This document provides an overview of physical science, including:
1) Physical science involves the study of matter and energy, with chemistry focusing on forms of matter and physics focusing on how energy affects matter.
2) The scientific method involves asking a question, forming a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis through experimentation, analyzing results, drawing a conclusion, and communicating results.
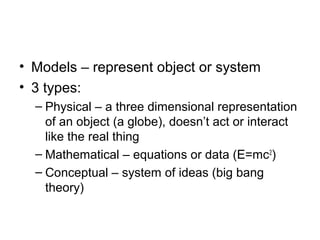
3) Models are used to represent objects or systems and can be physical, mathematical, or conceptual representations.