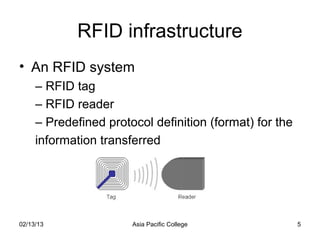
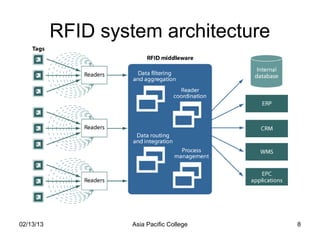
The document proposes developing a warehouse management system using RFID technology. Key benefits would include automating manual processes, reducing labor costs and errors, and improving tracking of inventory. The project aims to increase efficiency, lower costs, and provide faster access to information. Risks include ensuring proper implementation of the RFID devices that the system relies on for data. The project timeline, budget, and milestones are also outlined.