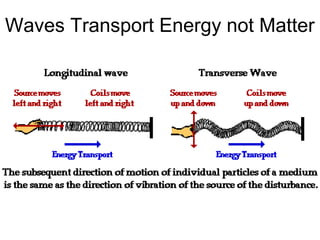
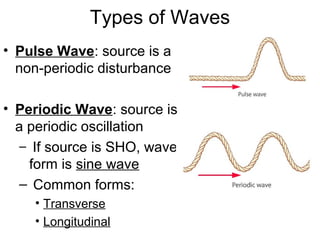
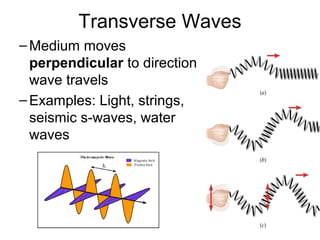
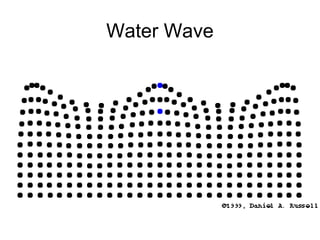
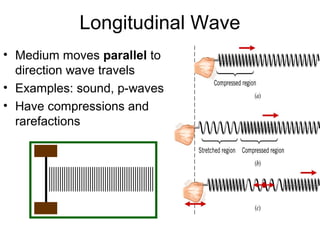
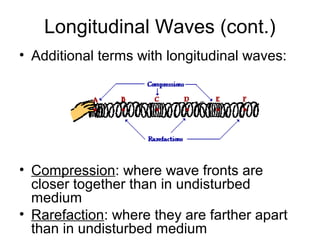
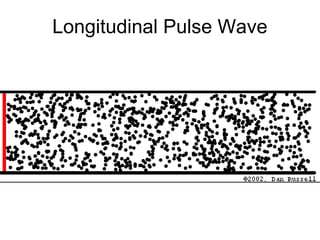
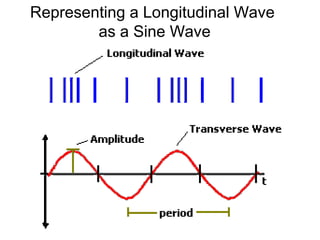
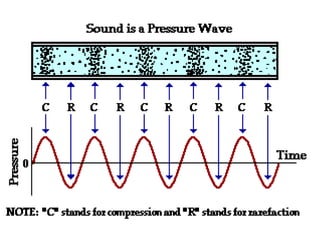
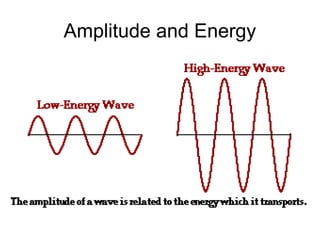
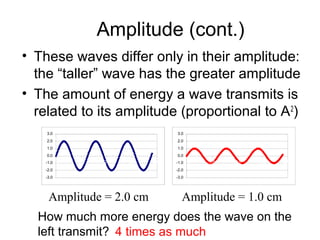
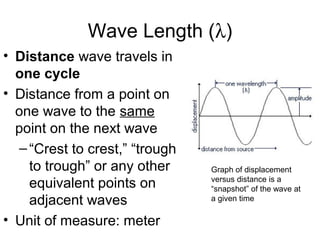
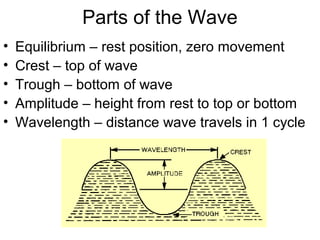
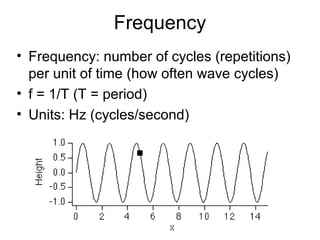
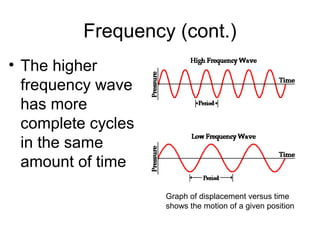
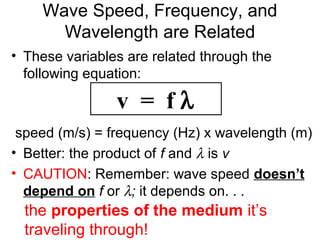
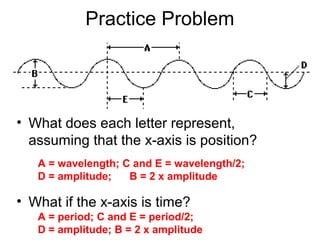
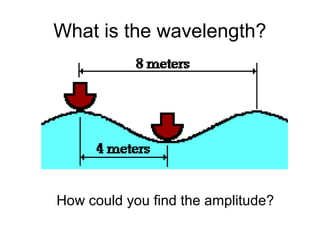
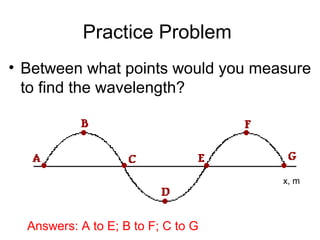
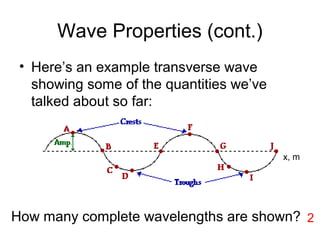
Waves transport energy through a medium rather than matter. There are two main types of waves: transverse waves, where the medium moves perpendicular to the wave's direction of travel, and longitudinal waves, where the medium moves parallel to the direction of travel. Key wave parameters include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, period, and speed. The wavelength is the distance between two equivalent points on consecutive waves, frequency is the number of waves passing a point per second, and speed depends on the properties of the medium and can be calculated as speed equals wavelength times frequency.