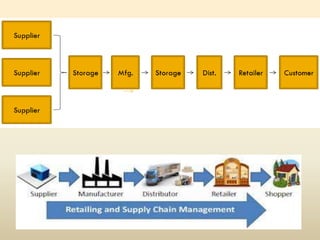
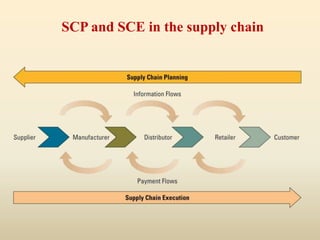
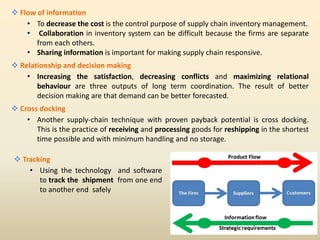
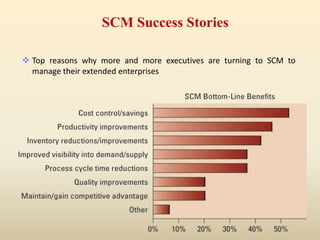
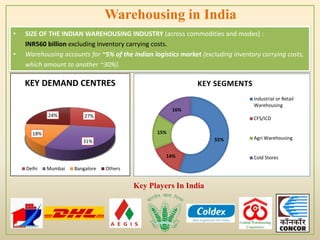
This document discusses efficiency in supply chain management and warehousing. It defines supply chain management and warehousing, and identifies factors that make them effective. For supply chain management, key factors include organizational structure, distribution network optimization, information sharing, and relationship building. For warehousing, factors include maximizing space utilization, adopting technology like RFID, organizing workstations, optimizing labor, and streamlining order fulfillment. The document contrasts traditional and advanced approaches to supply chain management and warehousing.