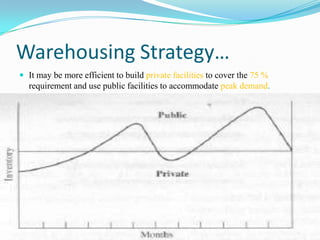
This document discusses various aspects of warehouse management including reasons for warehousing, benefits, types of warehouses, warehouse strategies, location strategies, and transport. Reasons for warehousing include supporting customer policies, maintaining supply, and achieving transportation economies. Benefits include consolidation and break bulk. Warehouse strategies consider private, public and contract facilities to handle base and peak demand. Location strategies consider proximity to markets and products. Transport selection involves considering factors like cost, transit time, reliability, and potential for loss or damage.