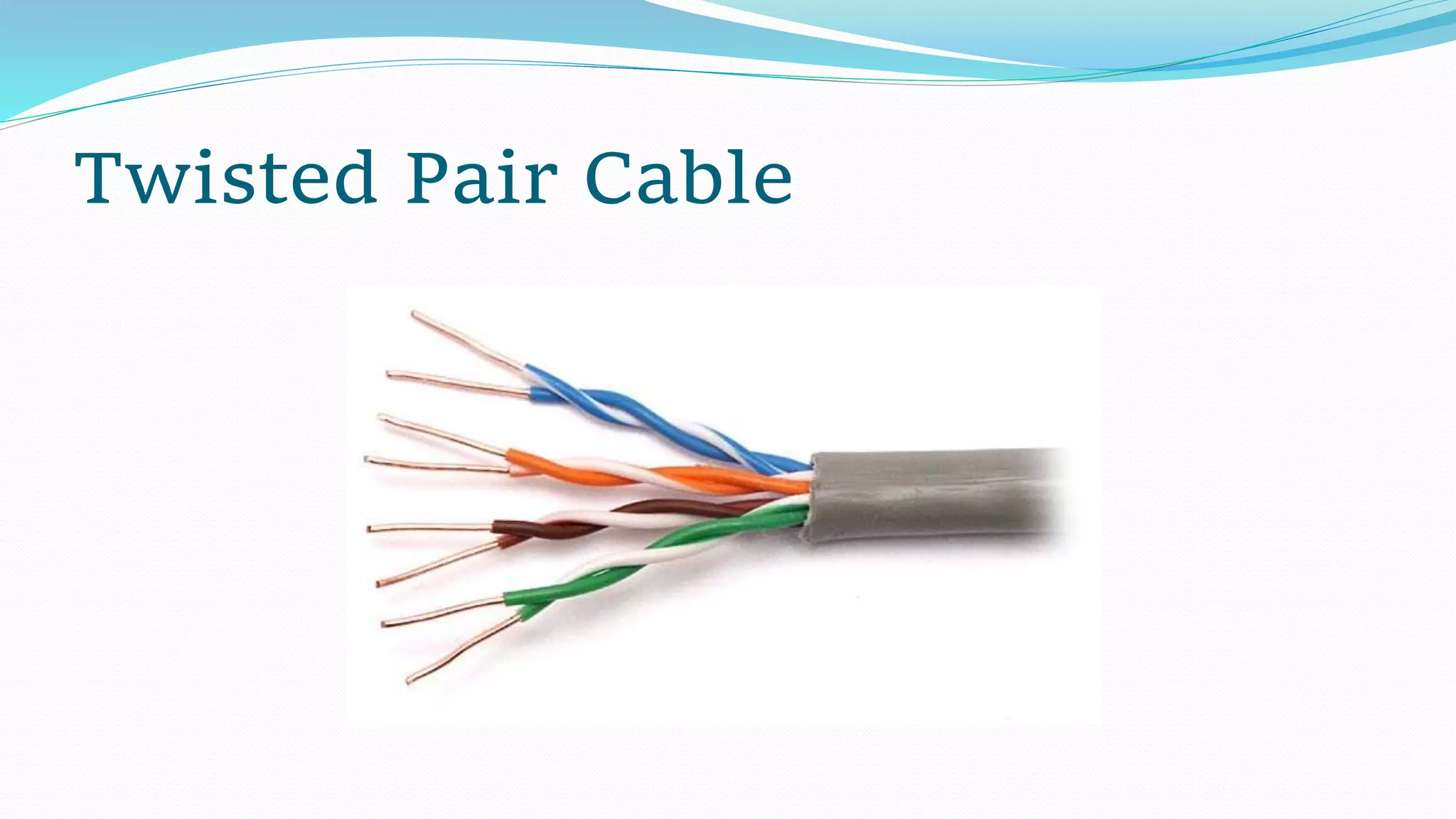
The document provides an overview of guided and unguided media types used in data transmission. Guided media includes open wire, twisted pair, coaxial, and optical fiber cables, while unguided media encompasses radio waves, microwaves, and satellite communication. Each type is detailed with its advantages and disadvantages, highlighting factors like cost, installation difficulty, and performance capabilities.