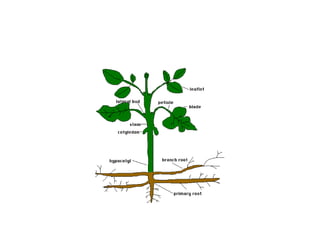
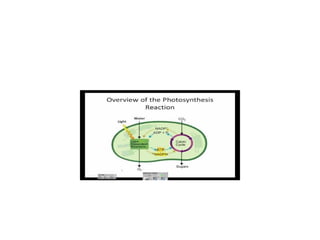
This document summarizes photosynthesis. It discusses the history of discoveries about photosynthesis and defines key terms like autotrophs and heterotrophs. It then explains that photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This occurs in two stages within the chloroplast - the light-dependent reaction uses light to produce ATP and NADPH, while the light-independent Calvin cycle uses those products to produce glucose from carbon dioxide. Factors like temperature, light intensity, and water affect the process.