Logistics involves the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and point of consumption. The document discusses logistics by roadways and railways in India. It provides details on:
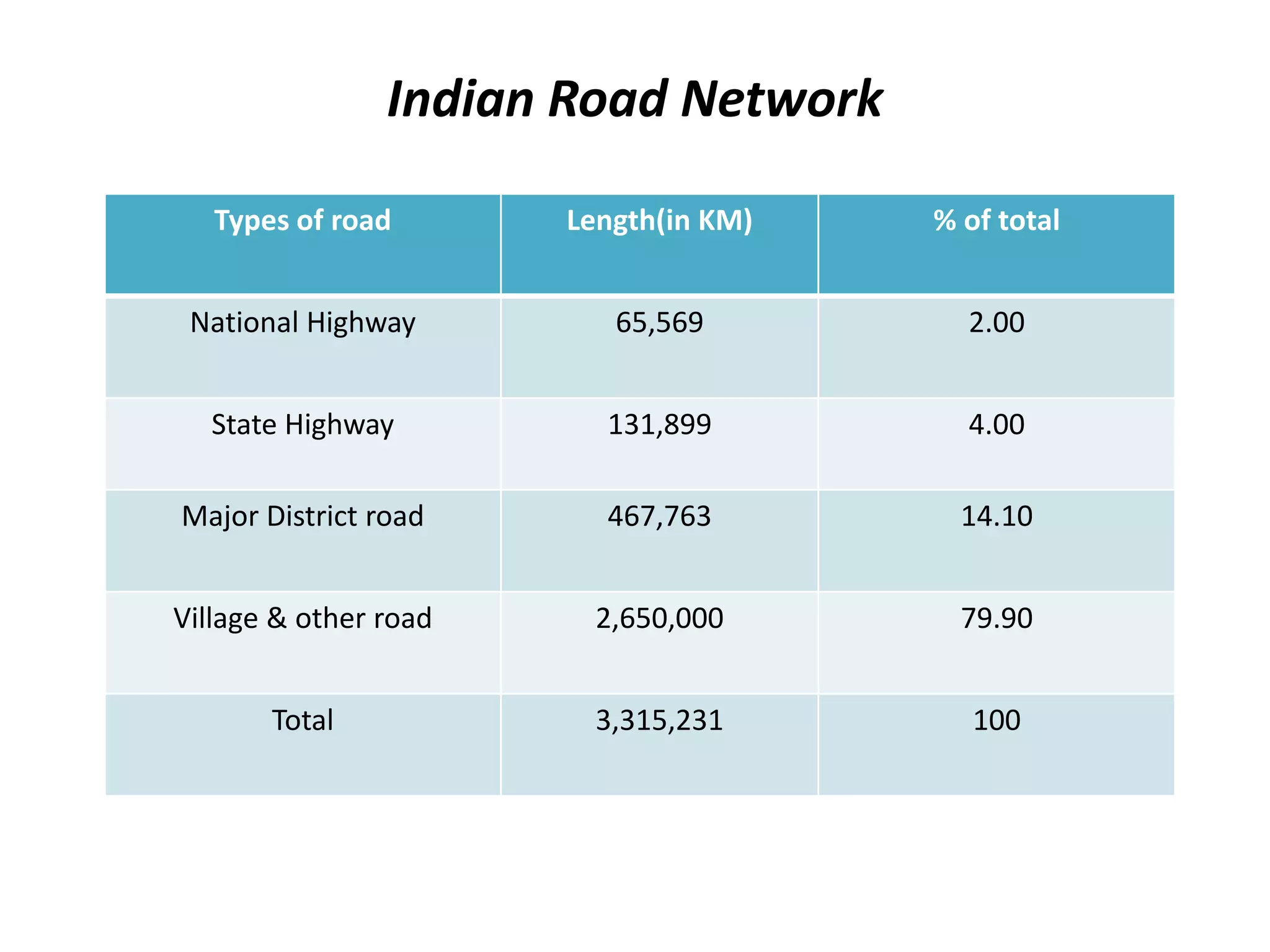
- India's large road and rail network that carries most freight and passenger traffic. Roadways face issues like congestion while rail faces capacity constraints.
- Key aspects of road logistics like types of vehicles used, and projects to expand highways. Rail freight includes transport of containers, bulk goods, and specialized wagons.
- Dedicated freight corridors are being developed to separate freight and passenger traffic on railways. This aims to boost rail's modal share through improved services and productivity.