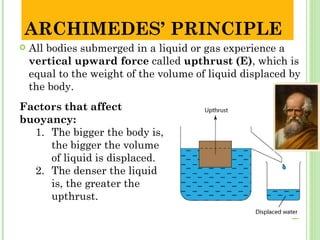
The document defines a force as that which causes changes in speed or deformation of an object. It describes different types of forces including contact forces and forces at a distance. Gravity is defined as an attractive force between masses that decreases with increasing distance. Weight is the force of gravity on an object and is measured in Newtons. Archimedes' principle states that immersed objects experience an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. Forces such as gravity, buoyancy and weight are used to explain why objects fall, float or are in equilibrium in fluids.