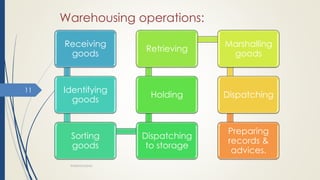
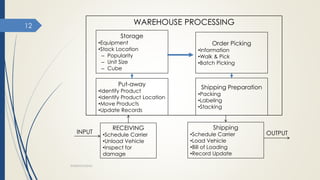
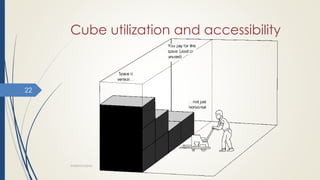
This document discusses warehousing and warehouse operations. It defines a warehouse as a location for receiving, storing, and shipping goods. Warehouses serve several purposes like ensuring continuous supply, adjusting production and consumption, and providing protection. The document outlines different types of warehouses like public, private, bonded, and cold storage warehouses. It also describes key warehouse operations like receiving, storage, order picking, and shipping. Finally, it discusses factors that influence effective warehouse use such as stock location, cube utilization, order picking, and physical control/security.