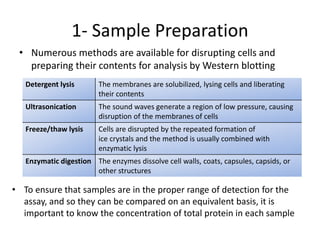
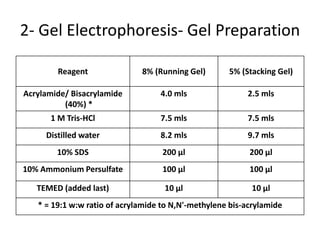
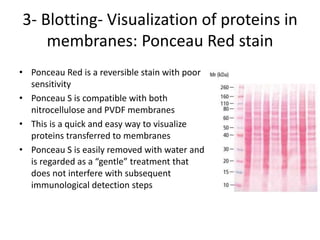
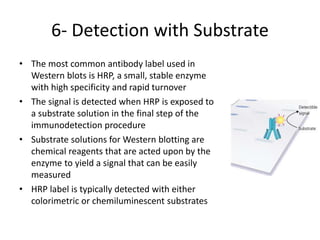
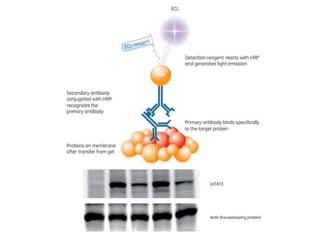
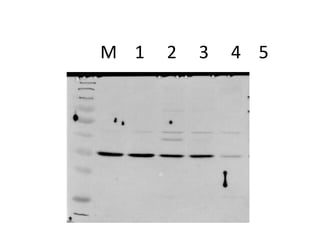
The western blot is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample. It involves separating proteins by size using gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and using antibodies to detect the target protein. The key steps are sample preparation, gel electrophoresis, blotting, blocking, antibody probing, and detection. Western blotting allows researchers to identify proteins from complex mixtures and is widely used in molecular biology and medical diagnosis, such as detecting HIV, HBV, and HSV infections.