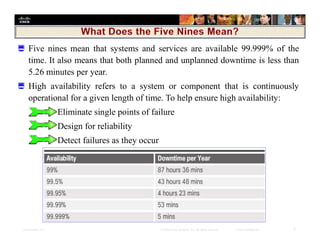
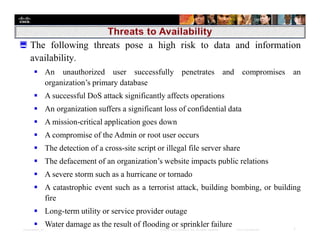
Chapter 6 focuses on the 'five nines' concept of high availability, which ensures systems are operational 99.999% of the time, addressing the importance of incident response plans, disaster recovery, and risk mitigation to maintain availability. Key principles include eliminating single points of failure, redundancy in systems, and continuous asset identification and risk analysis to protect critical information. Organizations in finance, healthcare, and public safety particularly require high availability, necessitating robust management strategies and layered security measures.