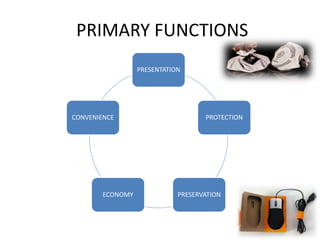
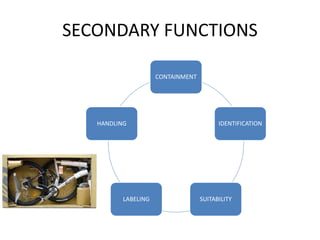
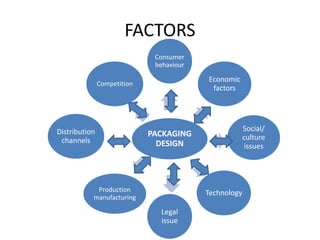
This document discusses the history and functions of packaging. It traces the origins of modern packaging back to the late 18th century with the industrial revolution. Packaging helps promote and differentiate products, aids in consumer decision making, and serves important protective and informative functions. The document outlines different types of packaging including consumer, industrial, primary, secondary and tertiary packaging. It also discusses factors that influence packaging design and the relationship between packaging and the product.