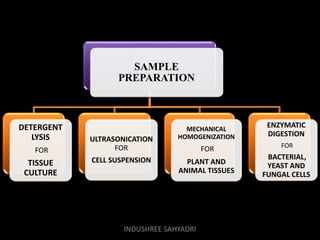
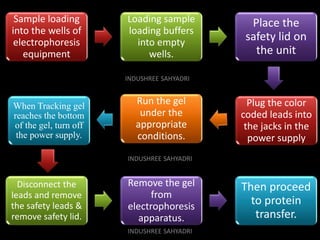
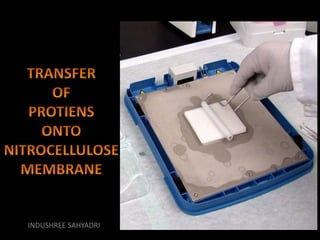
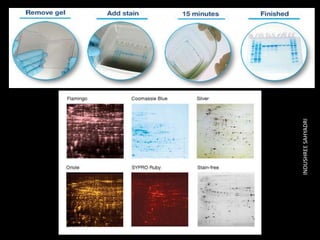
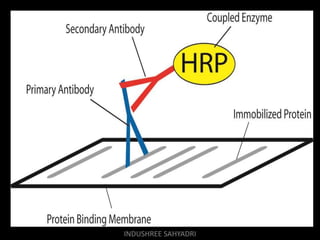
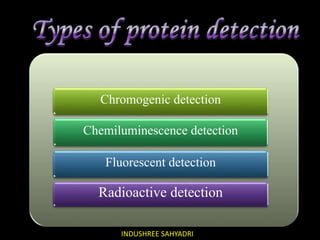
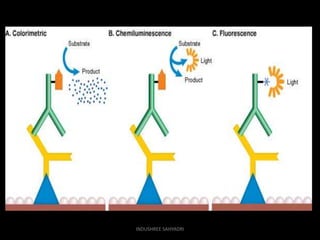
Western blotting is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in samples through gel electrophoresis and protein transfer to membranes. The process involves multiple steps, including sample preparation, separation, blocking, antibody probing, and detection, which require careful execution to avoid inaccuracies. It is widely used in molecular biology and medical diagnostics, despite being time-consuming and requiring expertise.