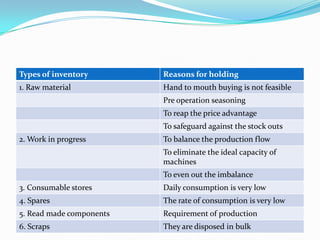
This document discusses material management and inventory in manufacturing. It covers key aspects like the purpose of inventory, types of inventory, reasons for holding inventory, and functions of the stores department. The document compares high and low inventory levels and discusses approaches to stores location, recording material, issuing material, and centralized vs decentralized storing. The overall aim is to ensure smooth material flow and quality control to reduce costs and meet production needs.