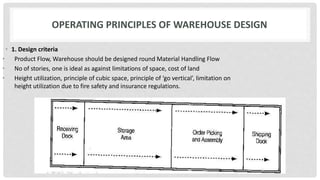
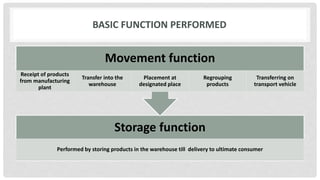
This document discusses warehousing and its role in supply chain management. It provides details on the functions of warehousing such as receiving goods, record preparation, identification, storage, packing, and delivery. It describes the basic storage and movement functions performed by warehouses. The document also discusses the economic and service benefits of warehousing models like consolidation, break bulk, and cross dock warehouses. It covers operating principles of warehouse design and factors to consider in warehouse location selection, including the benefits and drawbacks of centralized and decentralized warehousing approaches.





![Consolidation
warehouse
Plant B
[Product B for
Customer X]
Plant C
[Product C for
Customer X]
Customer X
[Product A+
Product B+
Product C]
Plant A
[Product A for
Customer X]
CONSOLIDATION
ECONOMIC AND SERVICE BENEFIT OF WAREHOUSING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehousing-160216005659/85/Warehousing-7-320.jpg)
![Plant A
[Product A
for
Customers
X+Y+Z]
Break bulk
warehouse
Customer
X
Customer
Y
Customer
Z
BREAK BULK WAREHOUSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehousing-160216005659/85/Warehousing-8-320.jpg)
![CROSS DOCK WAREHOUSE
Plant A
[Product A]
For
W, X, Z
Plant B
[Product B]
For
W,X,Y,Z
Cross Dock
warehouse
Customer W
[A+B+C]
Customer X
[A+B]
Customer Y
[B+C]
Customer Z
A+ C
Plant C
[Product C]
For
W, Y, Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warehousing-160216005659/85/Warehousing-9-320.jpg)