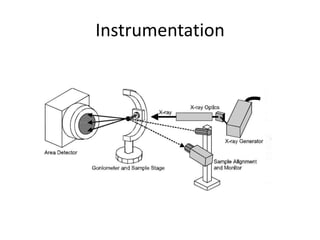
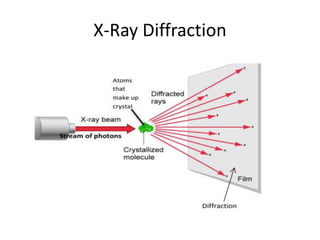
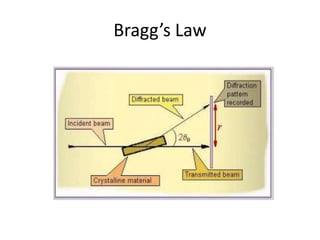
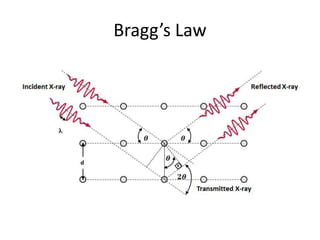
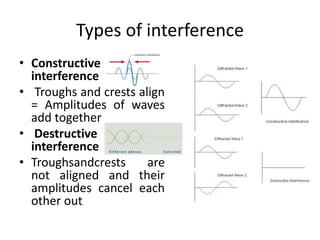
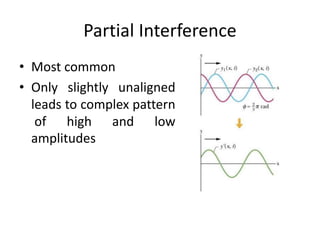
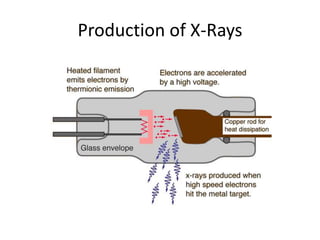
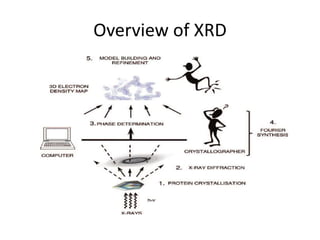
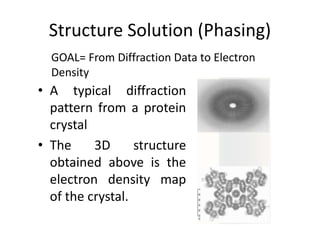
X-ray crystallography is a method for determining atomic structures of crystals by directing X-ray beams to create diffraction patterns that reveal electron density maps. The process involves multiple steps including protein purification, crystallization, and data collection, leading to a three-dimensional representation of the crystal structure. This technique is widely used due to its convenience and ability to provide precise atomic arrangements, although it has limitations with lighter elements.