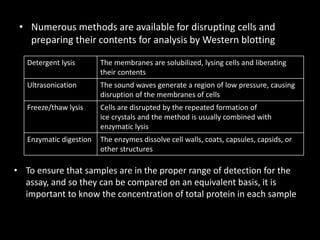
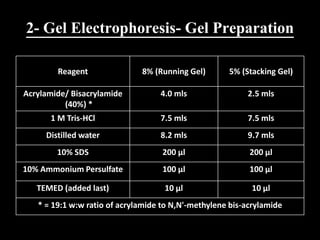
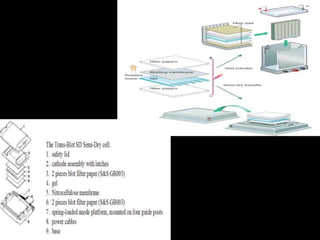
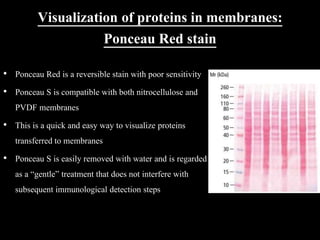
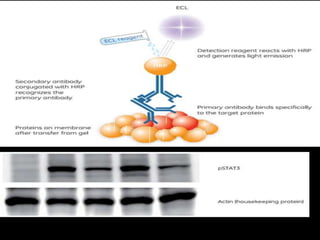
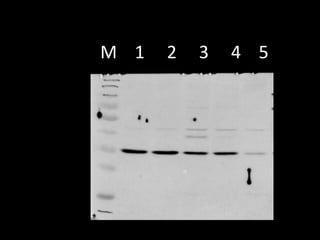
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a complex protein mixture. It involves separating proteins by gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and using antibodies to detect the target protein as a band on the membrane. The key steps are sample preparation, gel electrophoresis, blotting, blocking, antibody probing, and detection with a substrate. Western blotting is commonly used for medical diagnosis of conditions like HIV and hepatitis B.