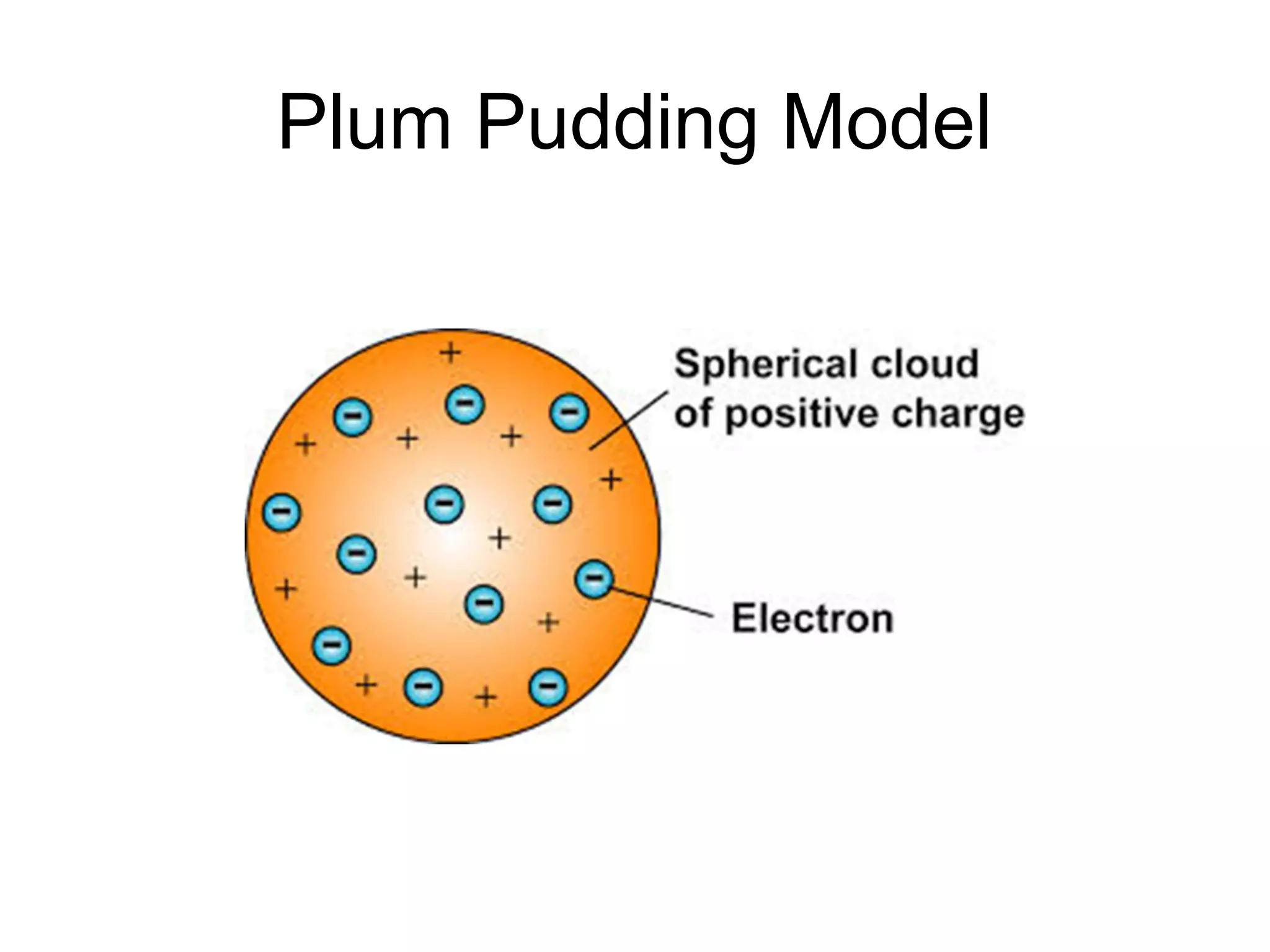
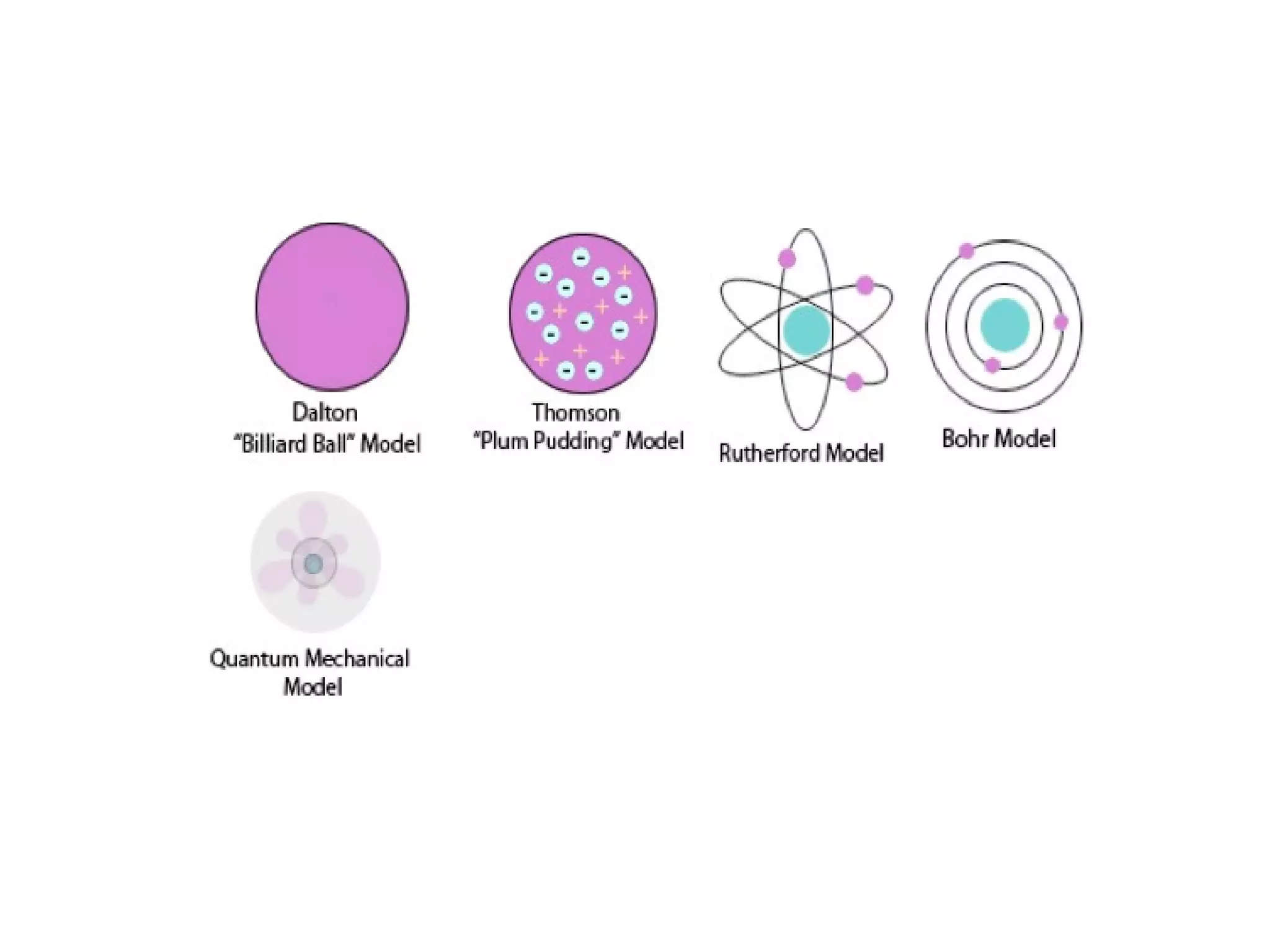
This document provides an overview of the development of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to modern atomic structure. It describes key contributors such as Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and Schrodinger who proposed models of the atom based on experiments and evidence available at the time. Their work established that atoms are the smallest particles of matter, have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons, and can combine to form all chemical elements.