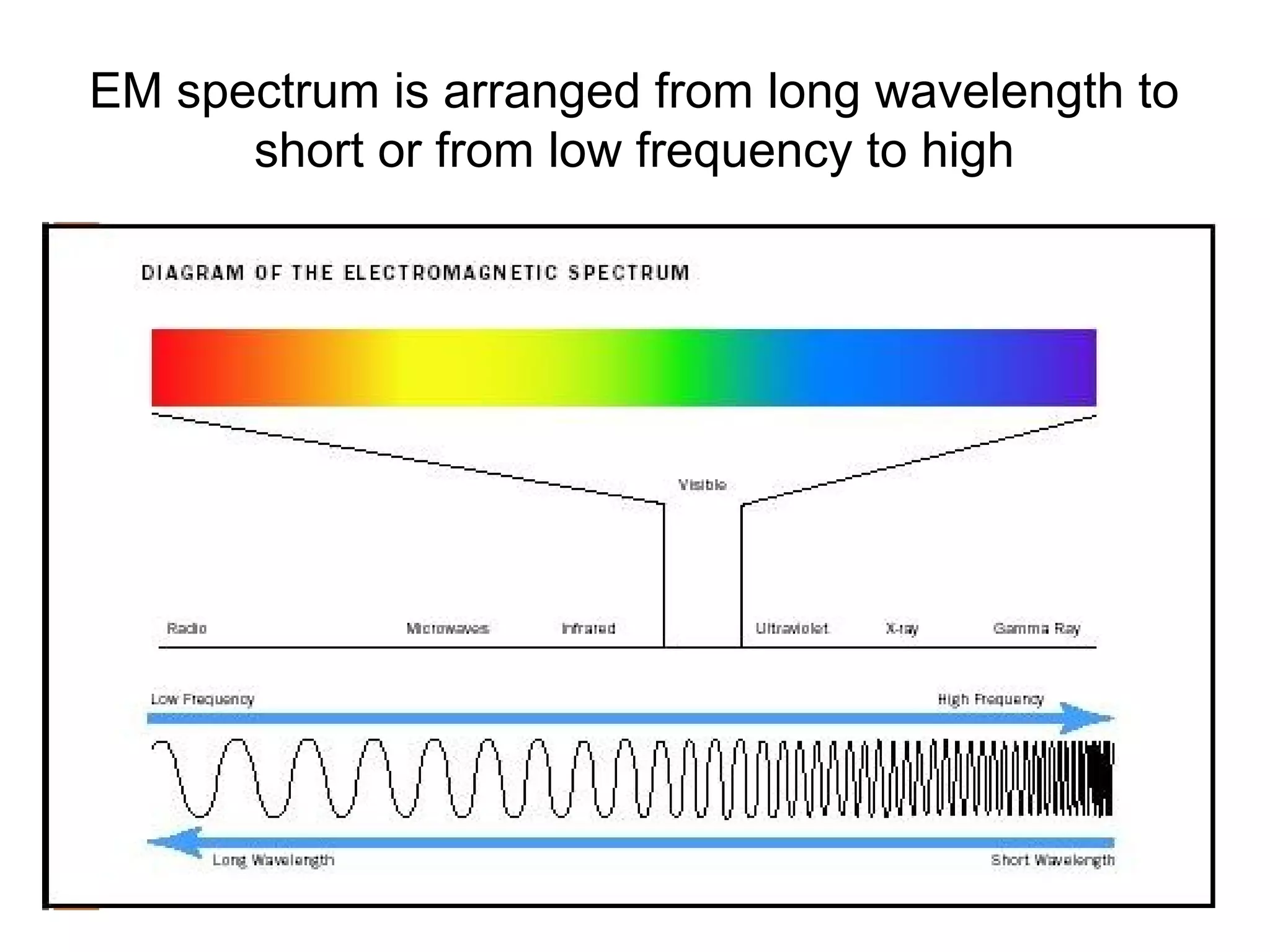
This document discusses different types of waves including mechanical waves, which require a medium, and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through empty space. It describes key wave properties such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. It also covers how waves interact through reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference. The document then focuses on electromagnetic waves, their ability to travel without a medium, and their composition of electric and magnetic fields. It provides examples of different types of electromagnetic waves and discusses theories about the nature of light.