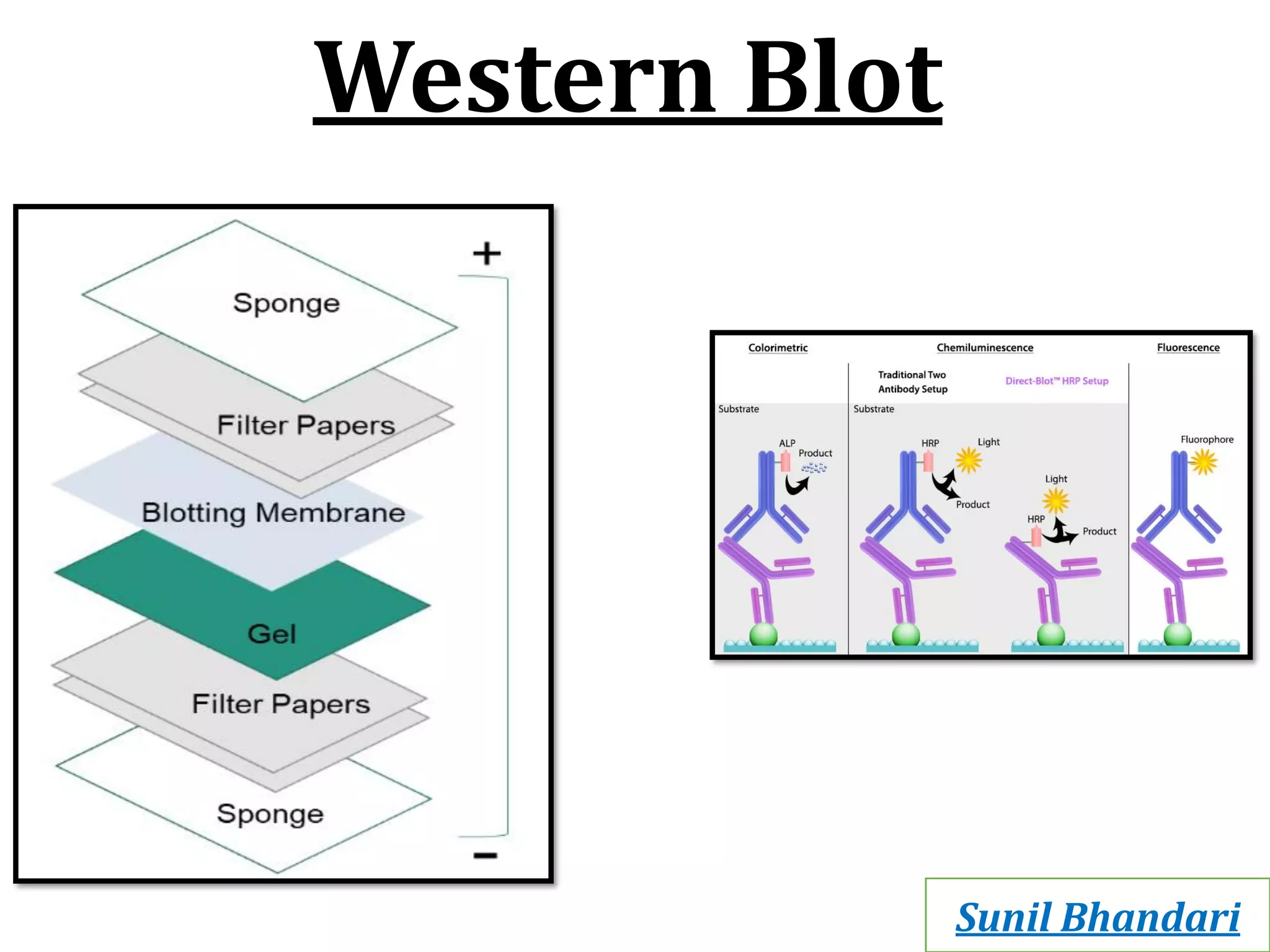
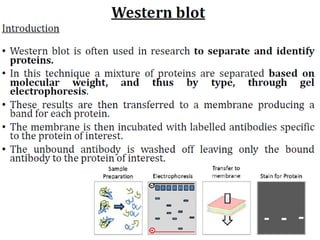
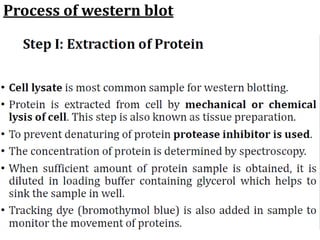
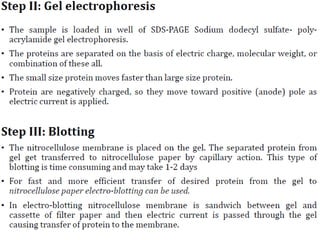
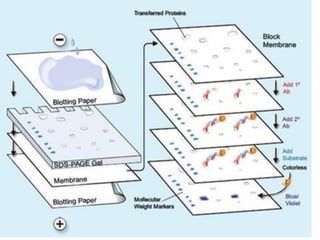
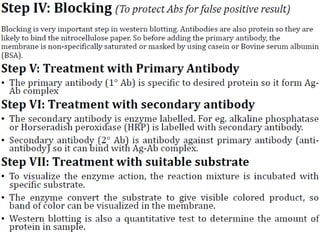
Western blots are used to confirm the identity of antigens by separating proteins by size using gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and detecting them using antibodies. The proteins are first separated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis, then transferred to a membrane where they are probed with patient sera or primary antibodies. Secondary labeled antibodies are then used to detect the presence and molecular weights of antigens recognized by the primary antibodies or patient sera.