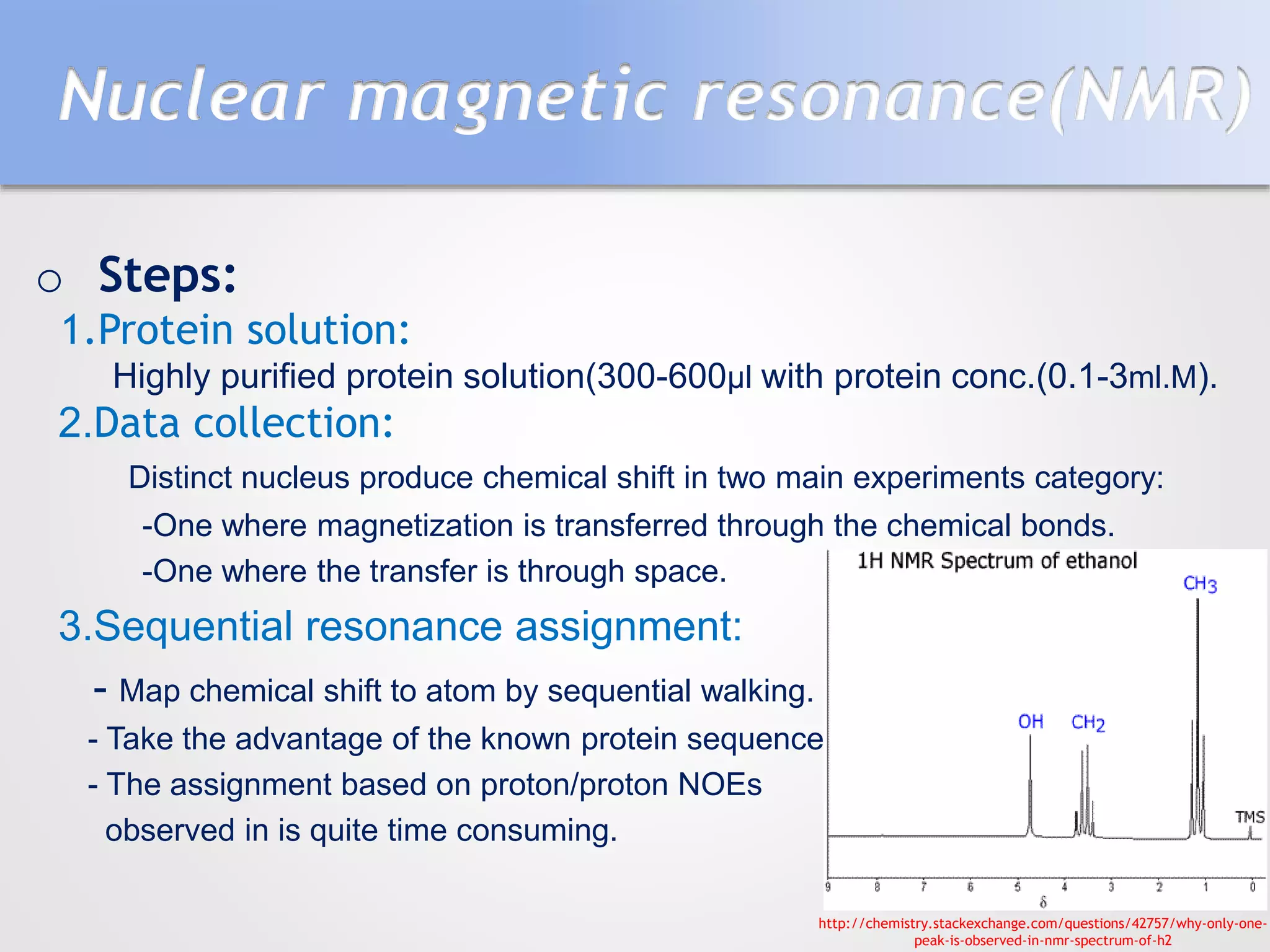
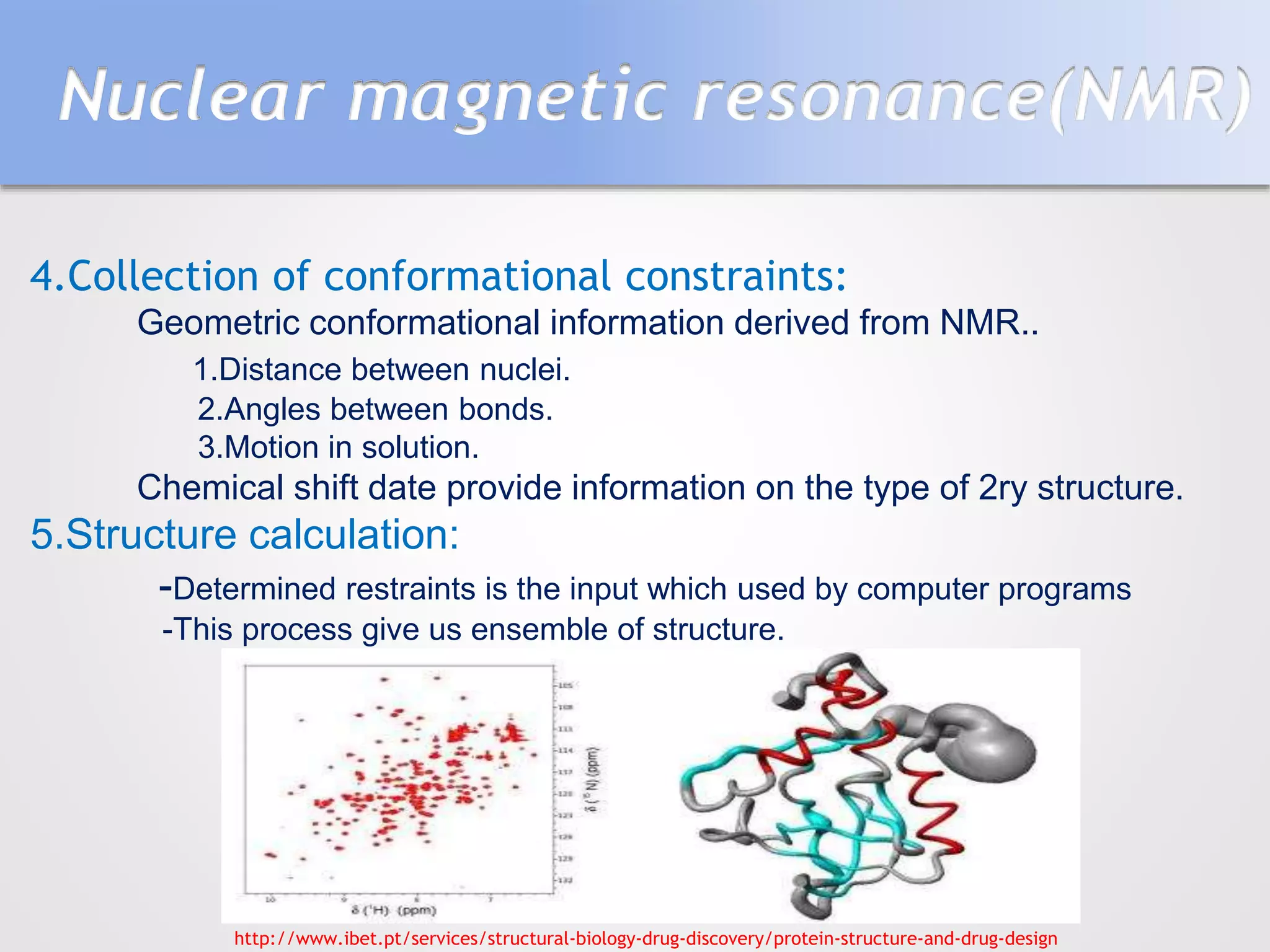
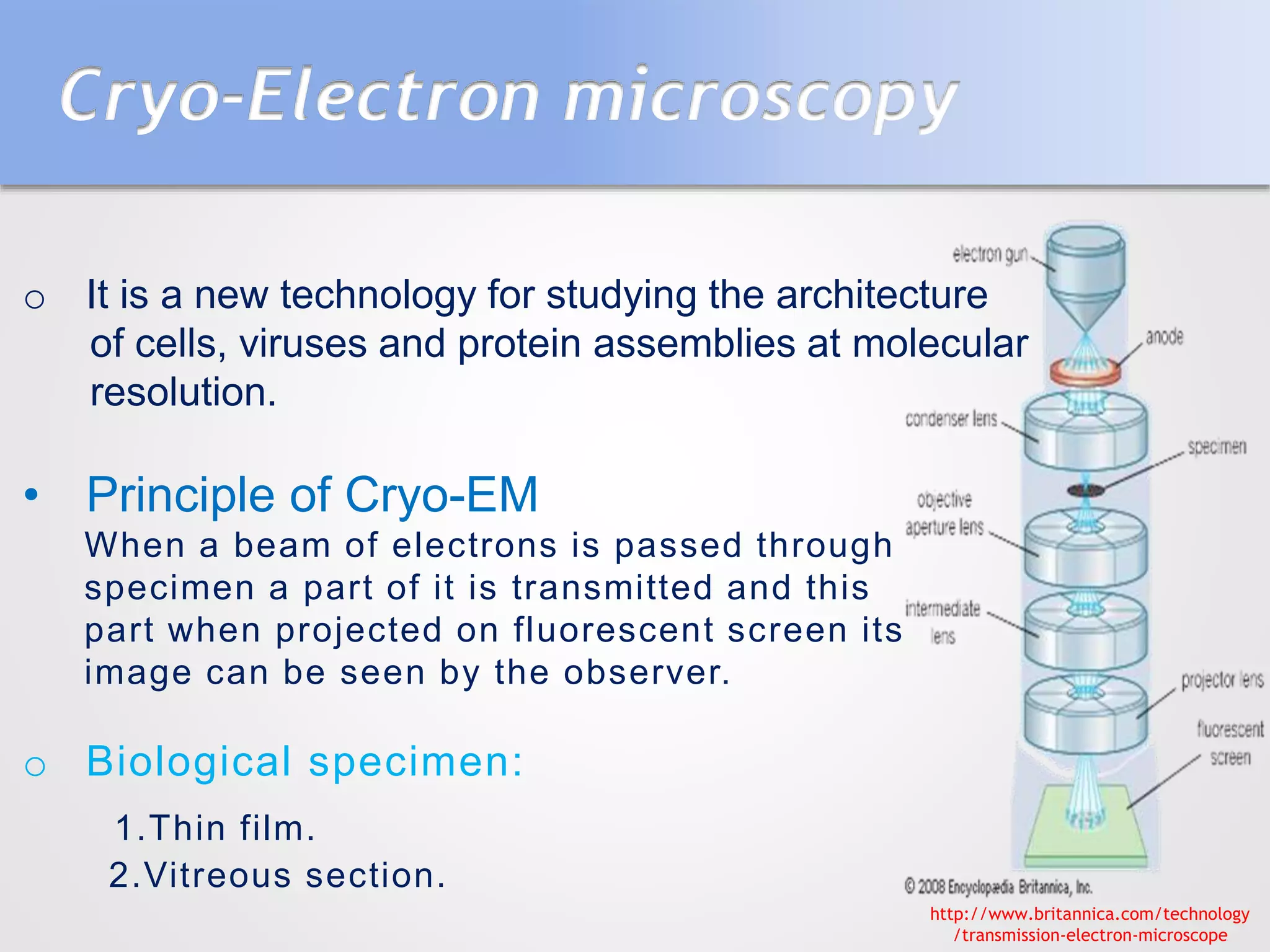
This document summarizes several methods for determining protein structure: X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and cryo-electron microscopy. X-ray crystallography involves growing protein crystals, exposing them to X-rays to generate diffraction patterns, and using the patterns to build 3D electron density maps of the protein. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy measures distances between atomic nuclei in soluble proteins by analyzing spectra from radiofrequency pulses applied in strong magnetic fields. Cryo-electron microscopy images frozen, hydrated protein samples with an electron microscope to determine large protein structures without the need for crystallization.