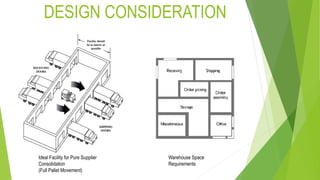
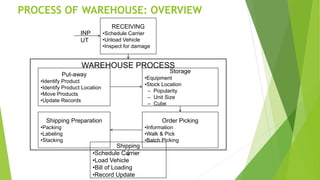
This document discusses warehouse management. It defines warehousing as receiving, storing, and preparing goods for reshipment. Warehouses serve important functions like storage, movement of goods, and preparation for customers. There are different types of warehouses including private warehouses owned by companies and public warehouses available for hire. Key considerations in warehouse design include product flow, space requirements, and location. Centralized and decentralized approaches each have benefits and drawbacks for efficiently serving customer demand.




![ECONOMIC AND SERVICE BENEFIT OF
WAREHOUSING
Economic benefits - Consolidation, Break
bulk, Cross Dock, processing postponement,
stock piling[seasonal storage]
Service benefits - spot stocking,
Assortment, mixing, production support,
market presence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-5-320.jpg)

![Consolidation
warehouse
Plant B
[Product B for
Customer X]
Plant C
[Product C for
Customer X]
Customer X
[Product A+
Product B+
Product C]
Plant A
[Product A for
Customer X]
CONSOLIDATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-7-320.jpg)
![Plant A
[Product A
for
Customers
X+Y+Z]
Break bulk
warehouse
Customer
X
Customer
Y
Customer
Z
BREAK BULK WAREHOUSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-8-320.jpg)
![CROSS DOCK WAREHOUSE
Plant A
[Product A]
For
W, X, Z
Plant B
[Product B]
For
W,X,Y,Z
Cross Dock
warehouse
Customer W
[A+B+C]
Customer X
[A+B]
Customer Y
[B+C]
Customer Z
A+ C
Plant C
[Product C]
For
W, Y, Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-9-320.jpg)

![In transit mixing
Warehouse
[transit mixing point,
mix & make product
C]
Plant A
[Product A]
Plant B
[Product B]
Customer X
Products
A+ B+ C
Customer Y
Products
A+B
TRANSMIT MIXING WAREHOUSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-11-320.jpg)
![MANUFACTURING WAREHOUSE
Manufacturing
Warehouse
Vendor A
[part A]
Vendor B
[part B]
Vendor C
[part C] Assembly Line X
Assembly Line Y
Assembly Line Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehouse-211004044150/85/Warehouse-12-320.jpg)